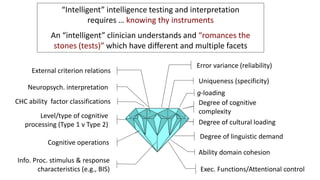
This document discusses the history and evolution of intelligence test interpretation. It outlines four waves of interpretation: 1) Quantification of general intelligence, 2) Clinical profile analysis, 3) Psychometric profile analysis, and 4) Applying psychological theory. It highlights Dr. Alan Kaufman's 1979 book "Intelligent Testing with the WISC-R" as pioneering the third wave of psychometric profile analysis. The document emphasizes that intelligent testing requires incorporating both quantitative test data and clinical expertise to develop interventions that improve individuals' lives.