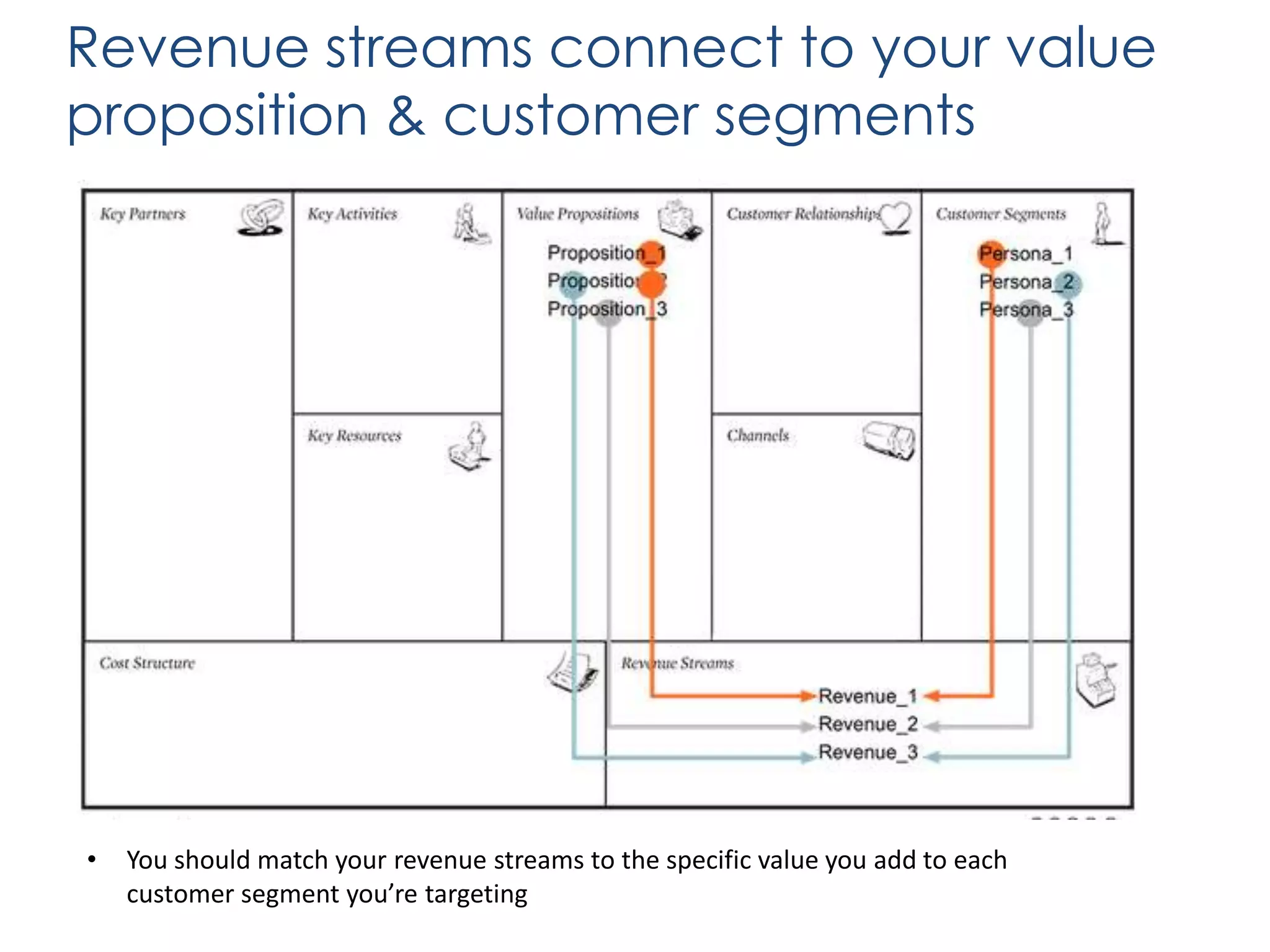
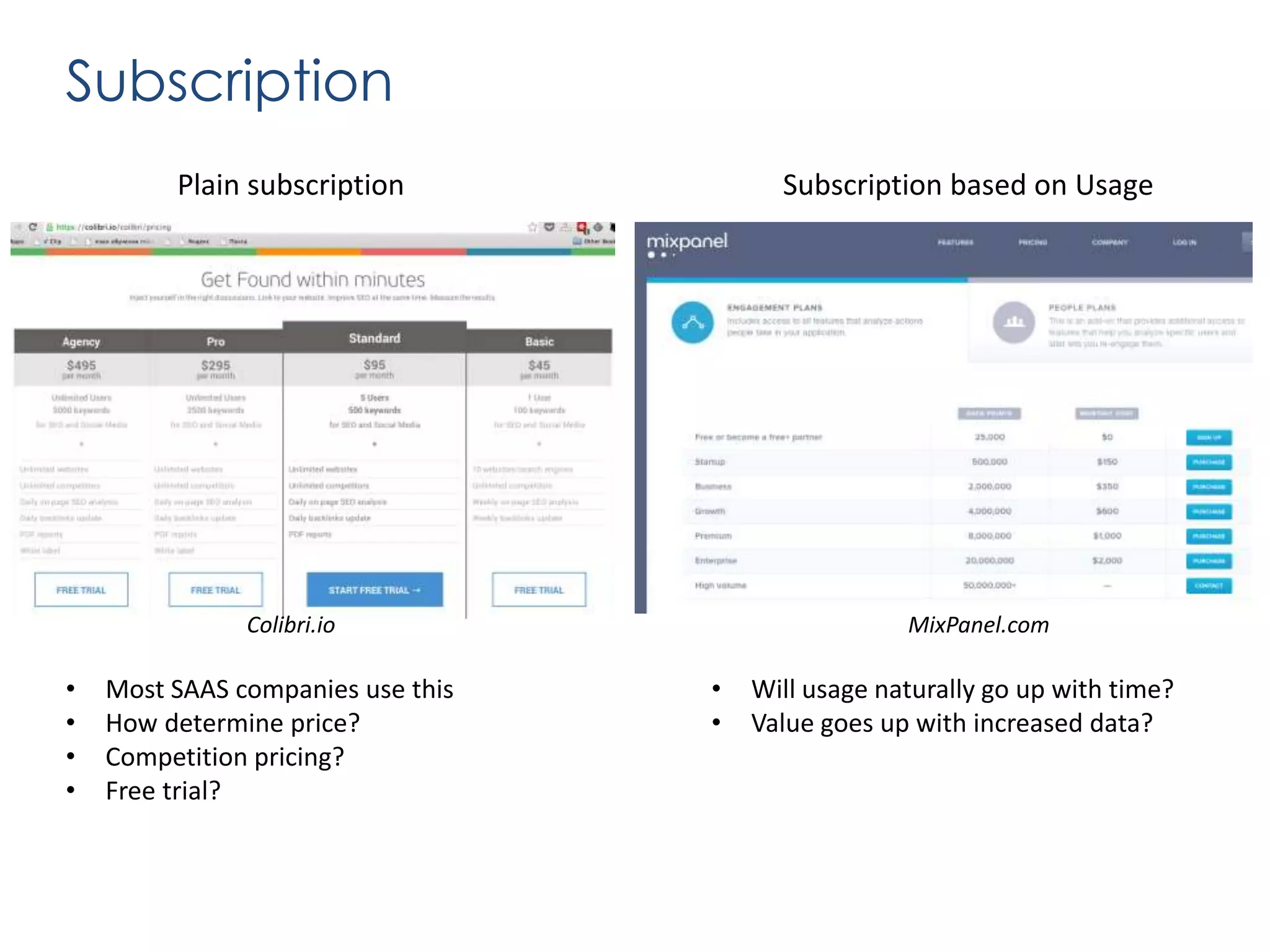
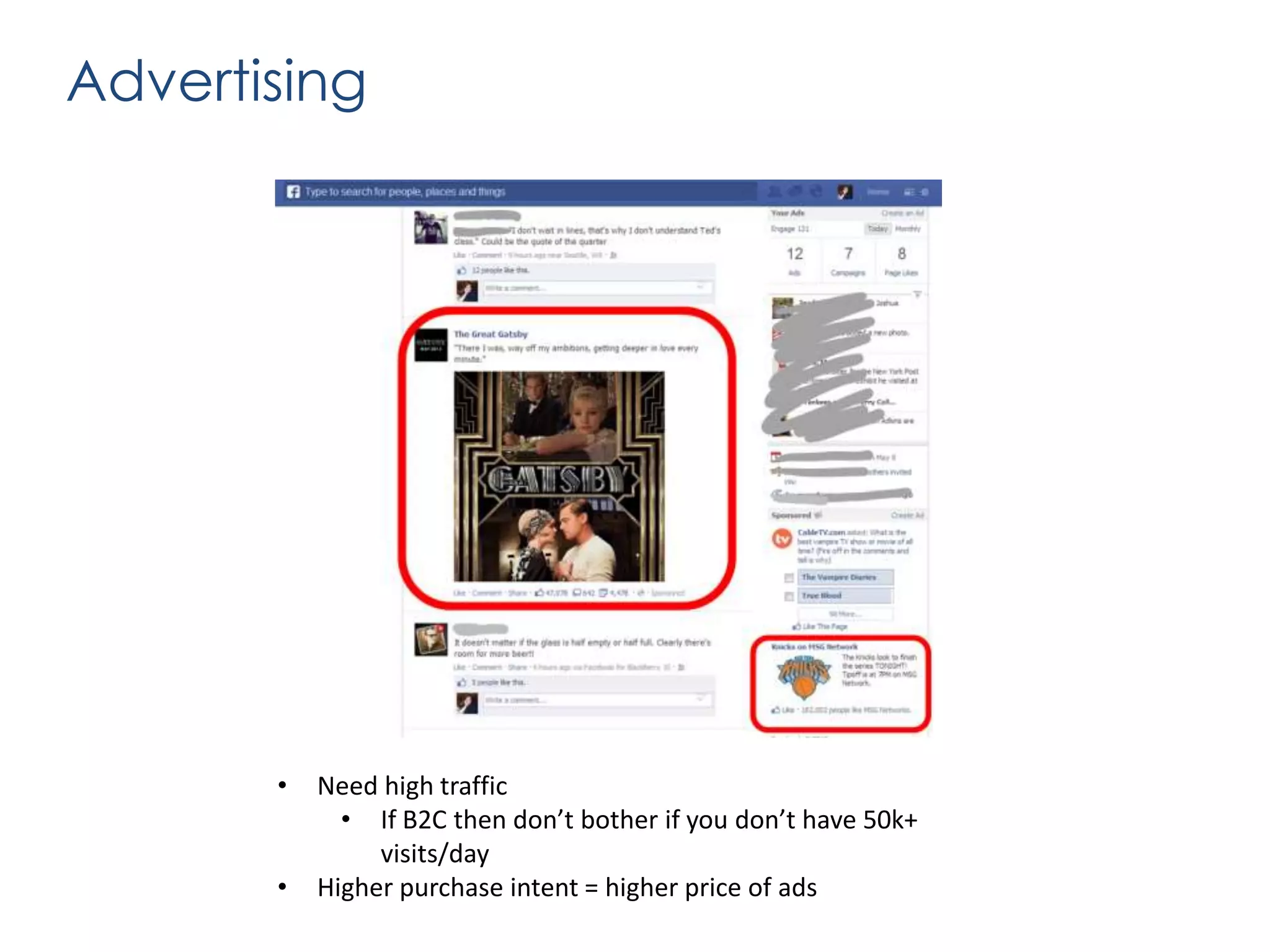
