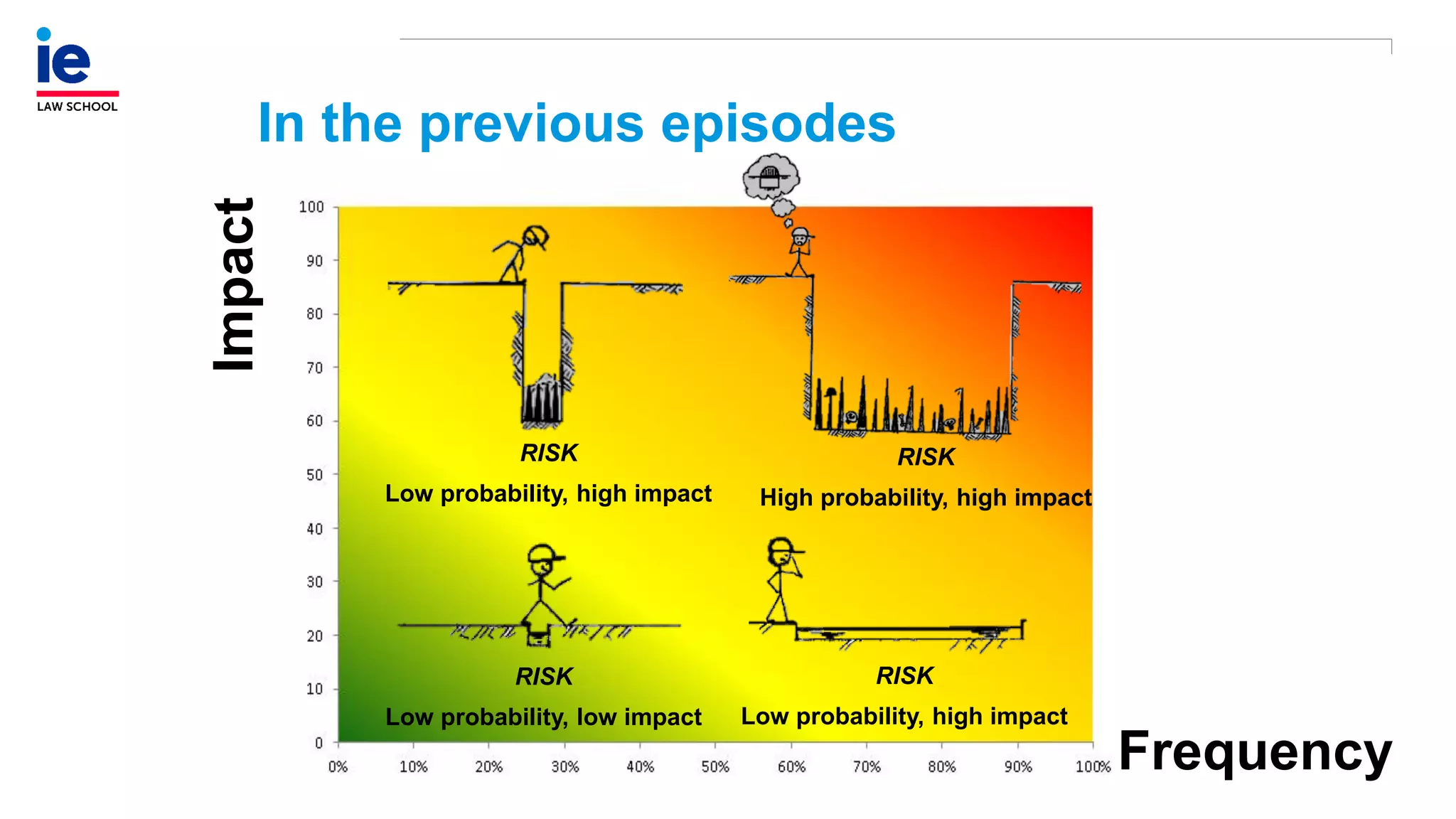
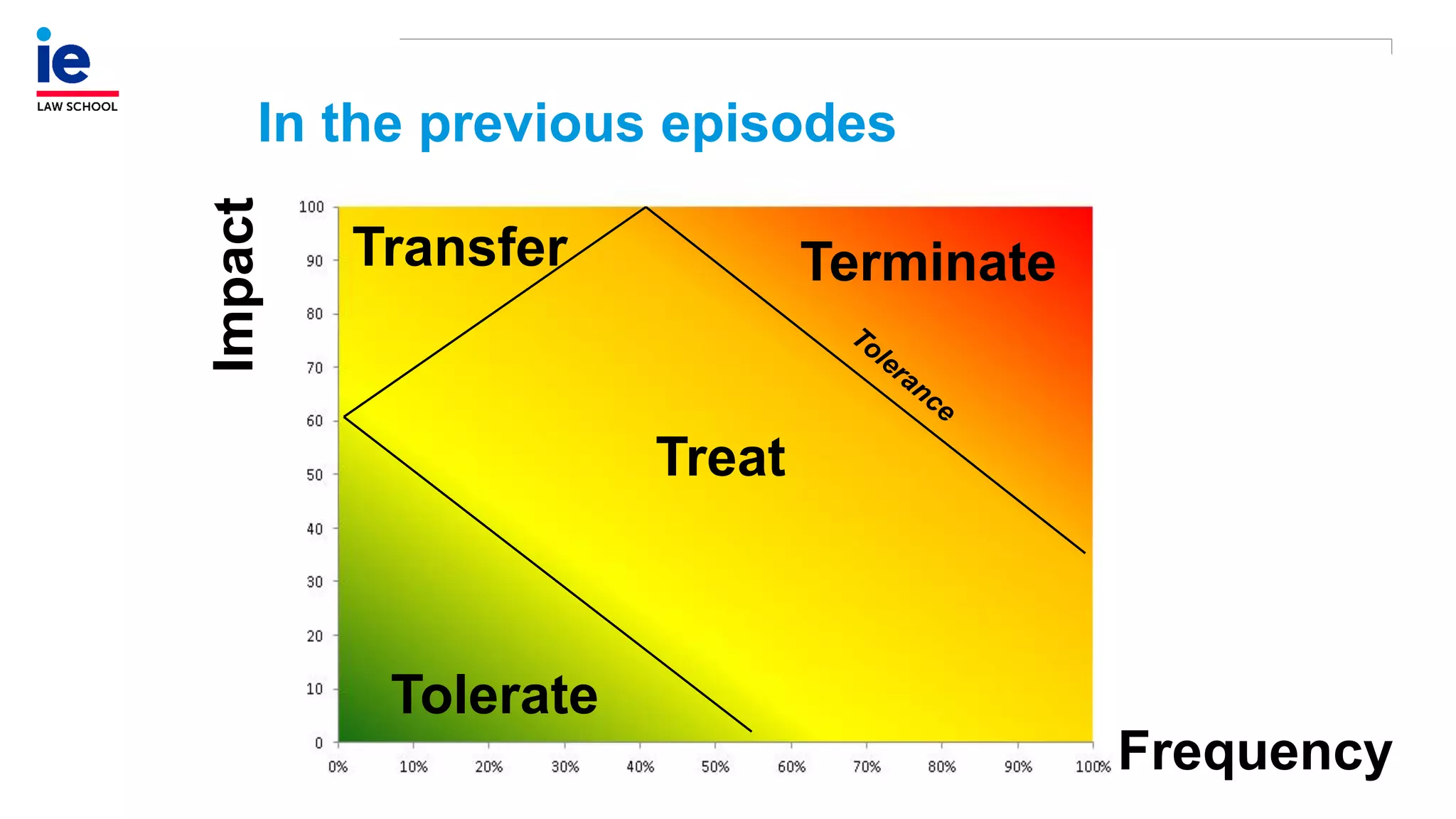
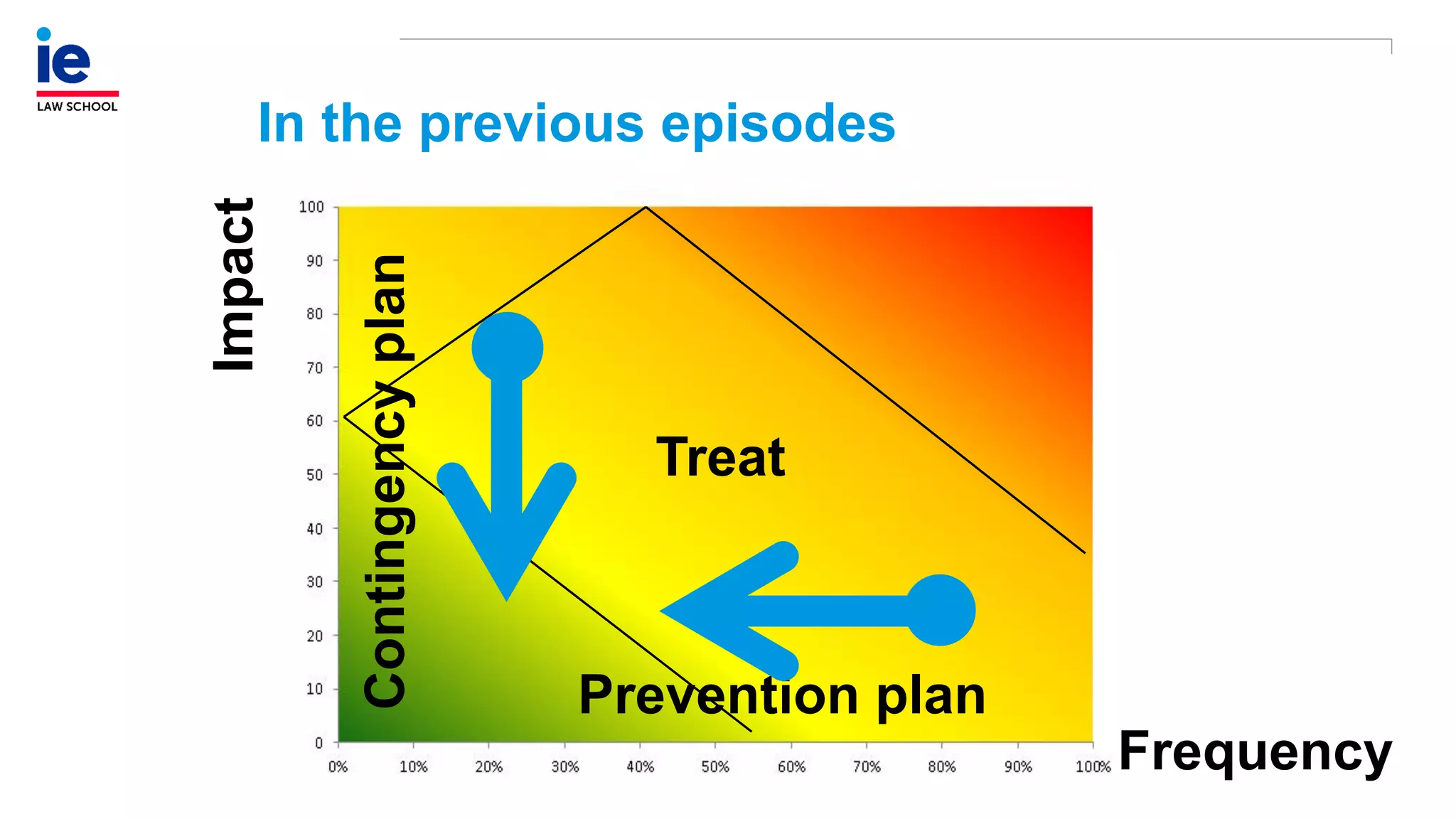
