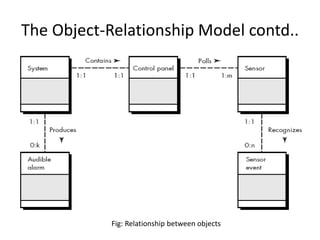
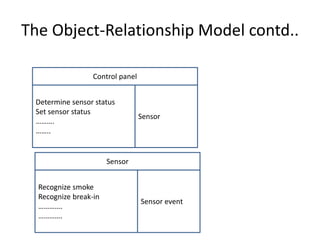
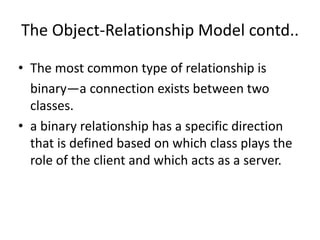
The document discusses the object-relationship model for modeling relationships between classes in object-oriented design. It explains that the first step is to understand the responsibilities of each class using CRC cards. The next step is to define collaborator classes that help achieve each responsibility, establishing connections between classes. Common relationship types like binary relationships are described, with the direction defined by which class acts as client or server. The document outlines steps for deriving an object relationship model from a CRC model by drawing collaborator objects, naming relationships, and determining cardinality.

![The Object-Relationship Model contd..
Identifying a relationship:
• Rumbaugh and his colleagues [RUM91] suggest that relationships can be derived by
examining the stative verbs or verb phrases in the statement of scope or use-cases
for the system.
• Using a grammatical parse, the analyst isolates verbs that
indicate physical location or placement (next to, part of, contained in),
communications (transmits to, acquires from),
ownership (incorporated by, is composed of), and
Satisfaction of a condition (manages, coordinates, controls).
• These provide an indication of a relationship.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectrelationshipmodel-140610123608-phpapp01/85/Object-relationship-model-of-software-engineering-a-subtopic-of-object-oriented-analysis-5-320.jpg)