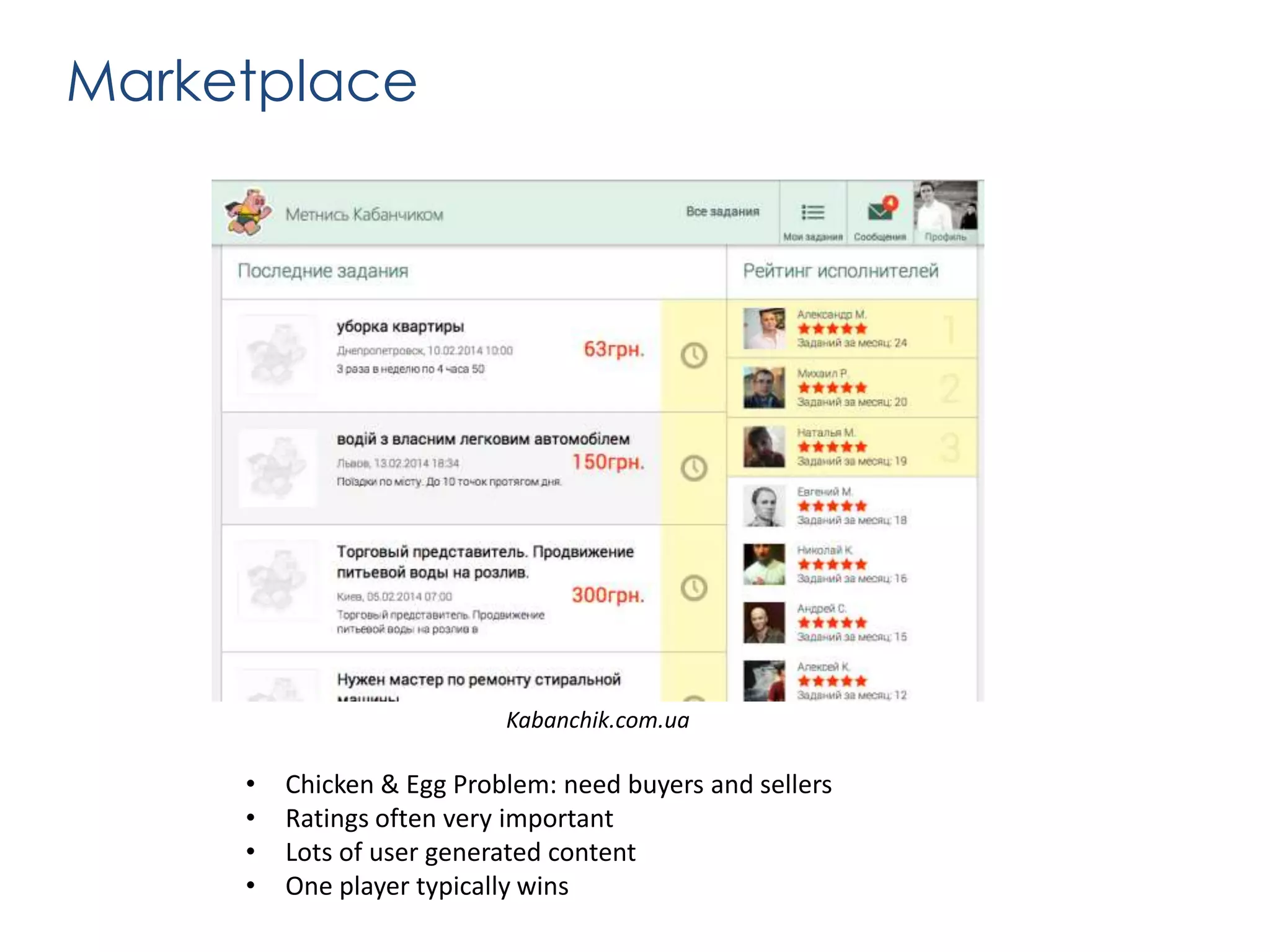
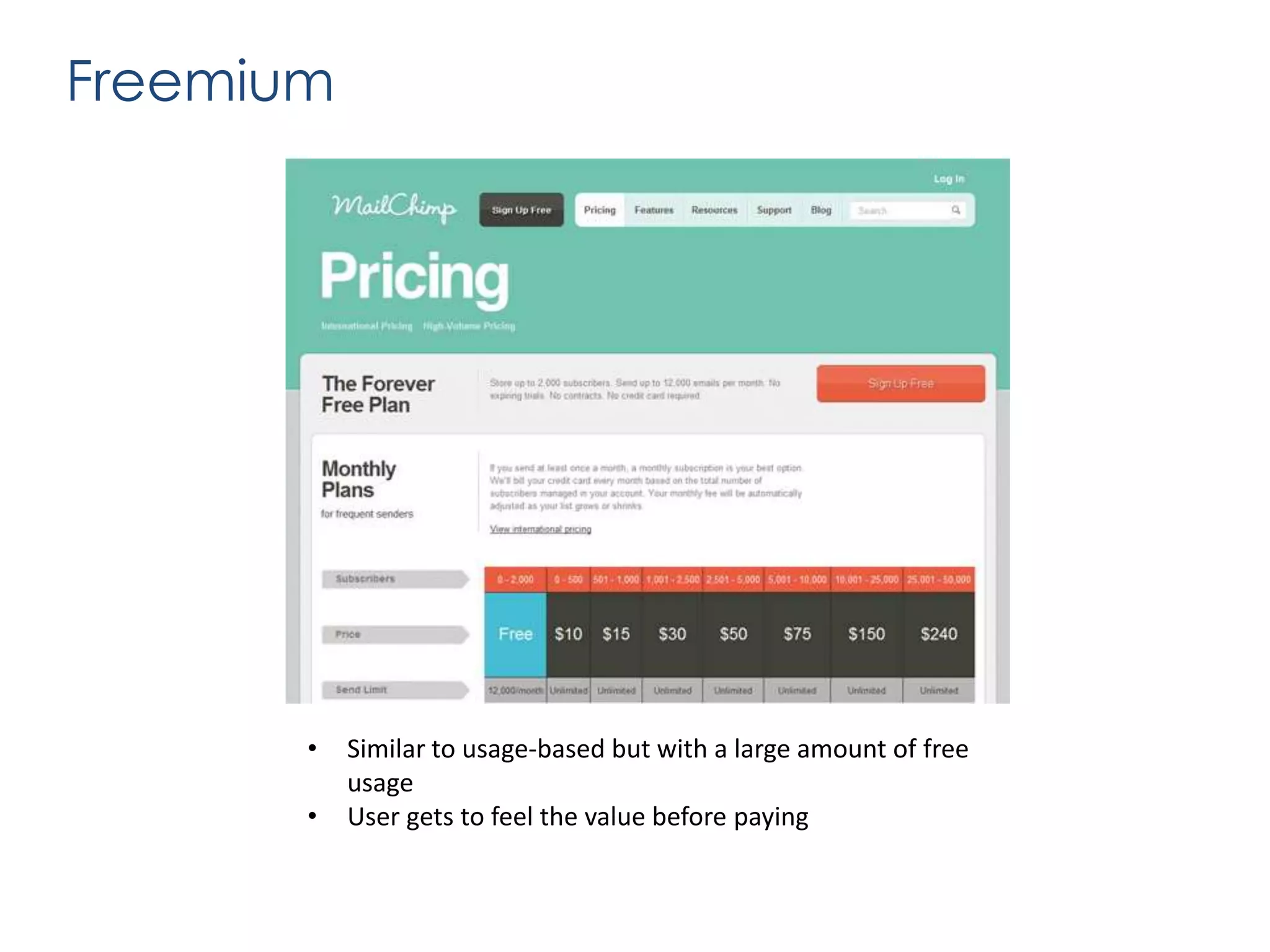
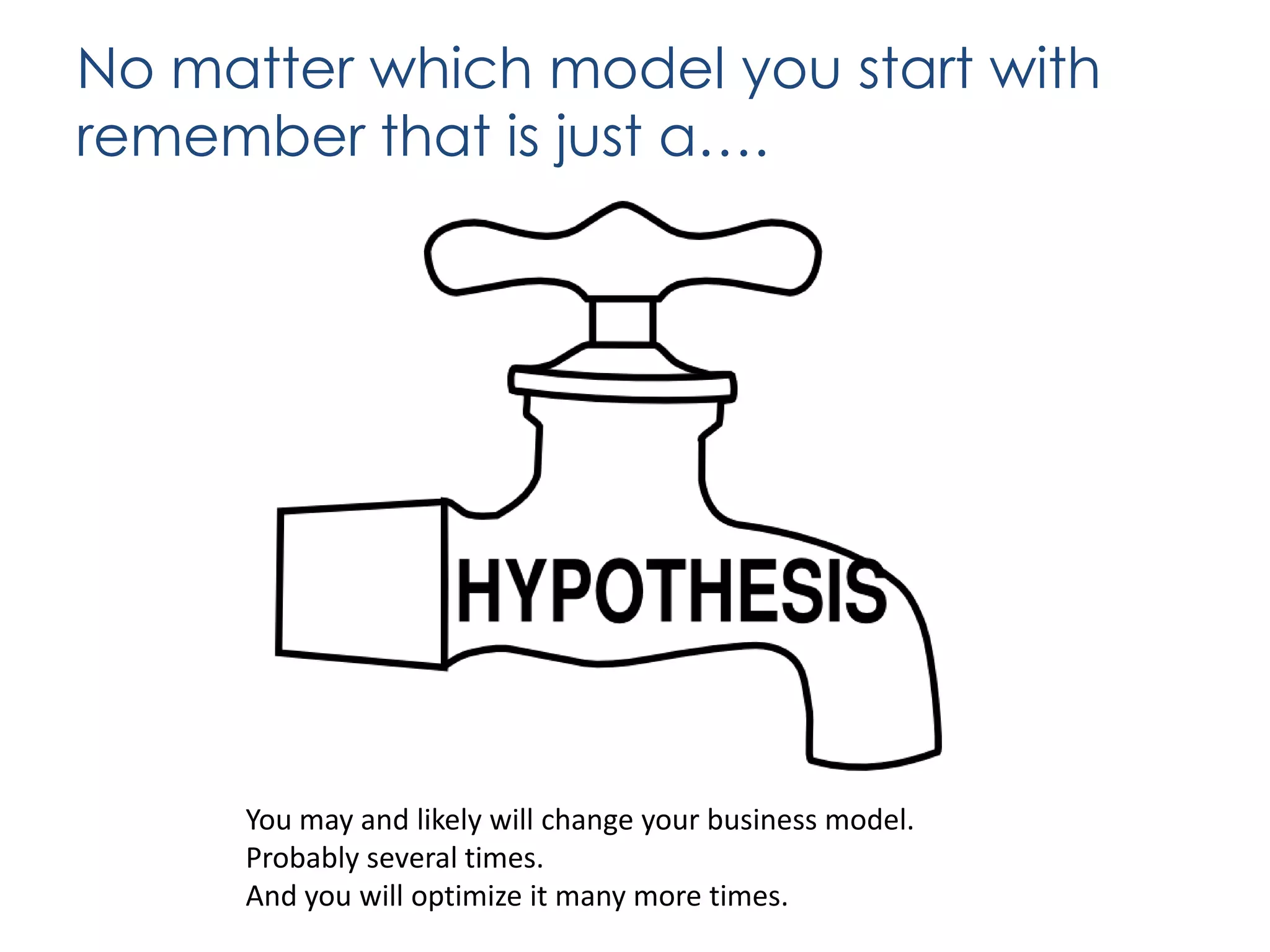
The document outlines various revenue models for startups and provides guidance on how to select the appropriate one based on customer segments and value propositions. It emphasizes the importance of solving a pain point and testing hypotheses regarding customer willingness to pay before finalizing a revenue model. The document also suggests that startups may need to adapt their business models over time and includes steps for defending the chosen model during presentations.