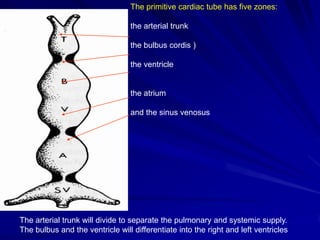
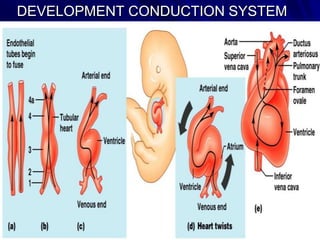
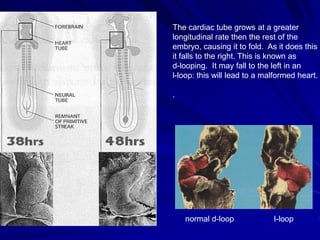
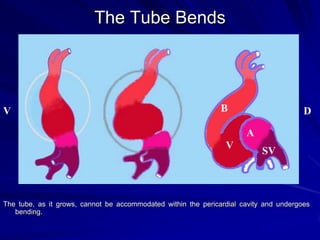
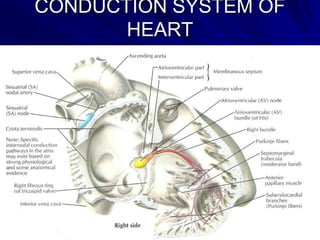
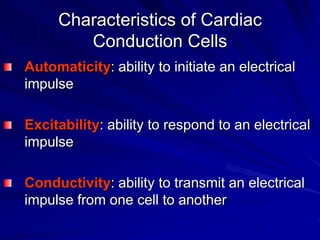
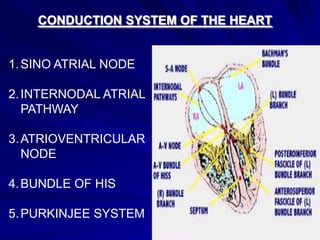
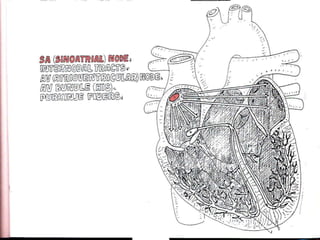
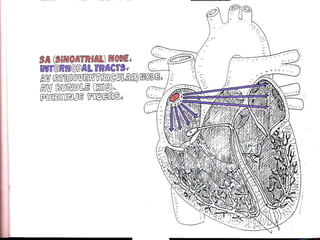
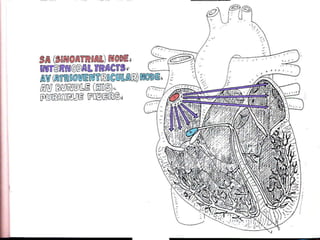
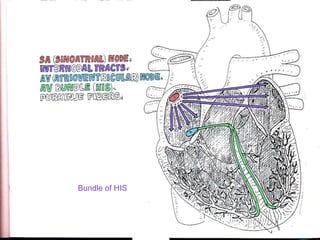
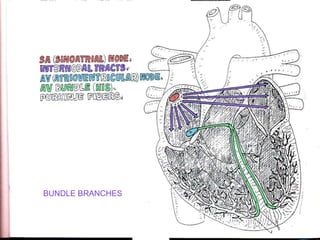
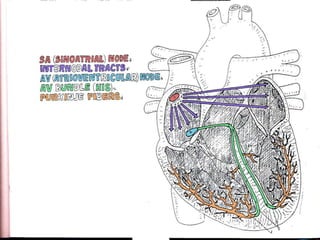
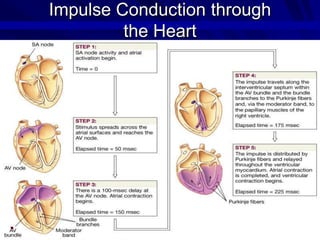
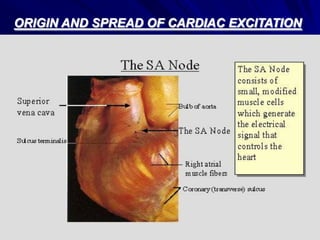
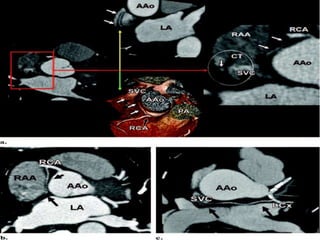
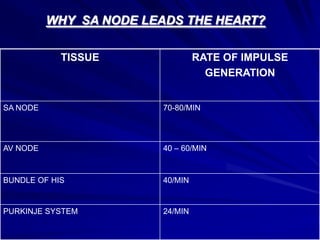
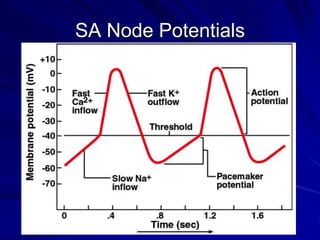
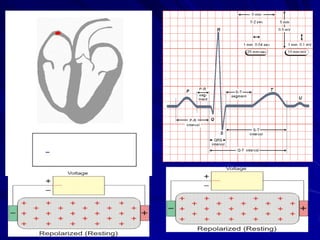