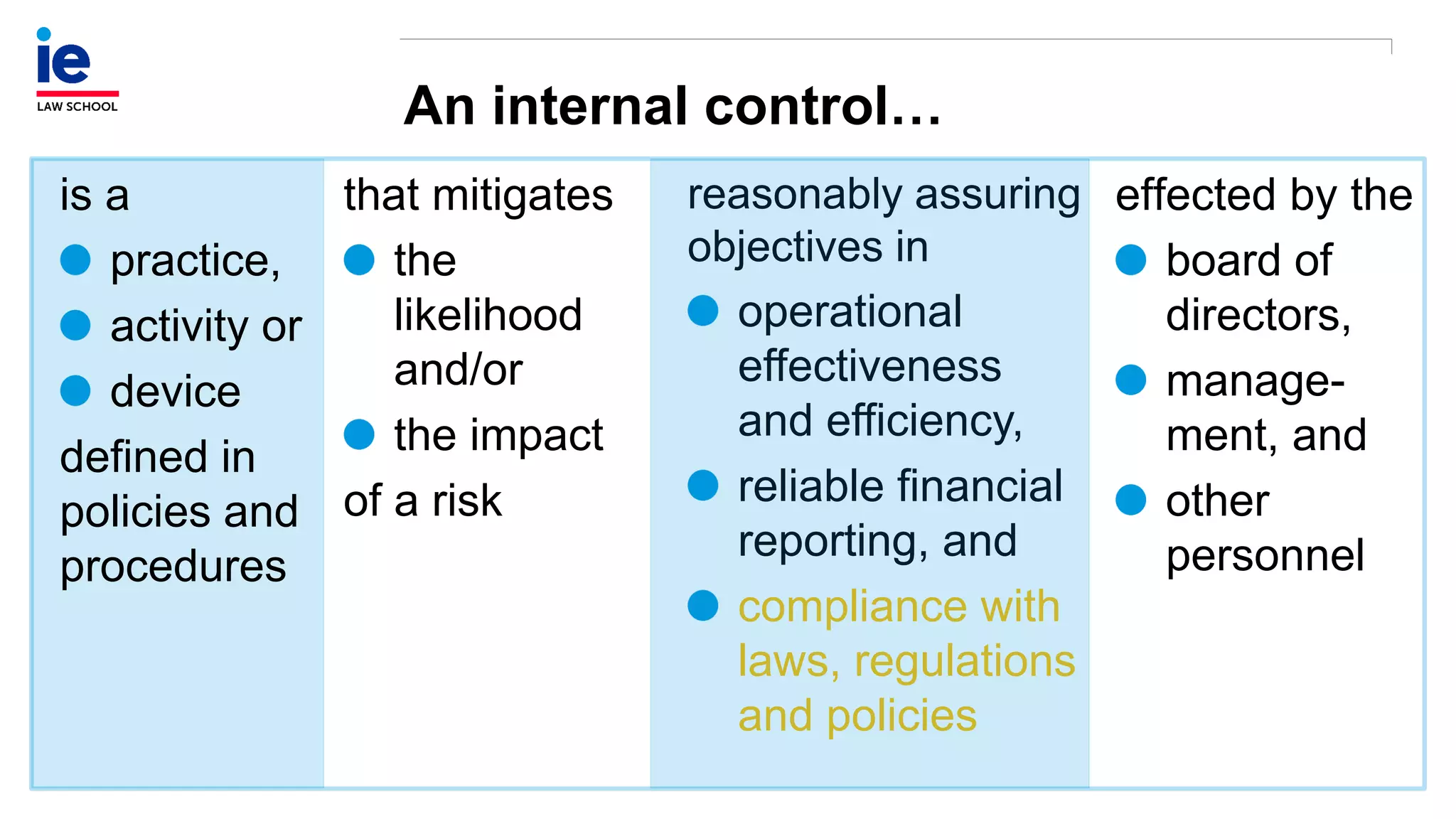
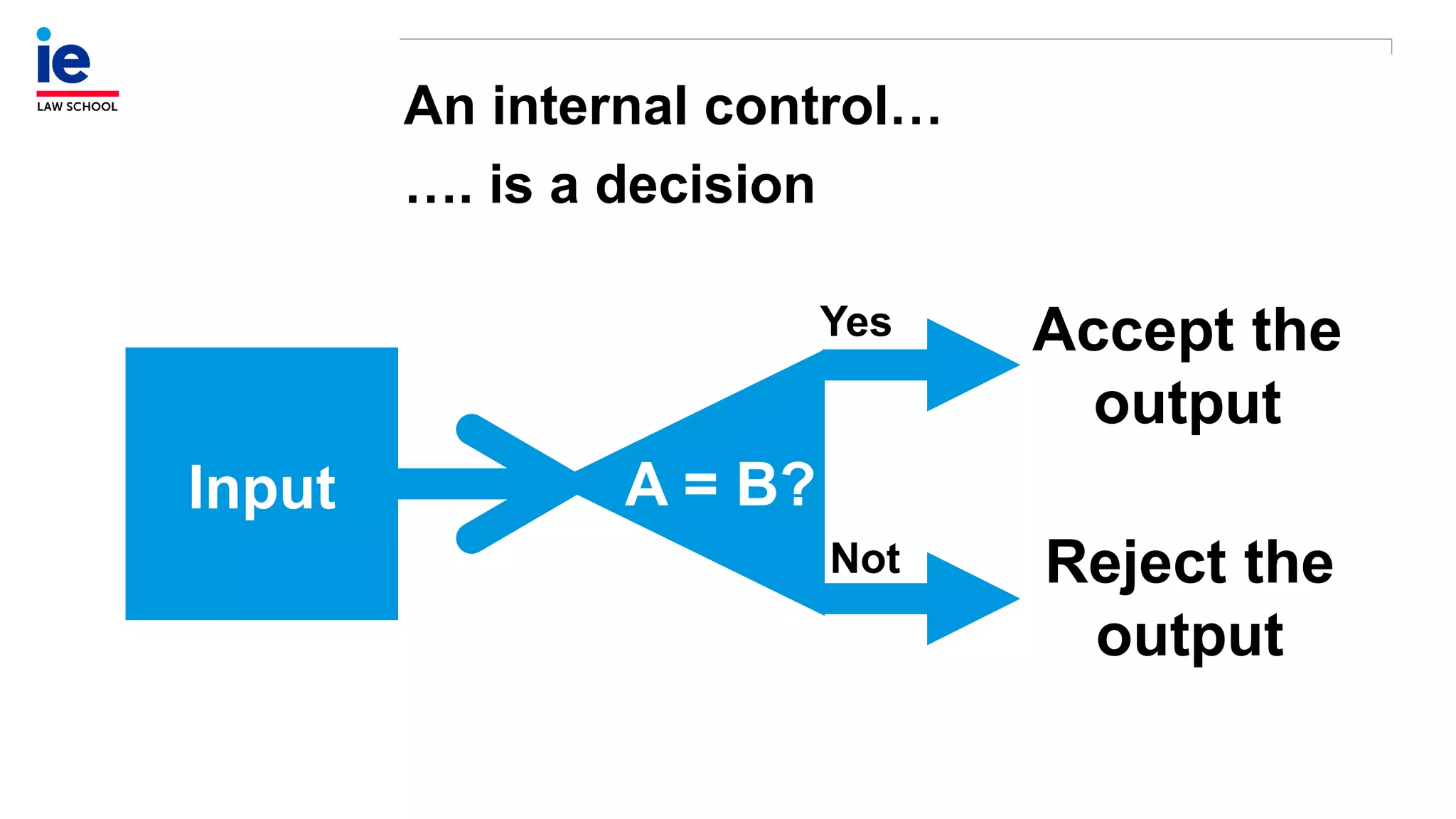
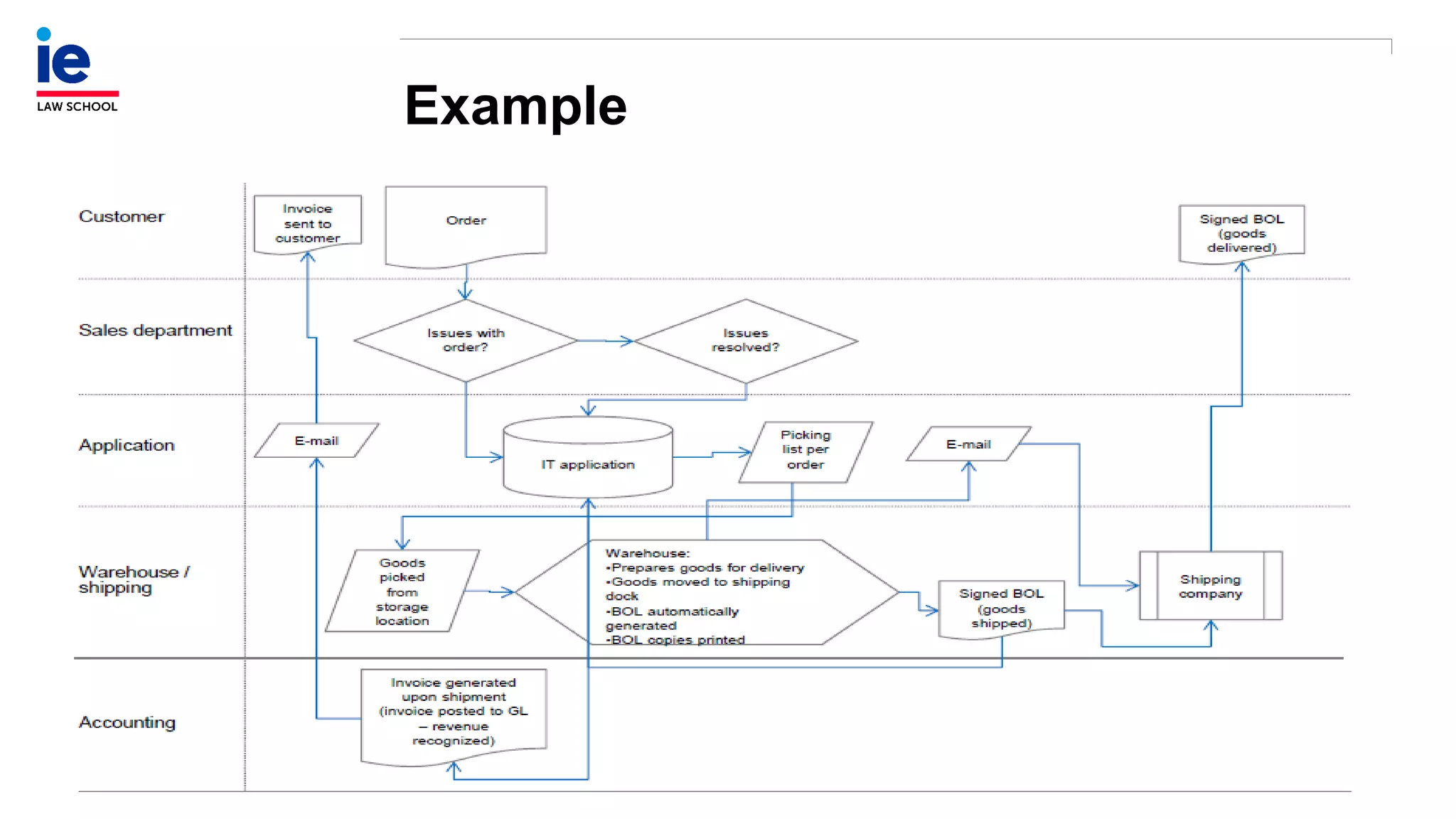
