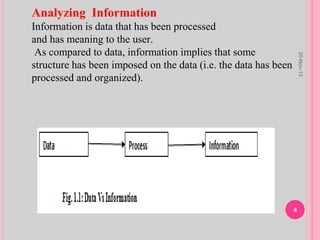
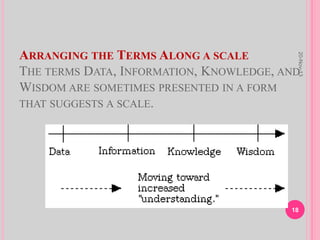
Data refers to raw facts without context, while information adds meaning by organizing data into a context. Knowledge builds upon information by incorporating understanding and experience to aid decision making. Wisdom represents accumulated knowledge and sound judgment developed over time through experience. Thus, data can be thought of as the base level, with information, knowledge, and wisdom each incorporating more processing and experience, with wisdom at the highest level as seasoned judgment.