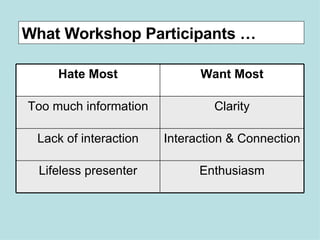
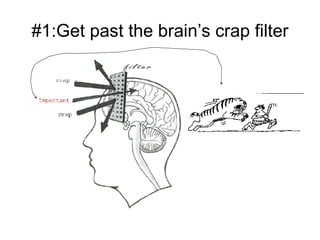
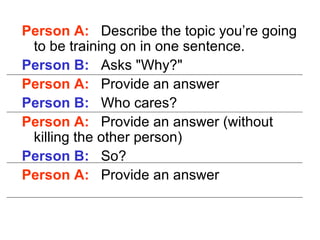
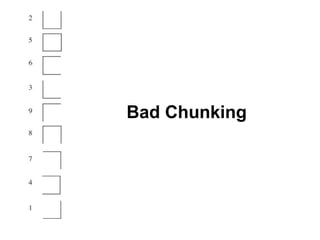
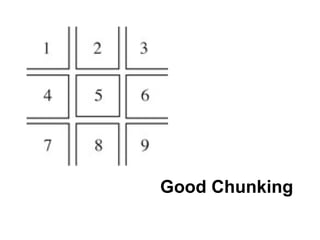
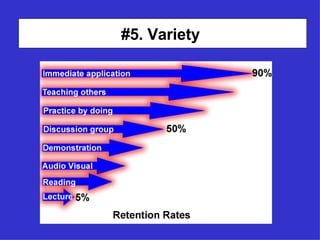
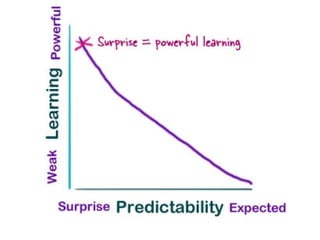
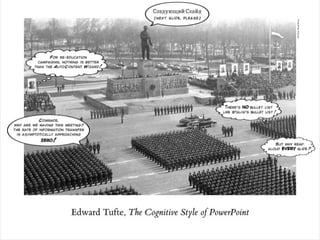
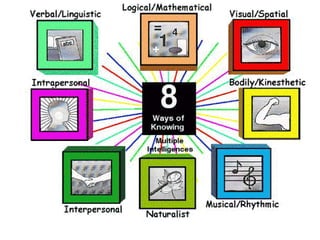
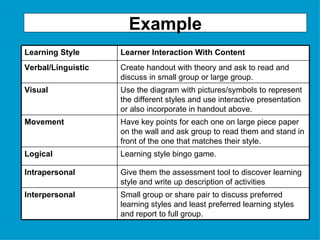
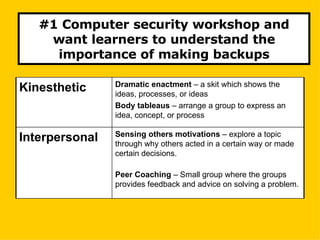
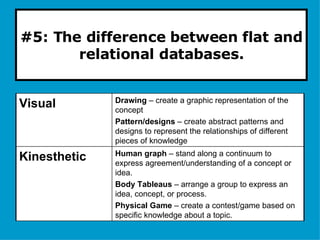
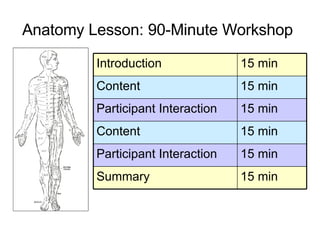
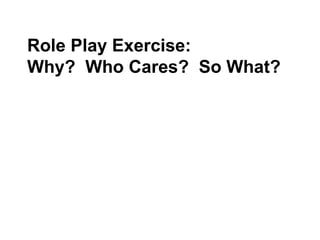The document provides guidance on designing effective learning experiences for technology training. It discusses common reasons why training fails, such as reading slides verbatim and lacking interactivity. It then covers seven principles of learning theory to apply: 1) engage learners, 2) use visuals, 3) chunk information, 4) vary pacing, 5) include variety, 6) leverage emotions, and 7) encourage two-way participation. The document demonstrates how to blend technology content with activities tailored to different learning styles. It also provides an example anatomy of a 90-minute workshop structure.