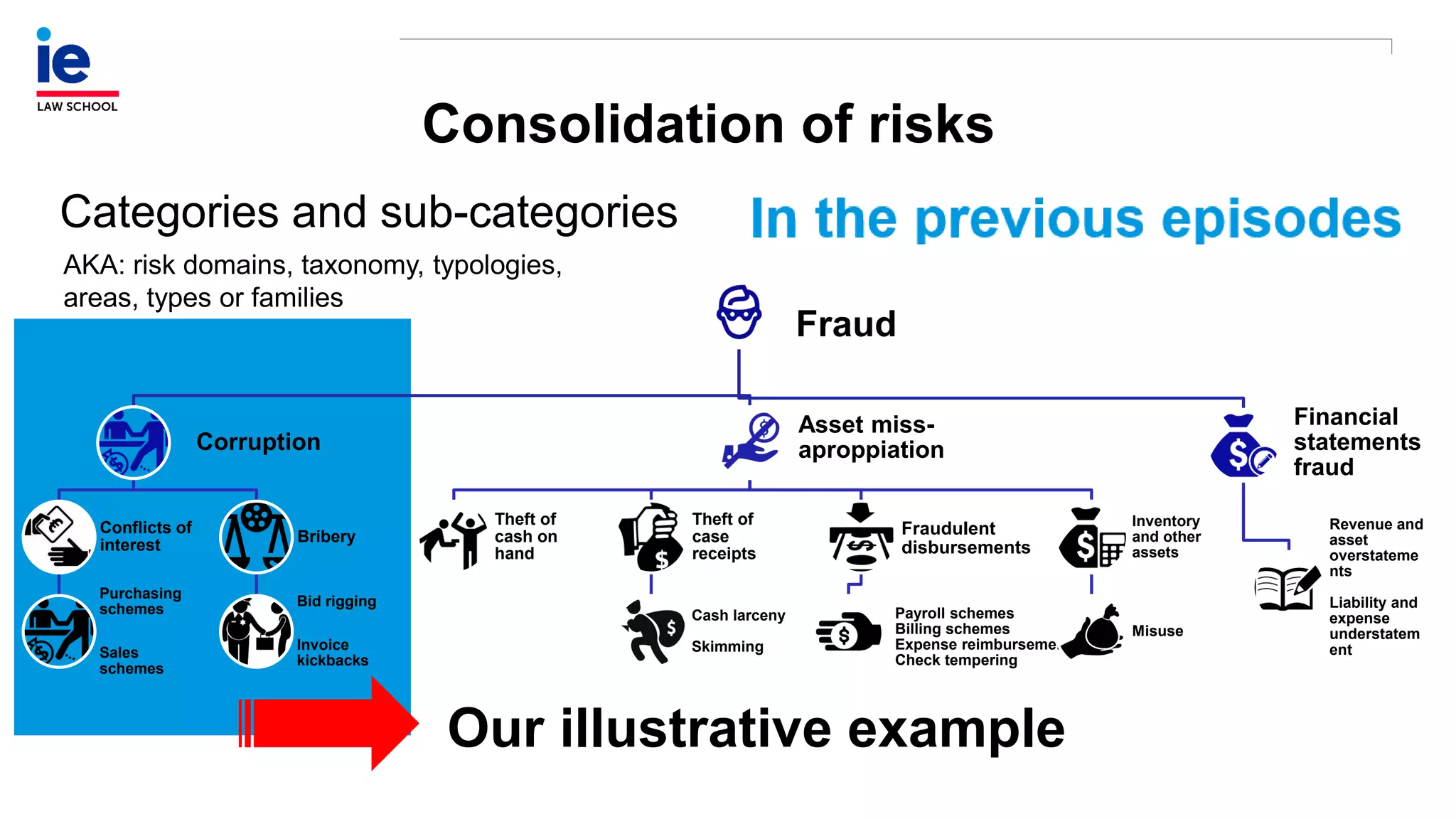
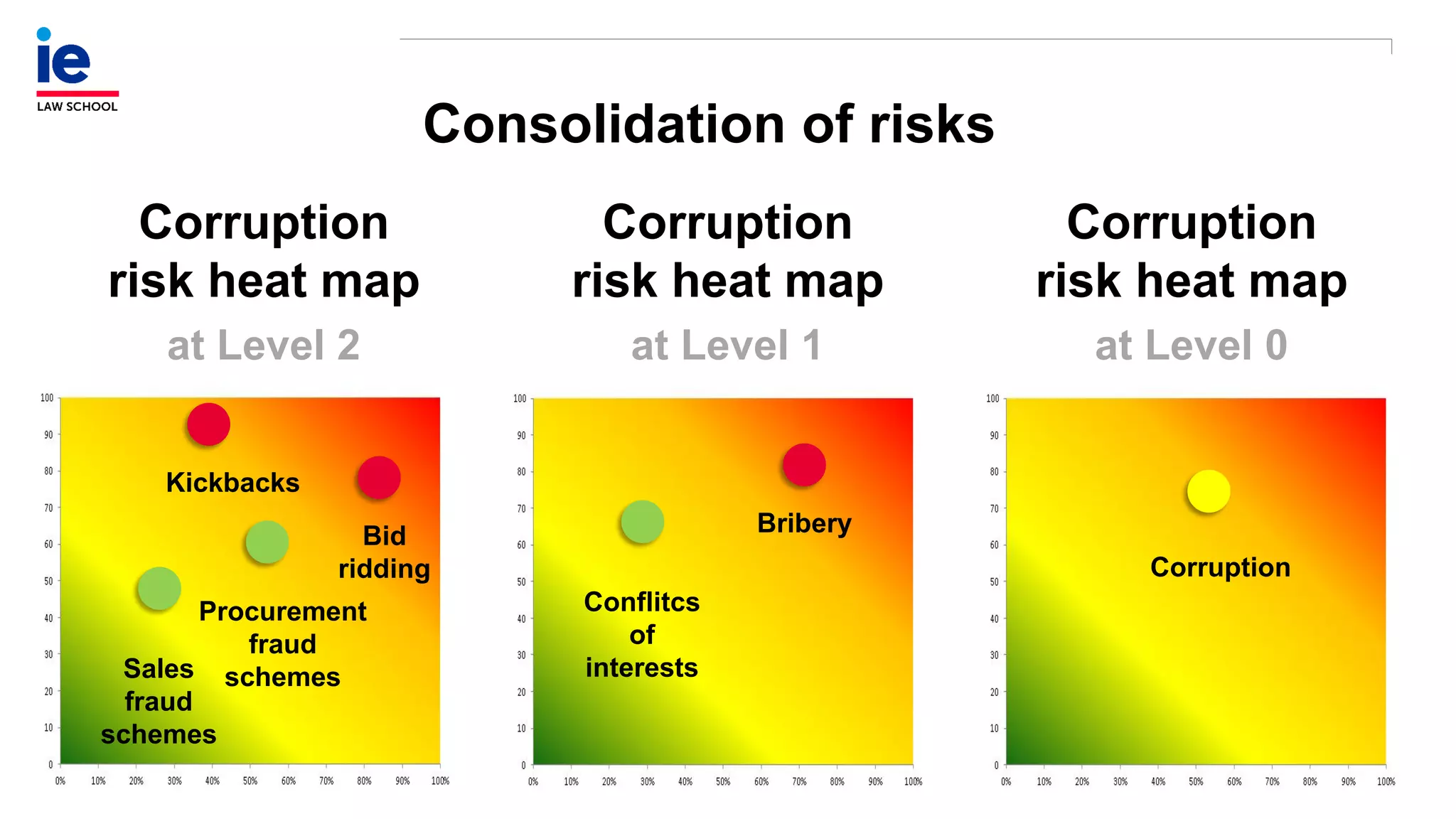
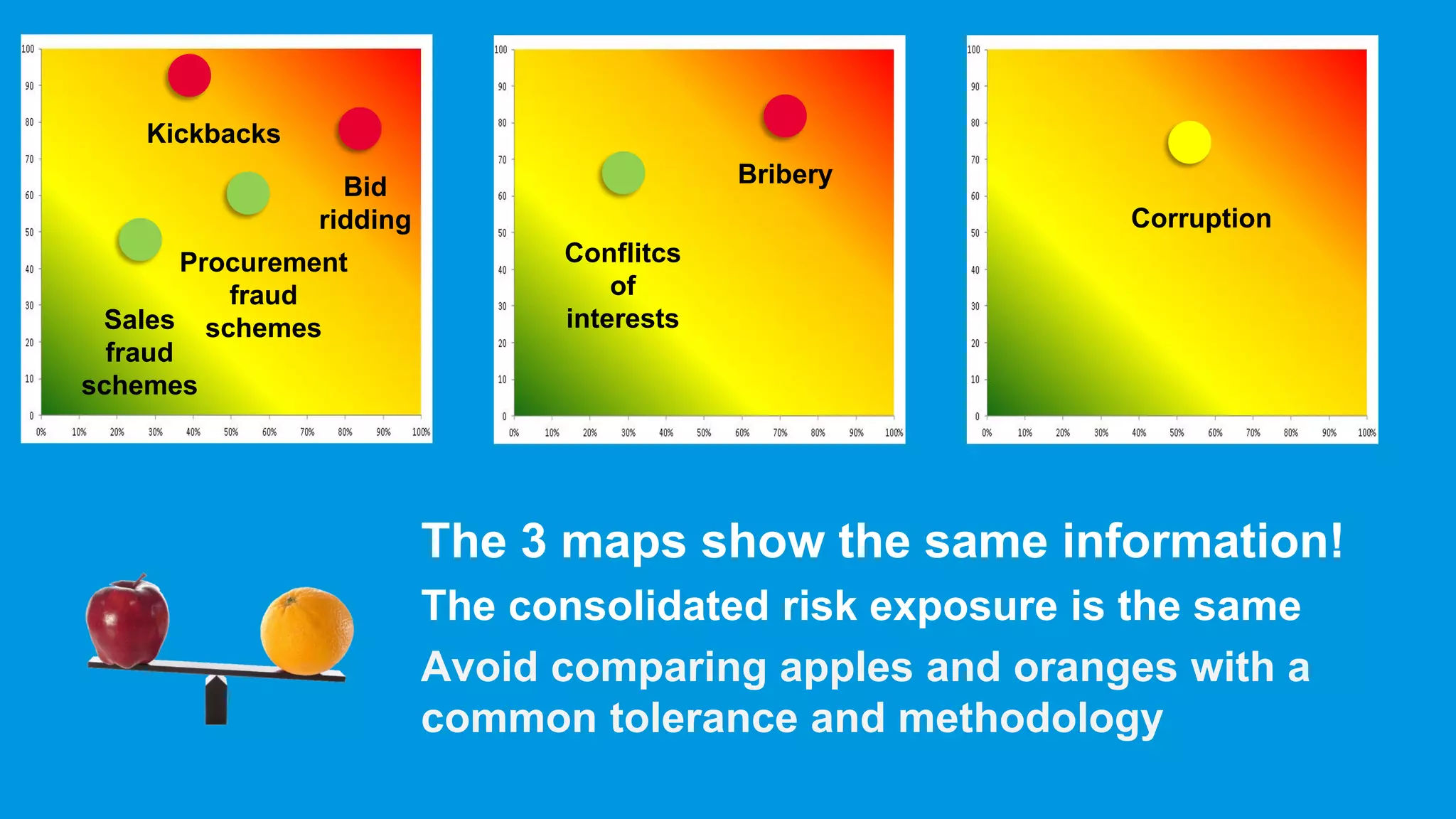