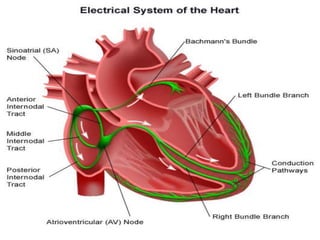
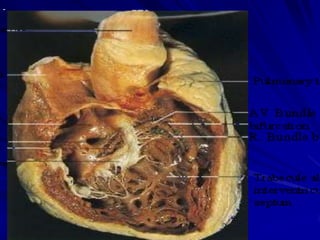
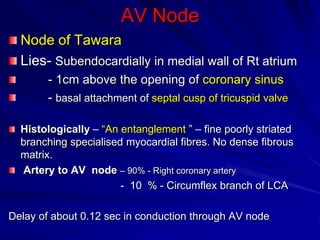
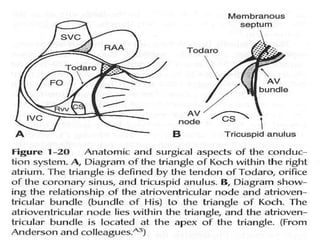
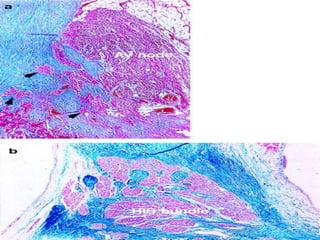
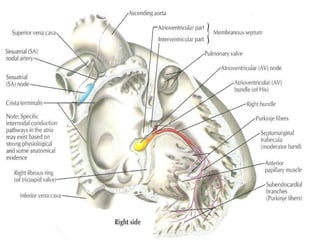
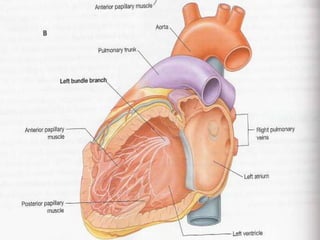
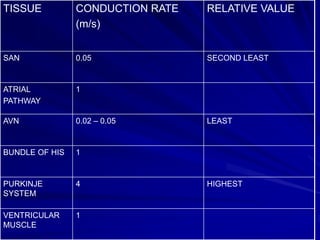
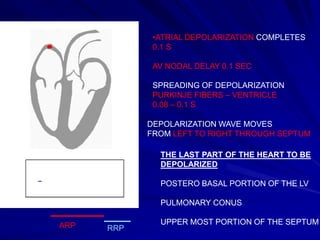
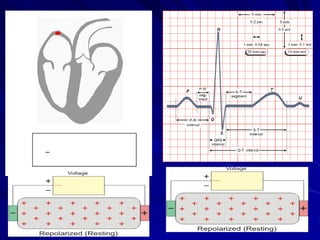
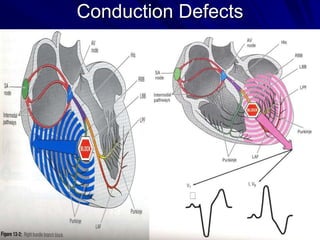
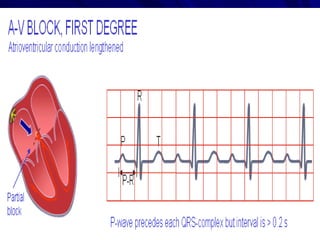
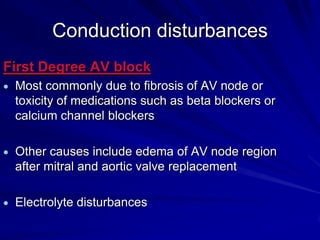
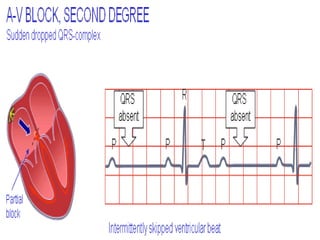
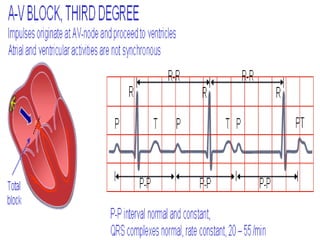
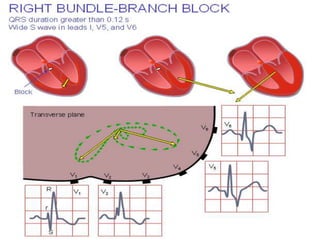
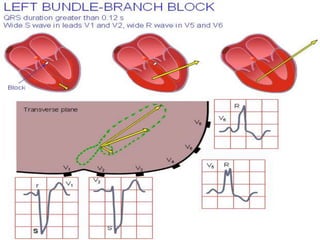
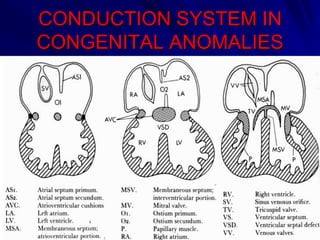
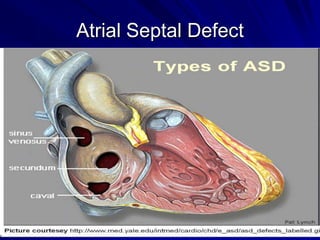
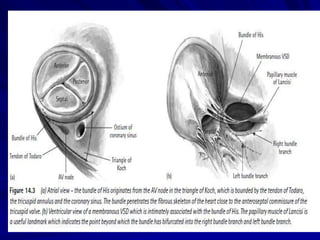
