1. The document outlines the five key tasks in the strategic planning process: develop the vision, set objectives, craft the strategy, implement the strategy, and evaluate performance.
2. It discusses the importance of developing a clear vision and mission, setting specific and measurable objectives, crafting the strategy based on organizational strengths and the external environment, and implementing through leadership, culture, policies and programs.
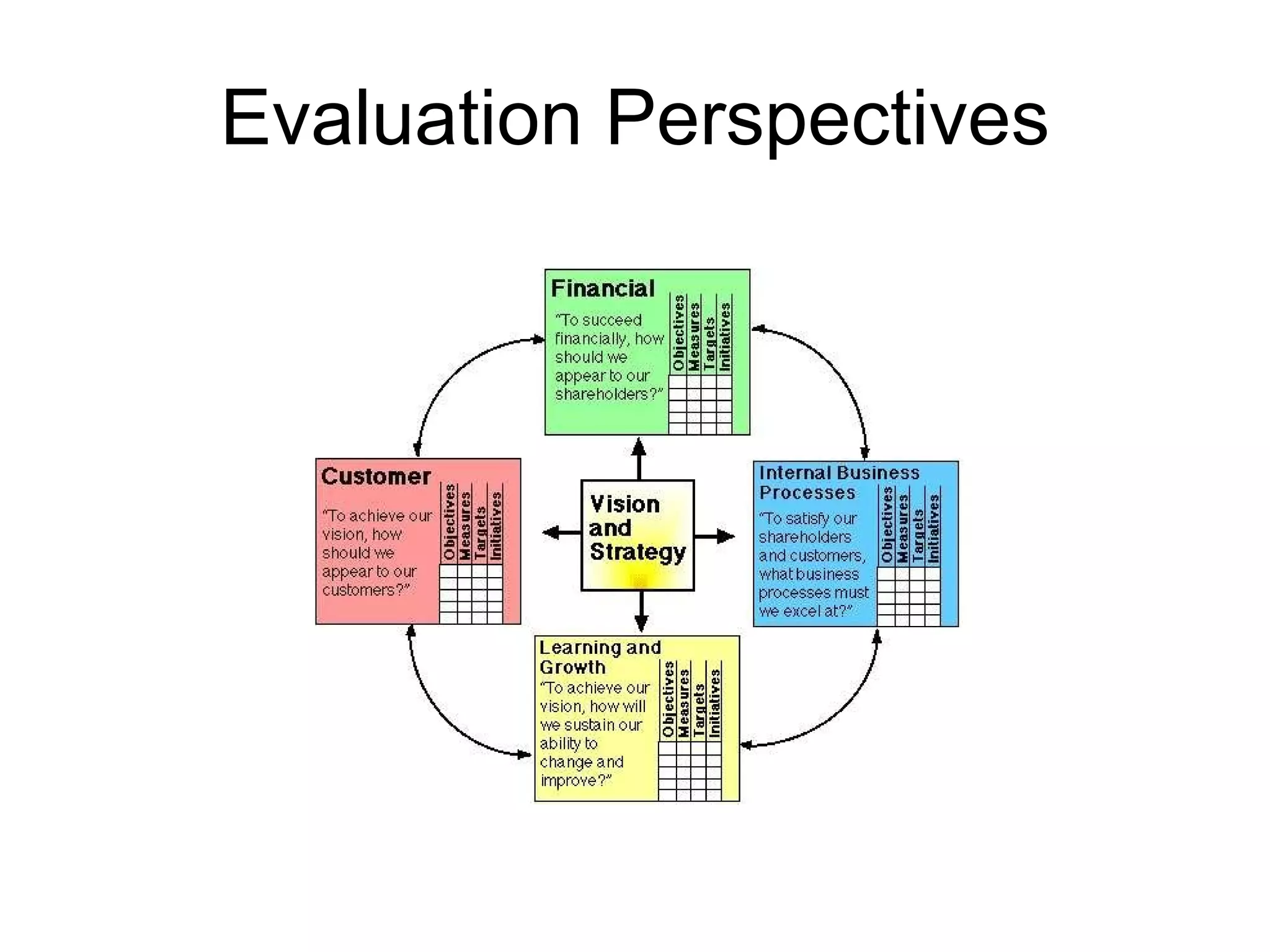
3. Evaluation requires assessing both financial and non-financial measures of performance, as well as balancing short-term results with long-term strategic goals using tools like the balanced scorecard.