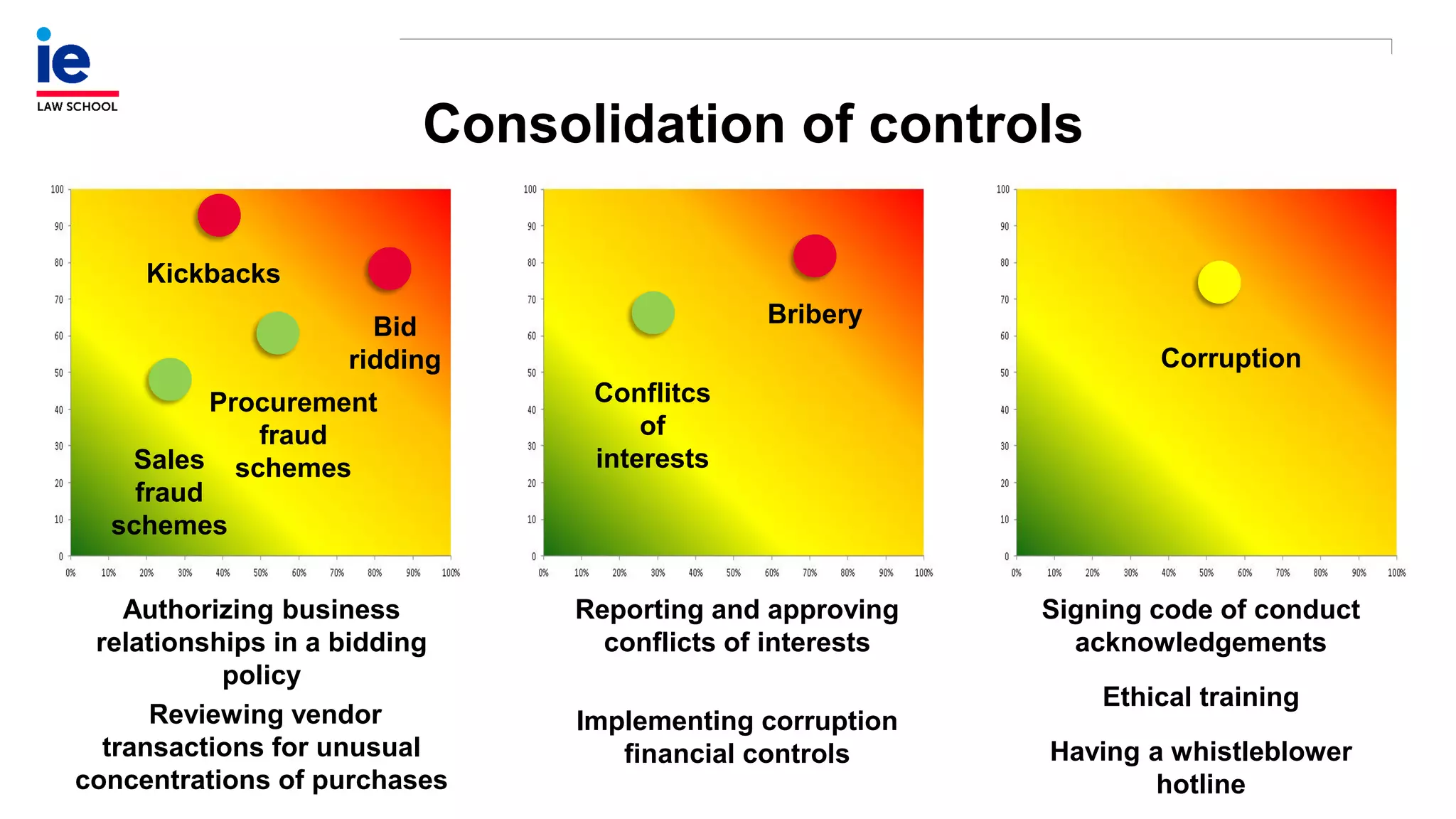
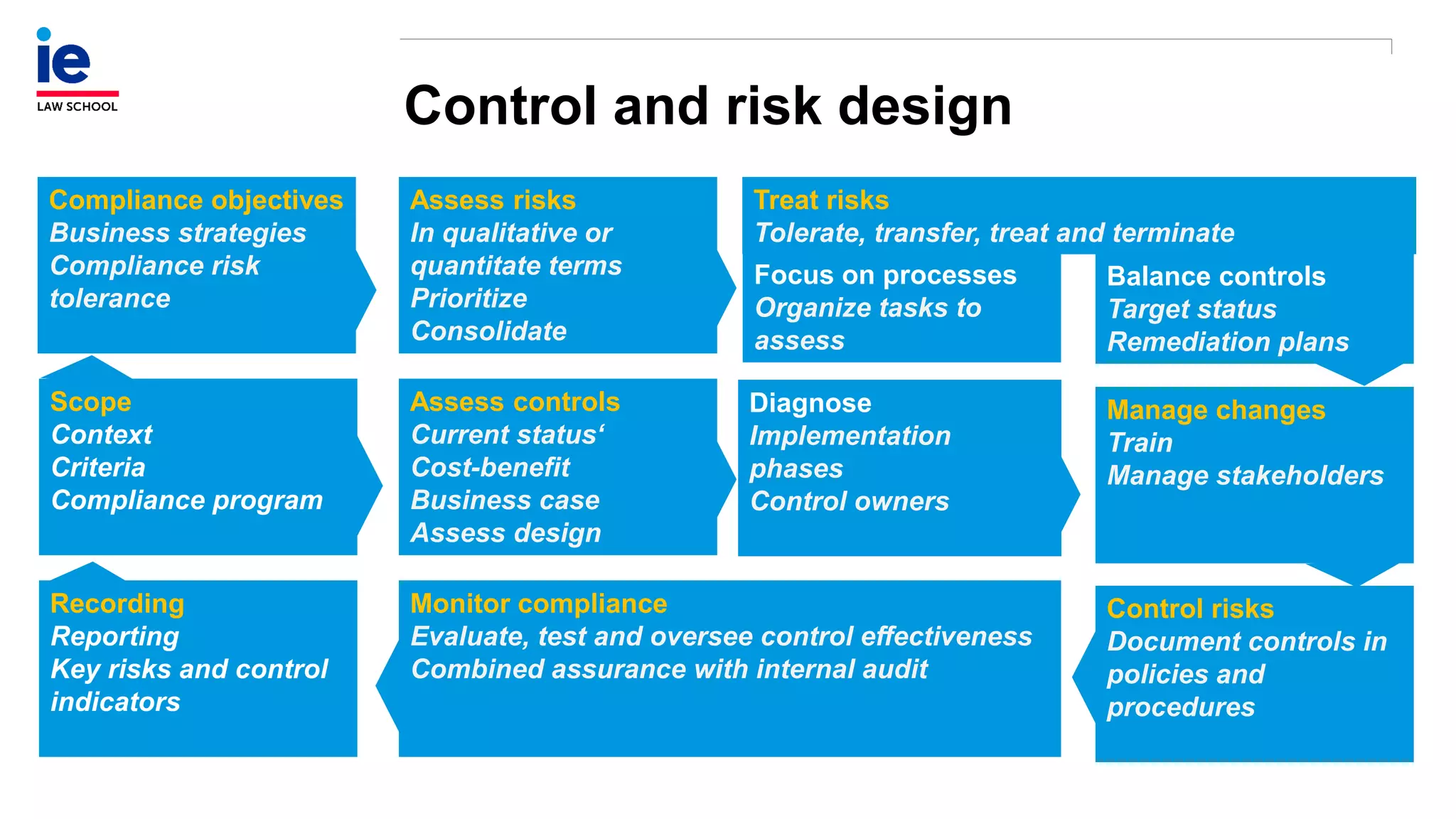
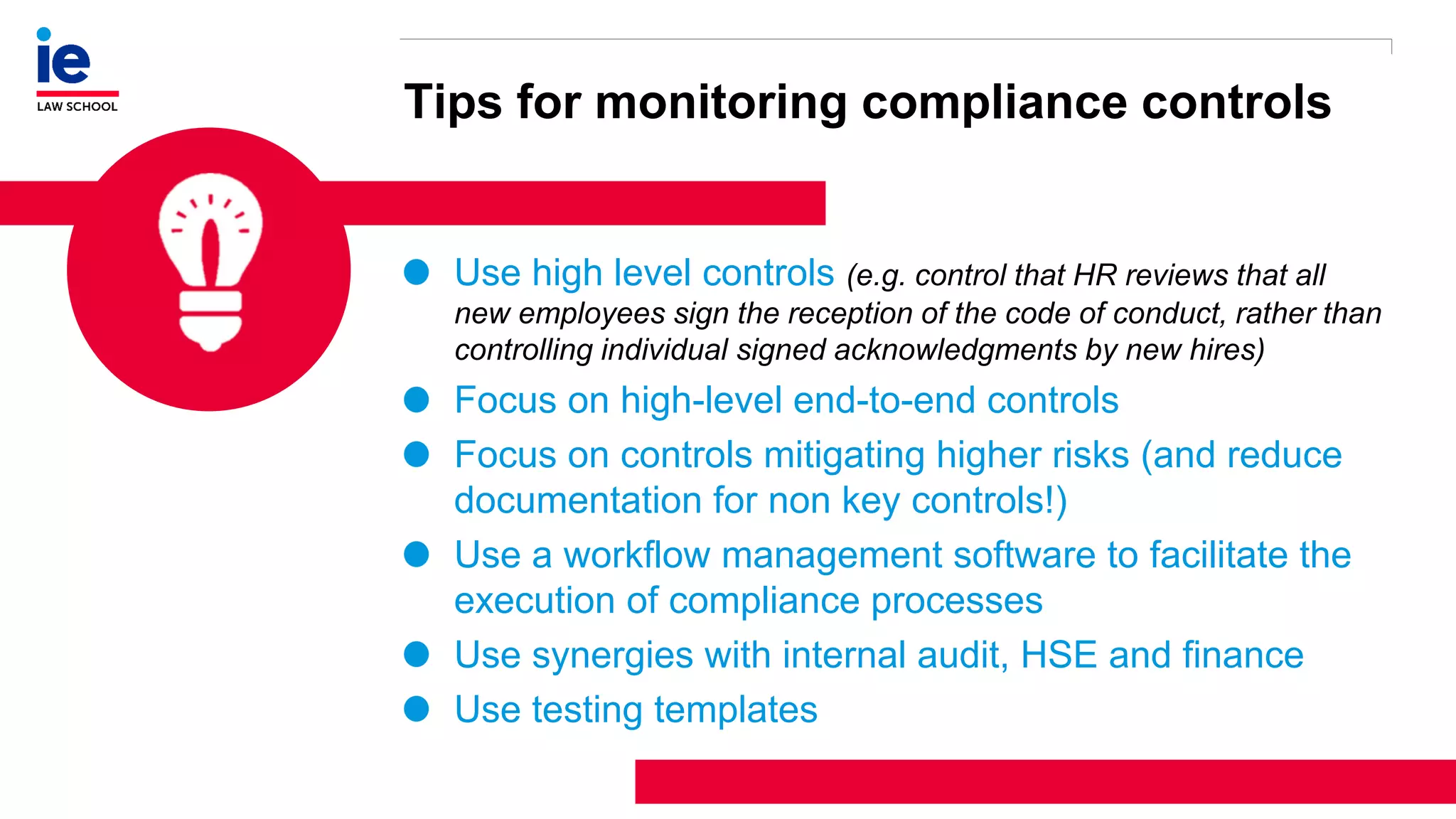