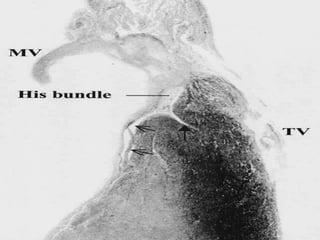
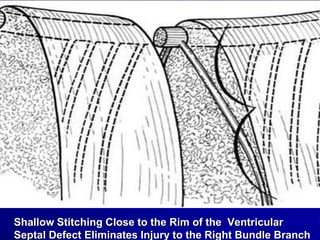
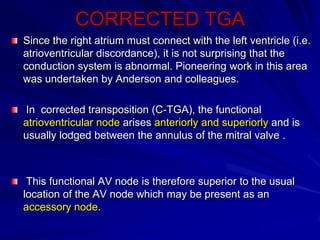
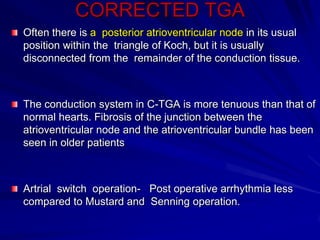
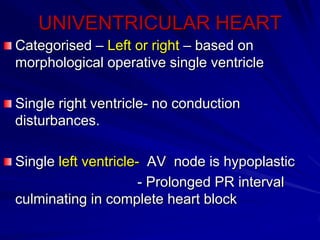
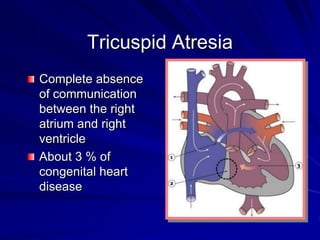
This document provides an overview of the conduction system of the heart. It begins with the development of the primitive cardiac tube and differentiation of heart structures. It then describes the specialized conduction tissues including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. It discusses impulse conduction through the heart and characteristics of cardiac conduction cells. Finally, it covers conduction defects, implications for congenital heart anomalies like ASD and VSD, and considerations for cardiac surgery.