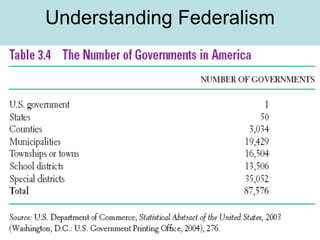
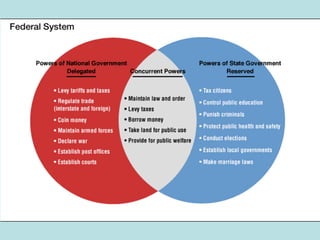
Federalism is a system of government where power is shared between a central federal government and state governments. Under federalism, the federal government has enumerated powers while states have reserved powers not granted to the federal government through the 10th Amendment. Over time, the scope of the federal government has expanded as it takes on new responsibilities in areas such as the economy, social policies, and issues that cross state boundaries. The balance of power between federal and state governments has shifted through Supreme Court rulings and policies that increase or decrease centralized power.