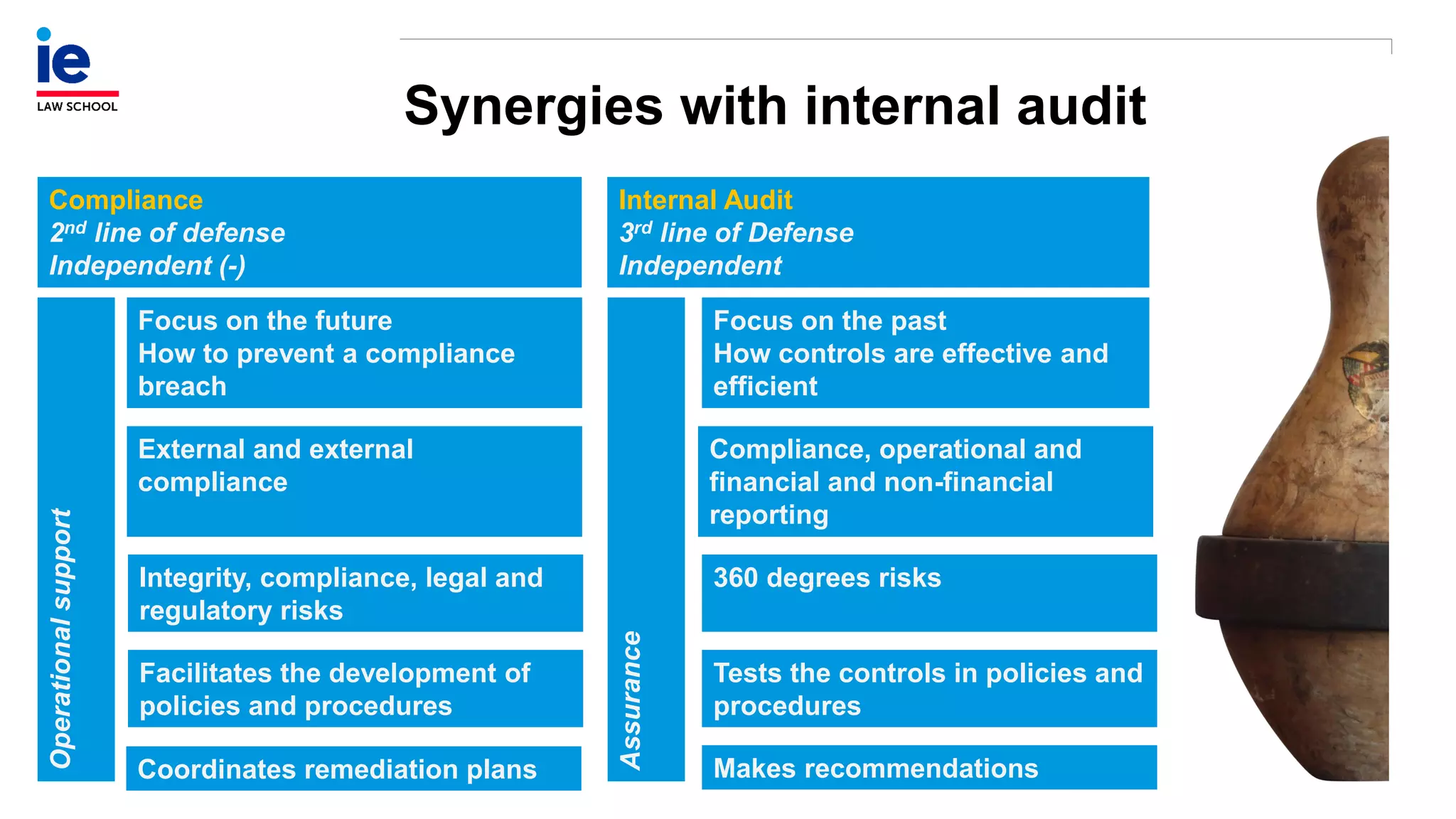
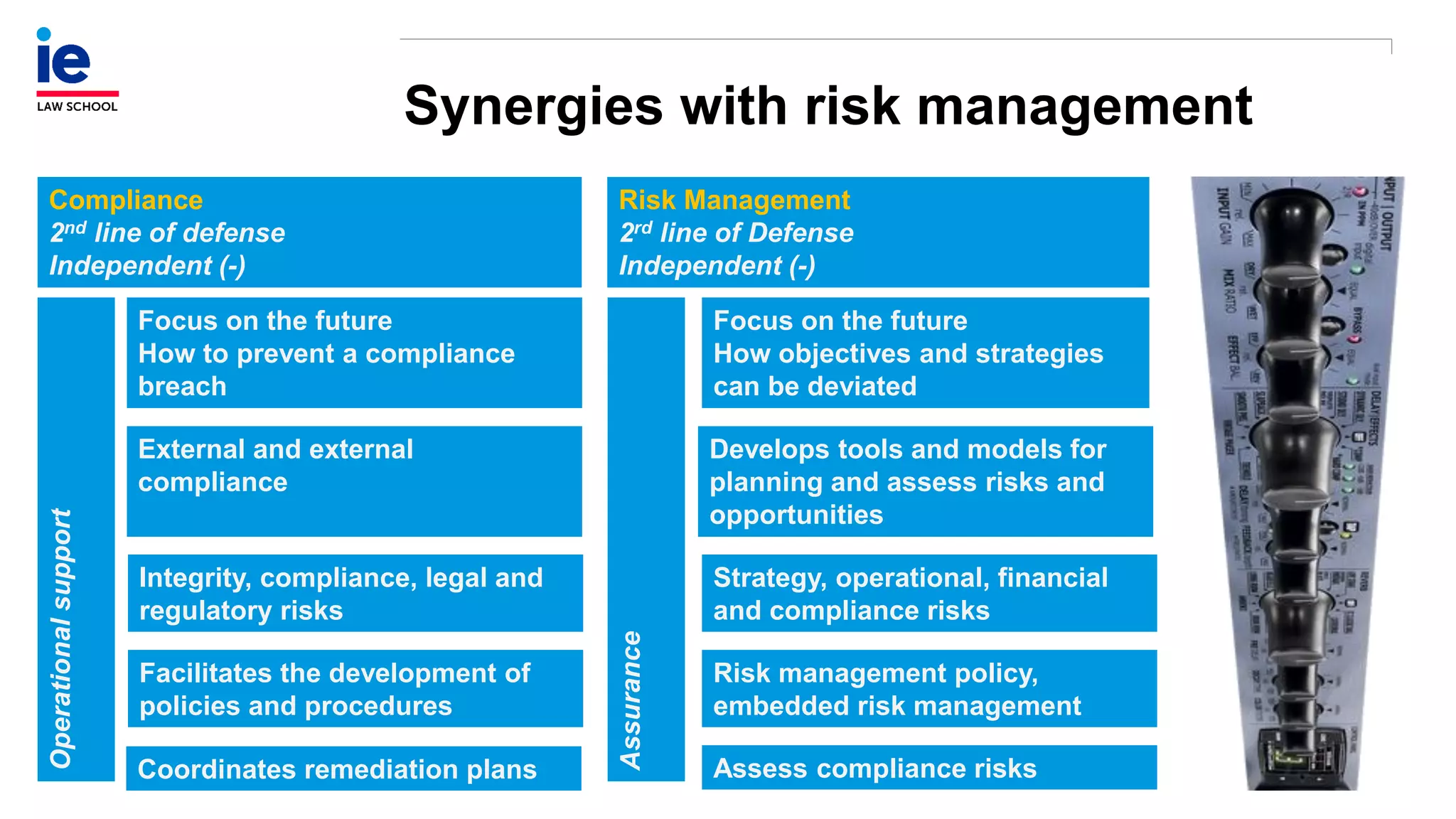
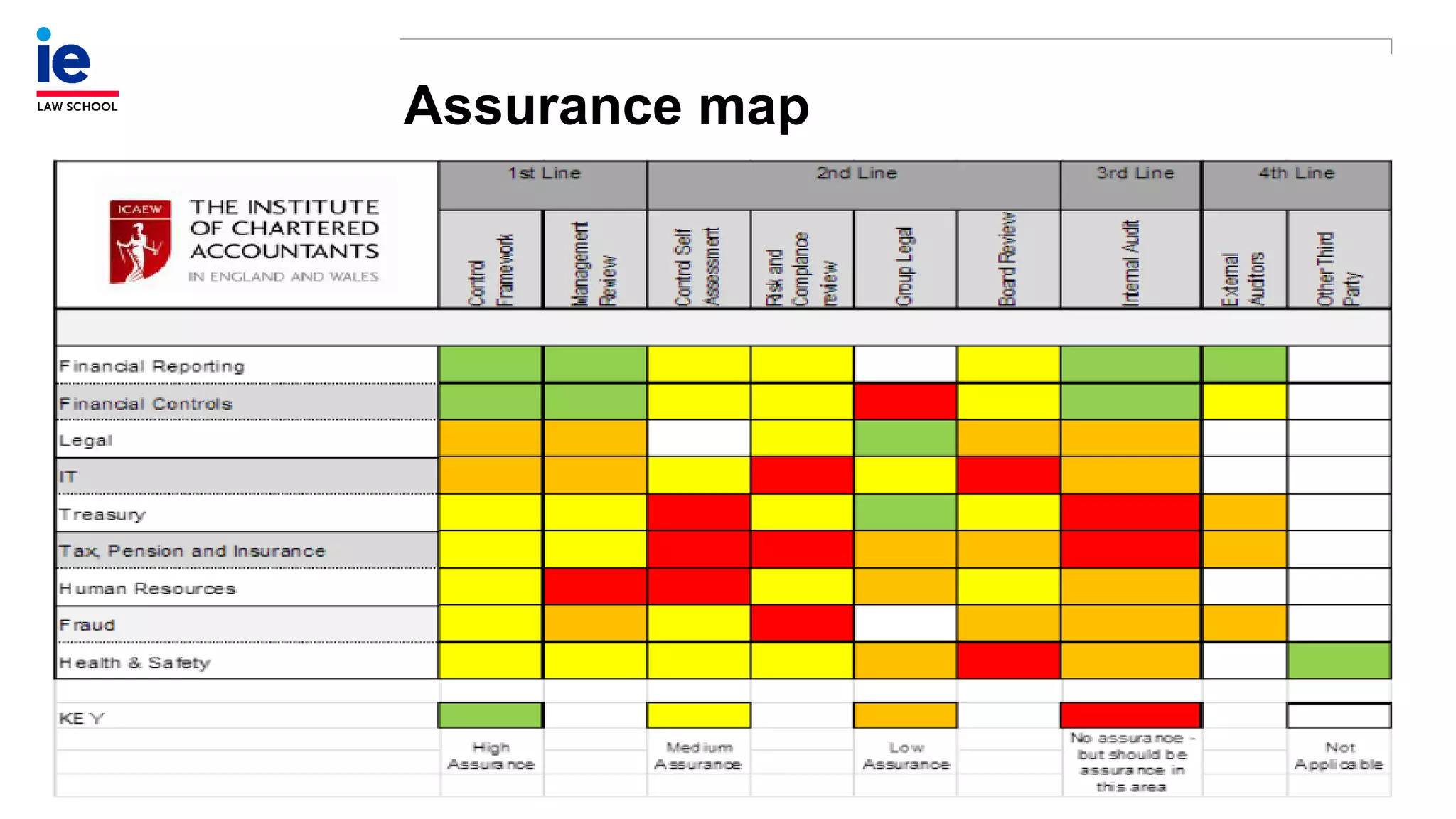
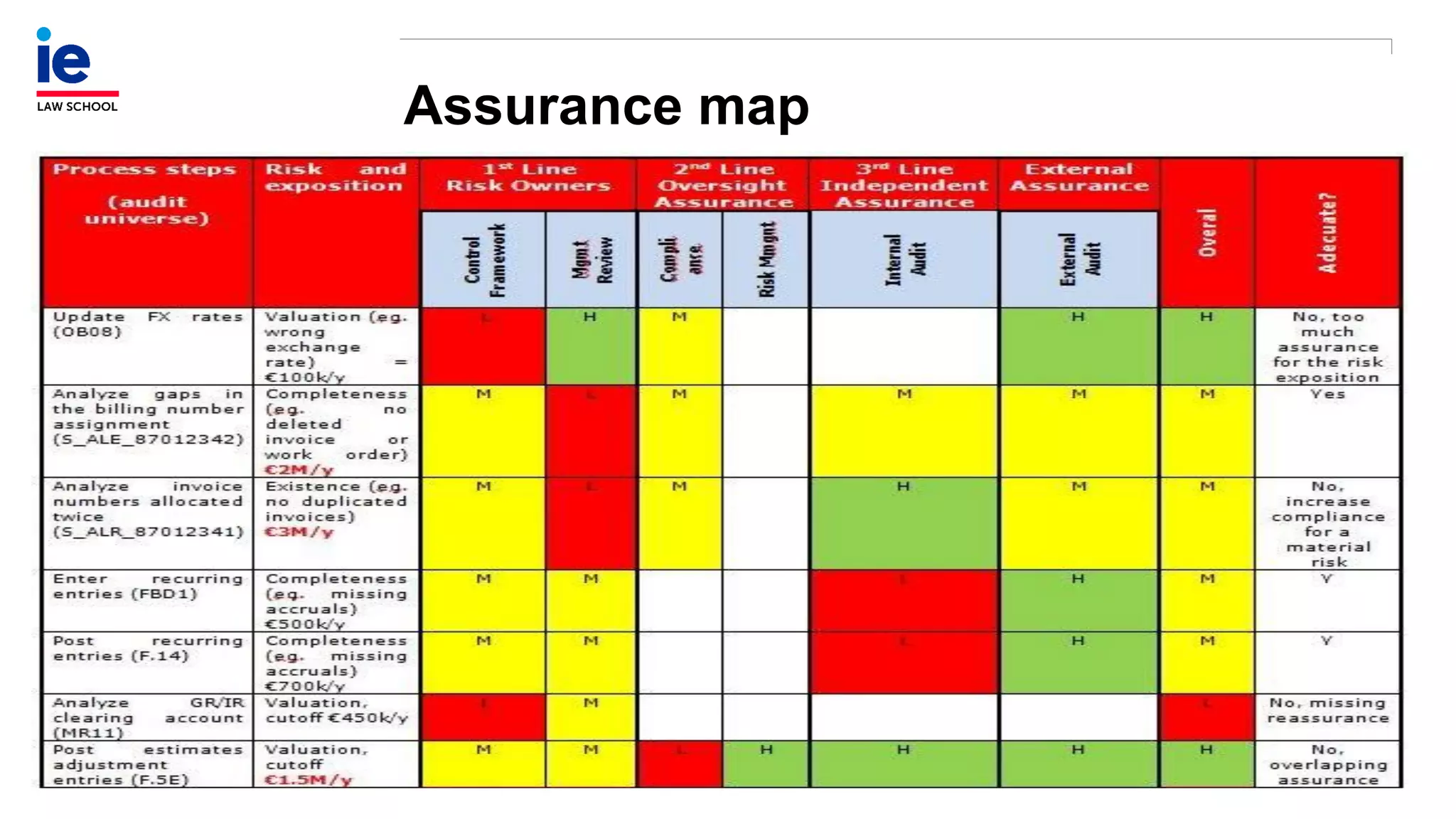
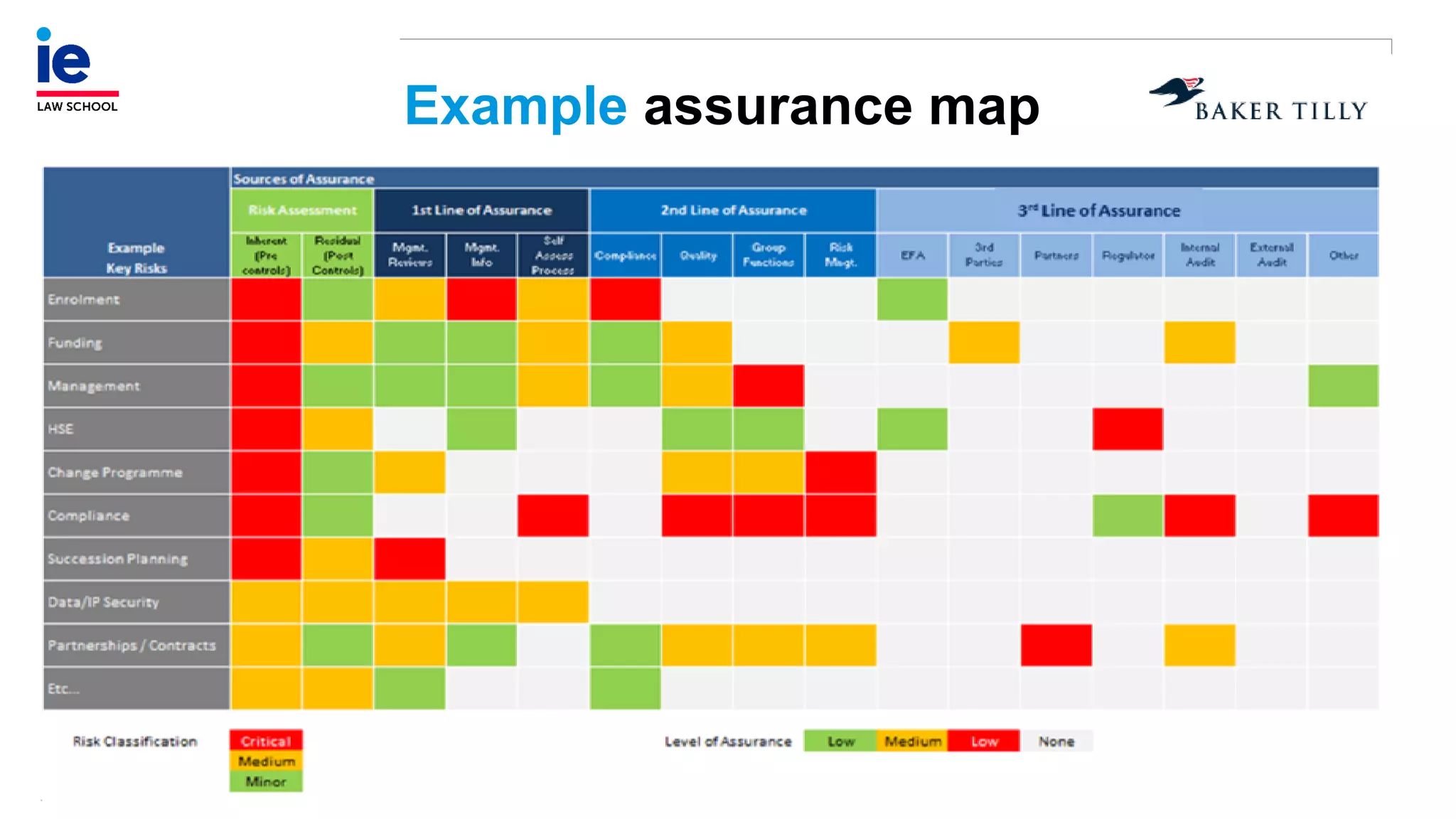
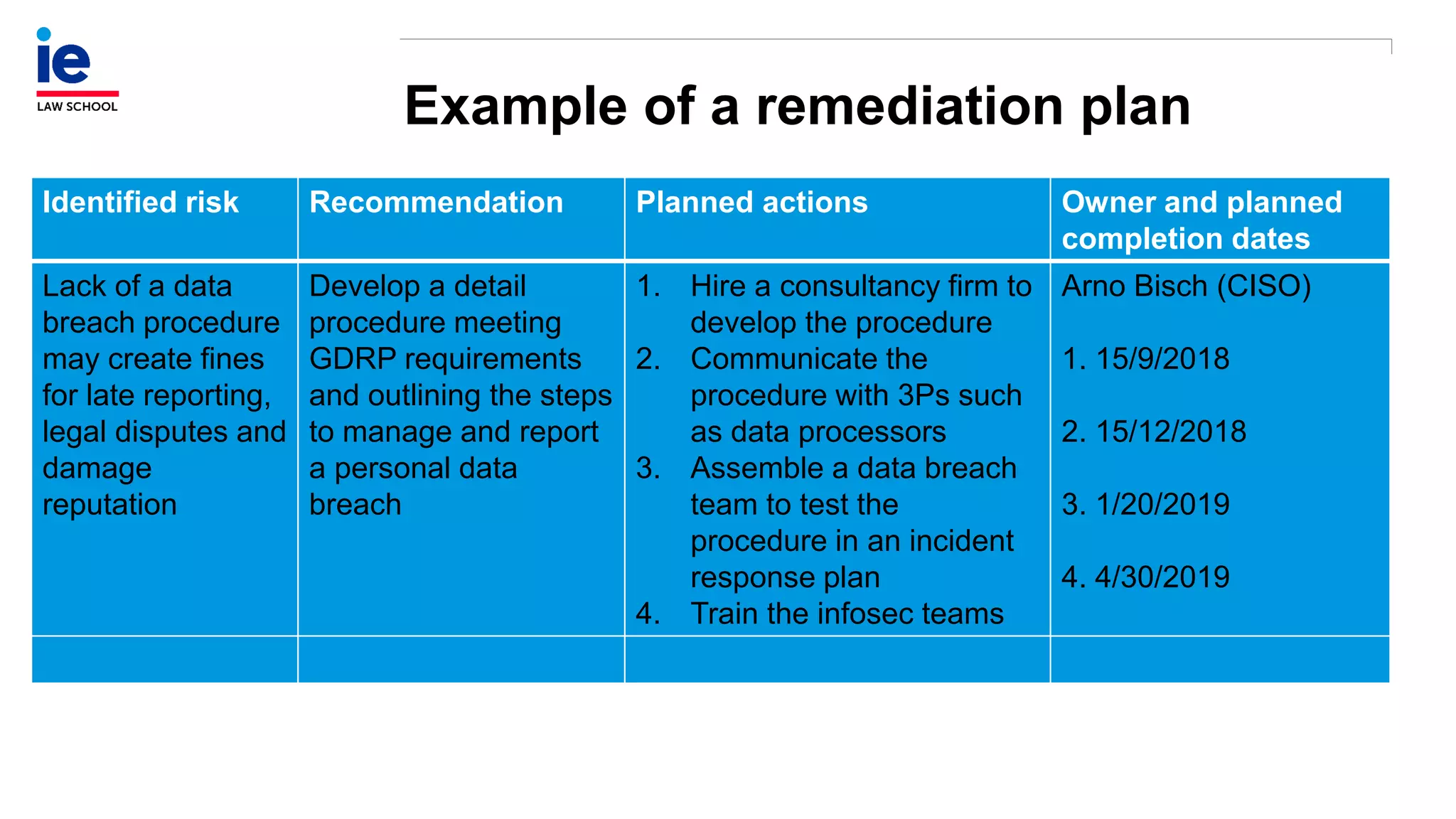
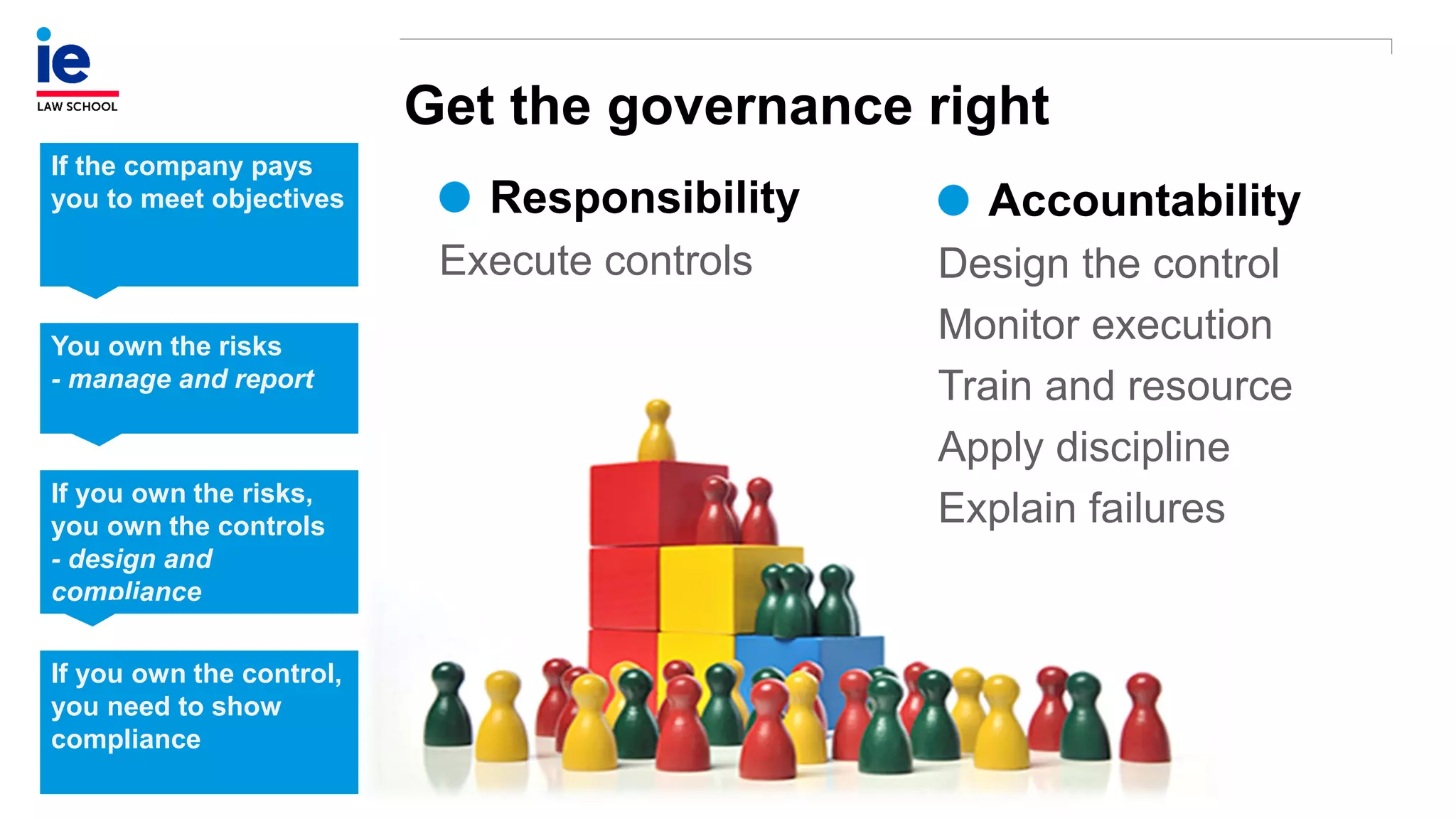
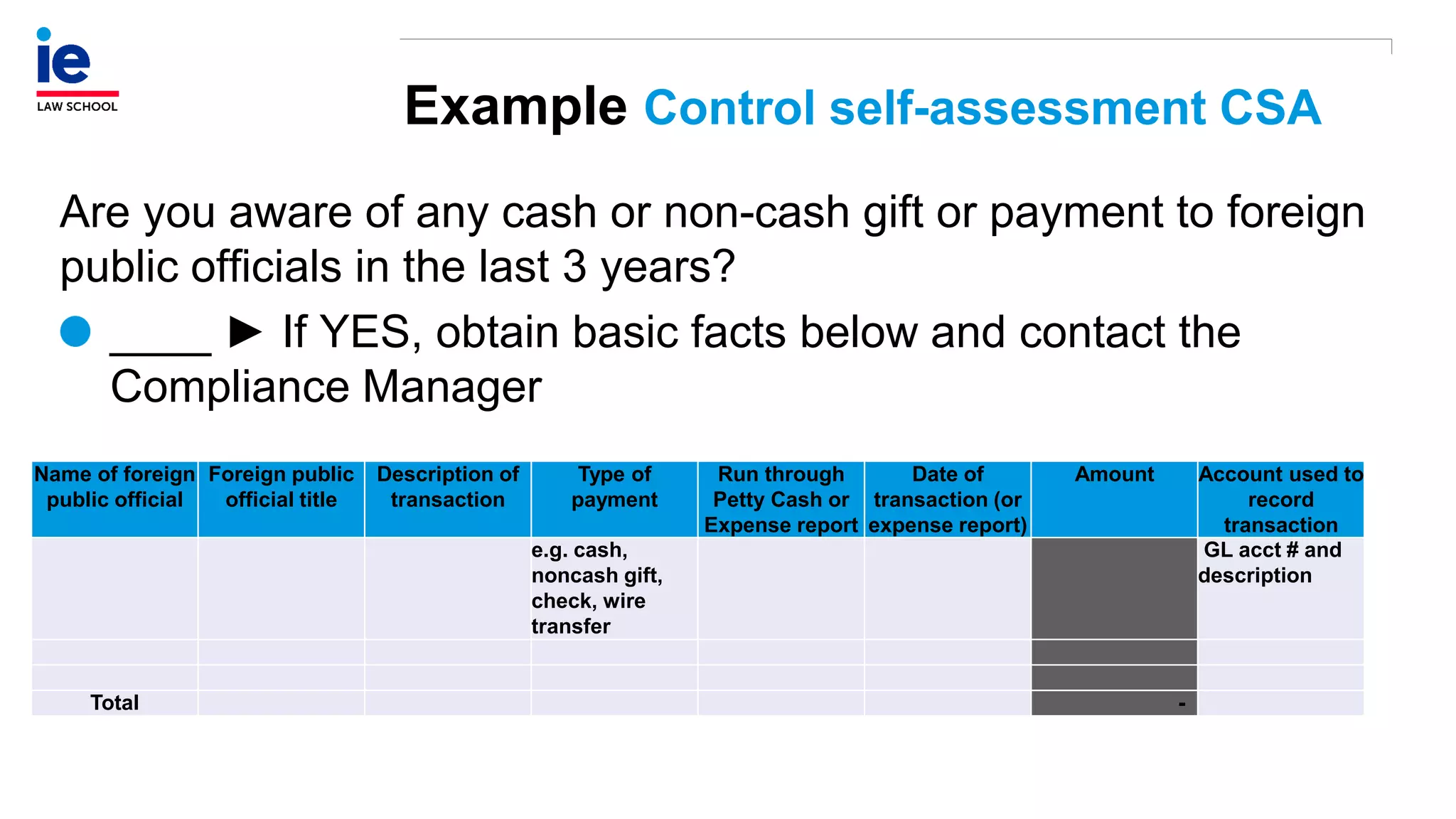
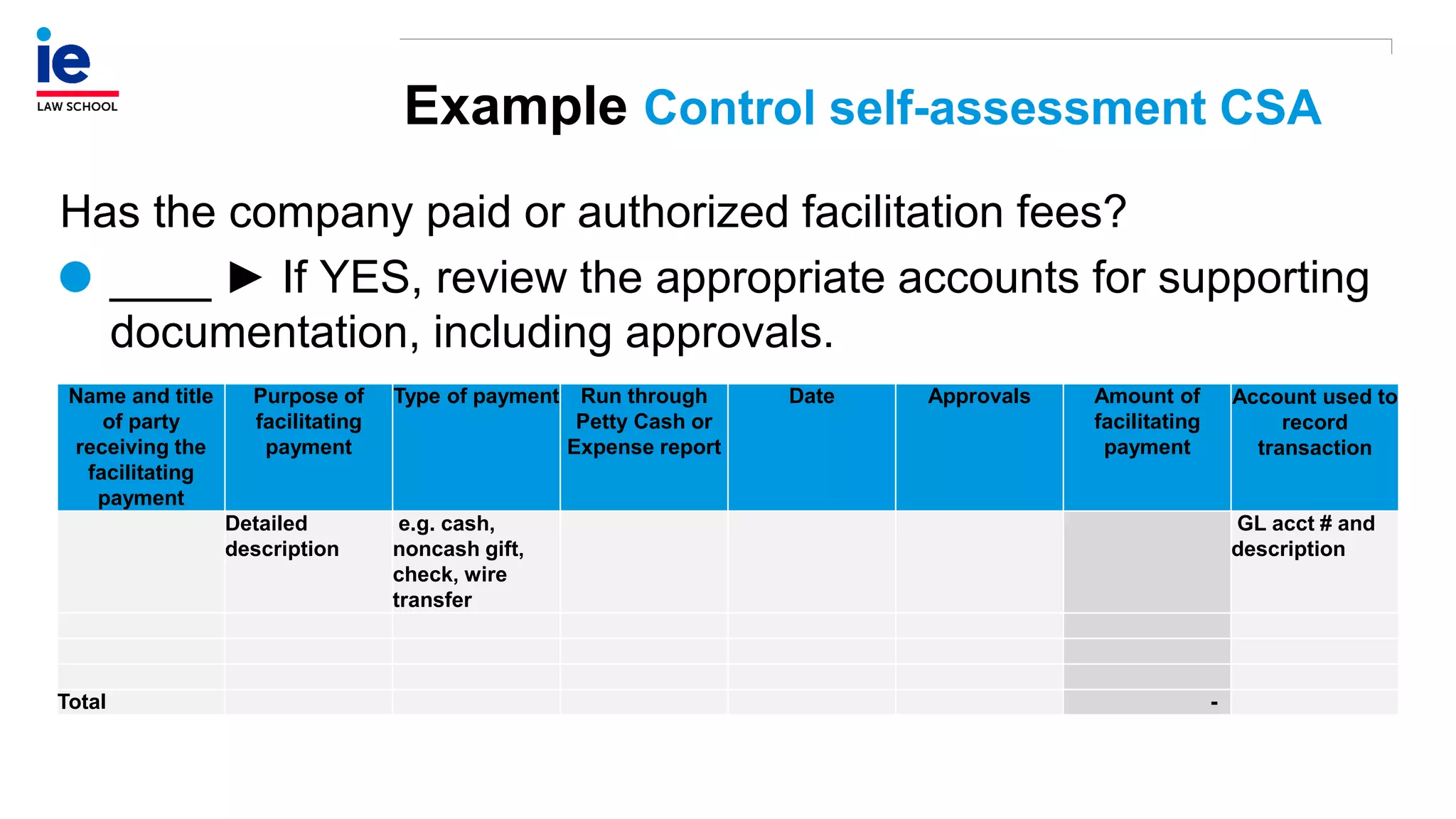
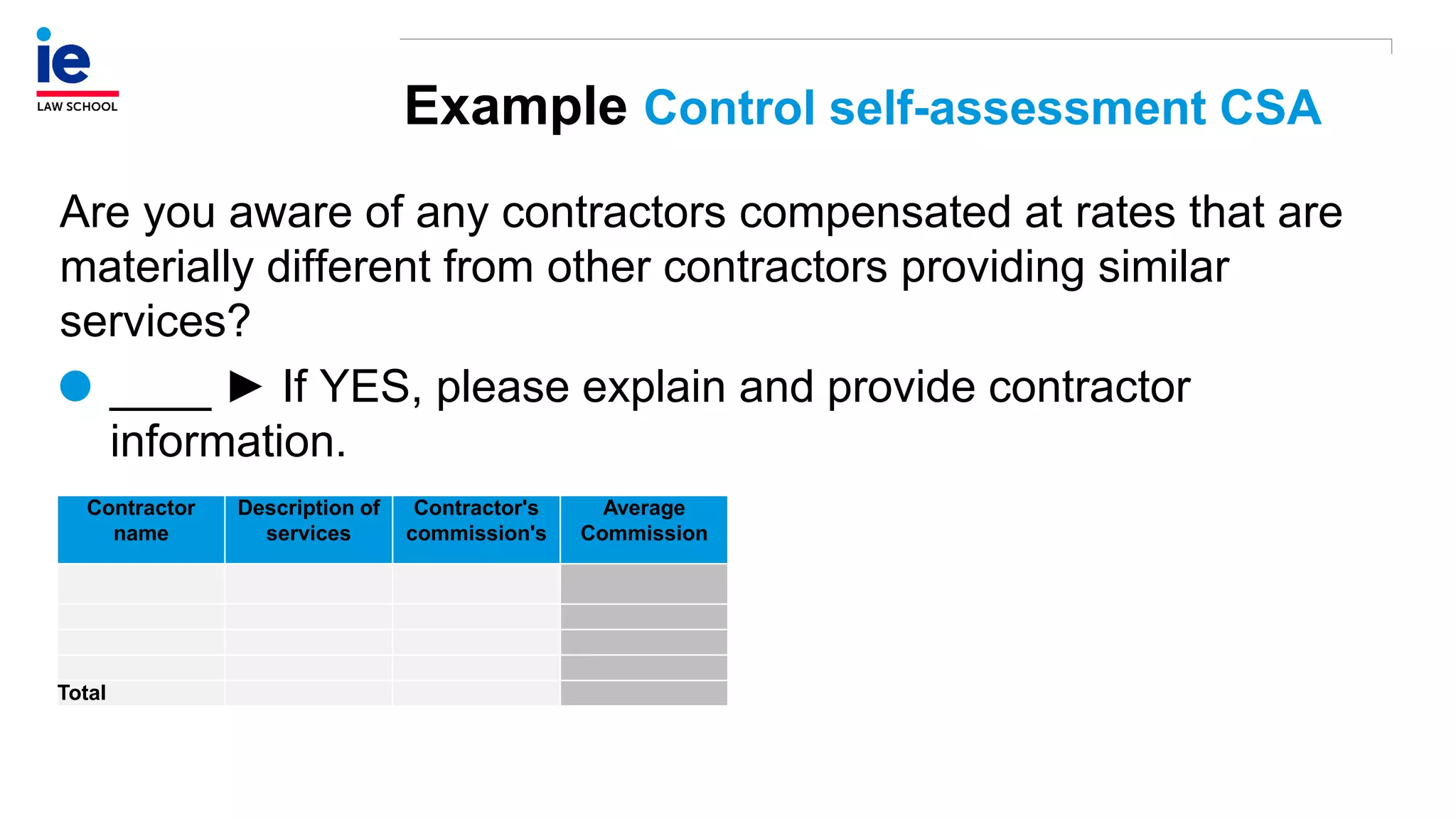
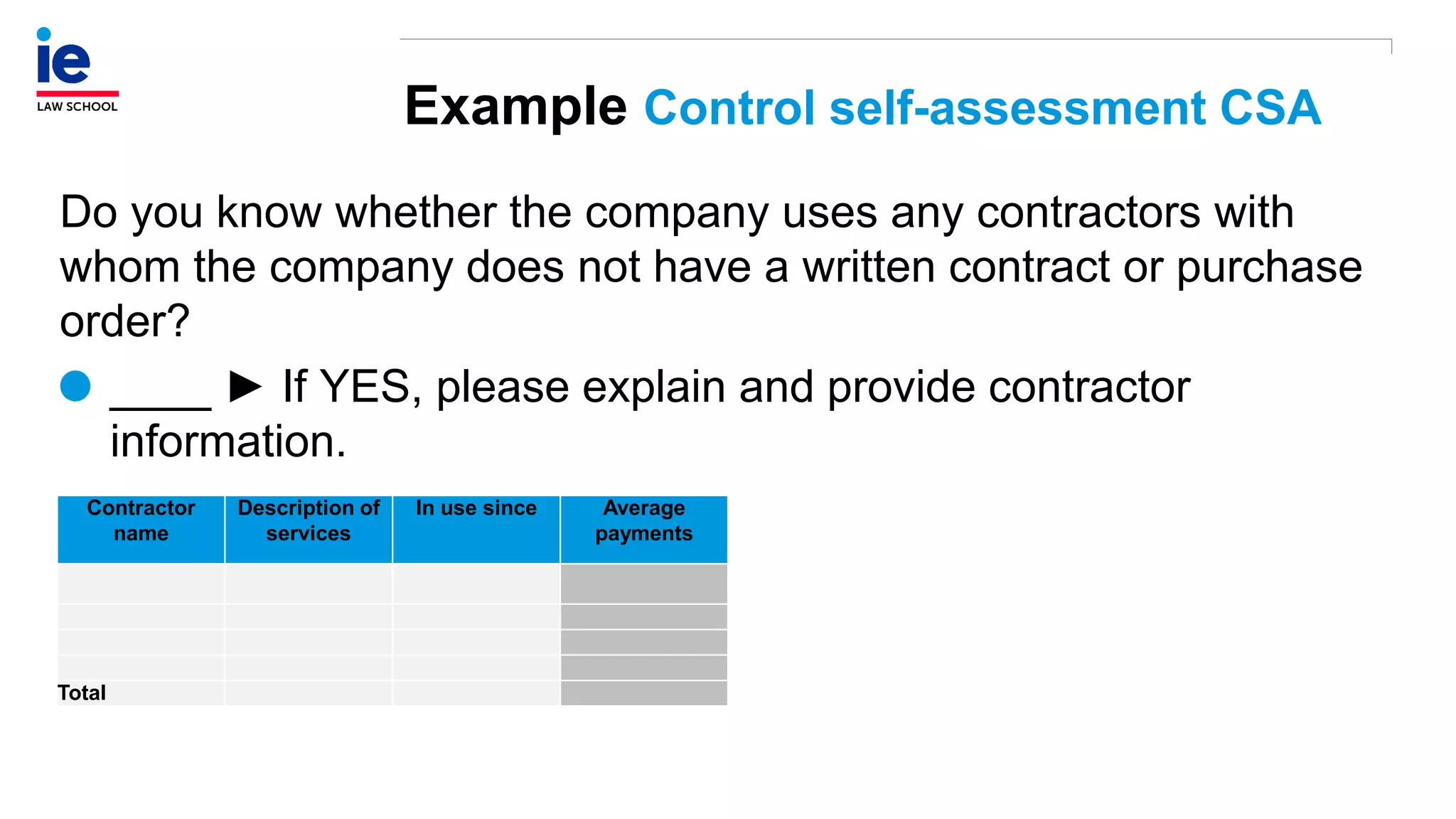
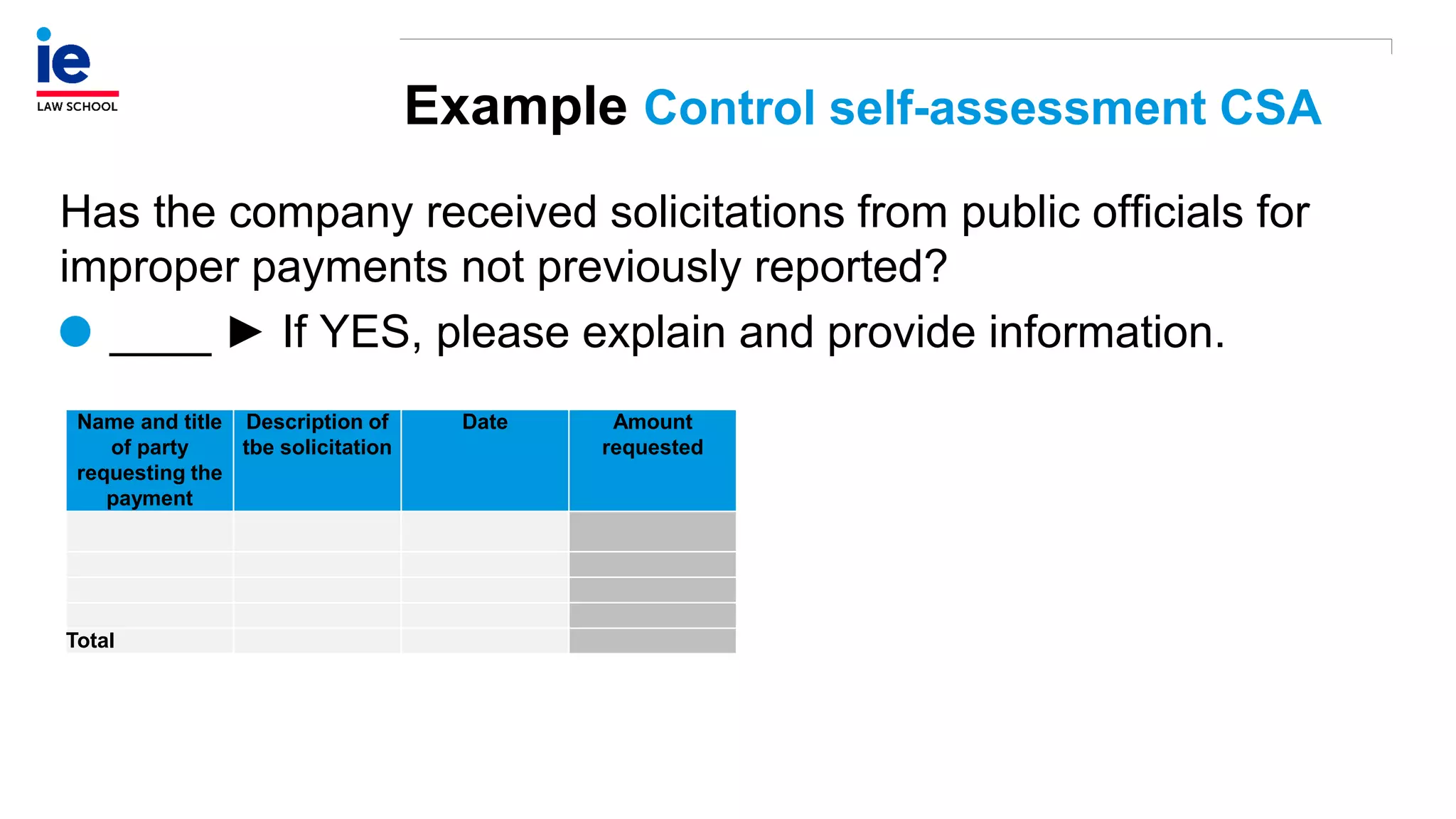
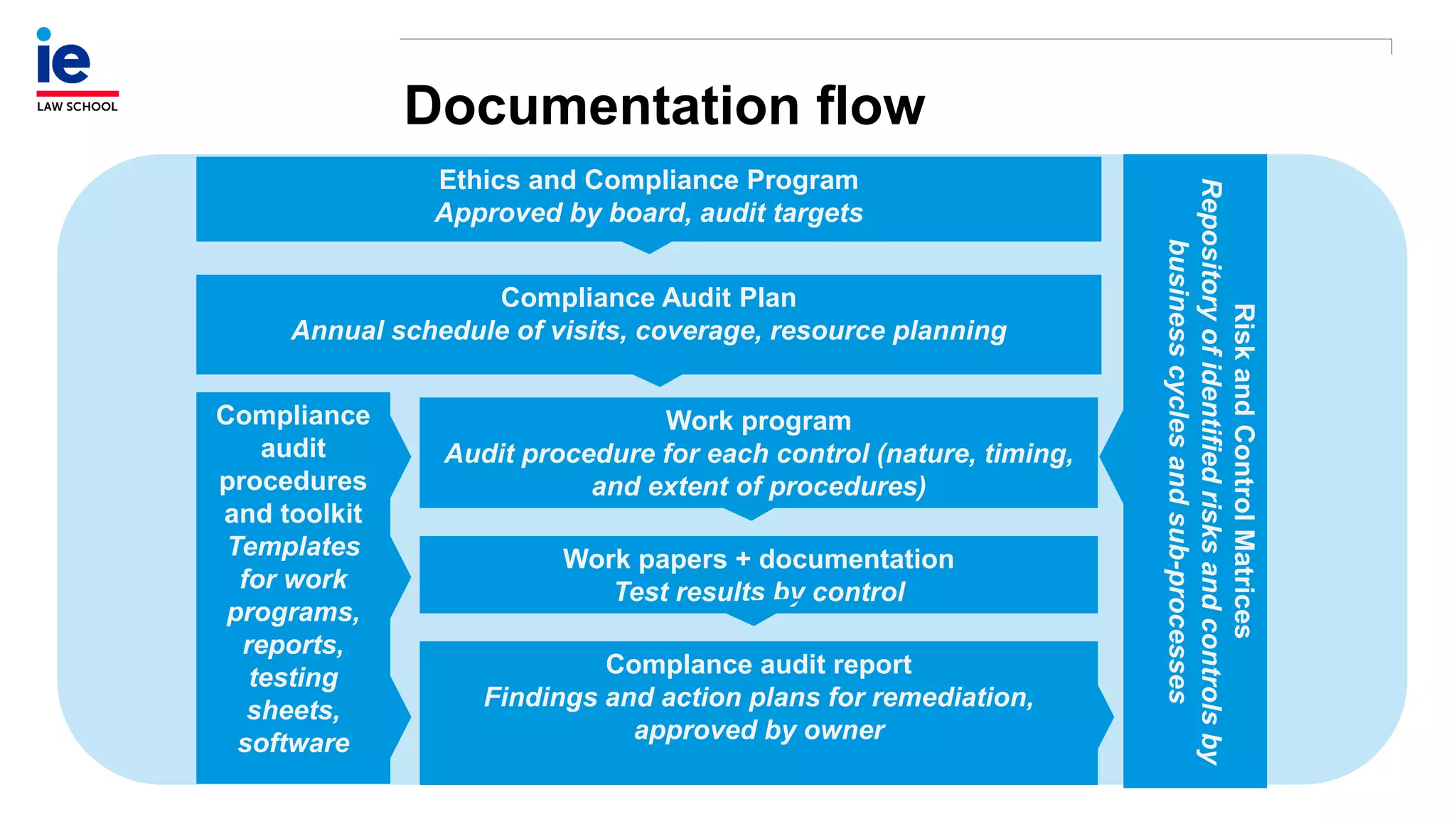
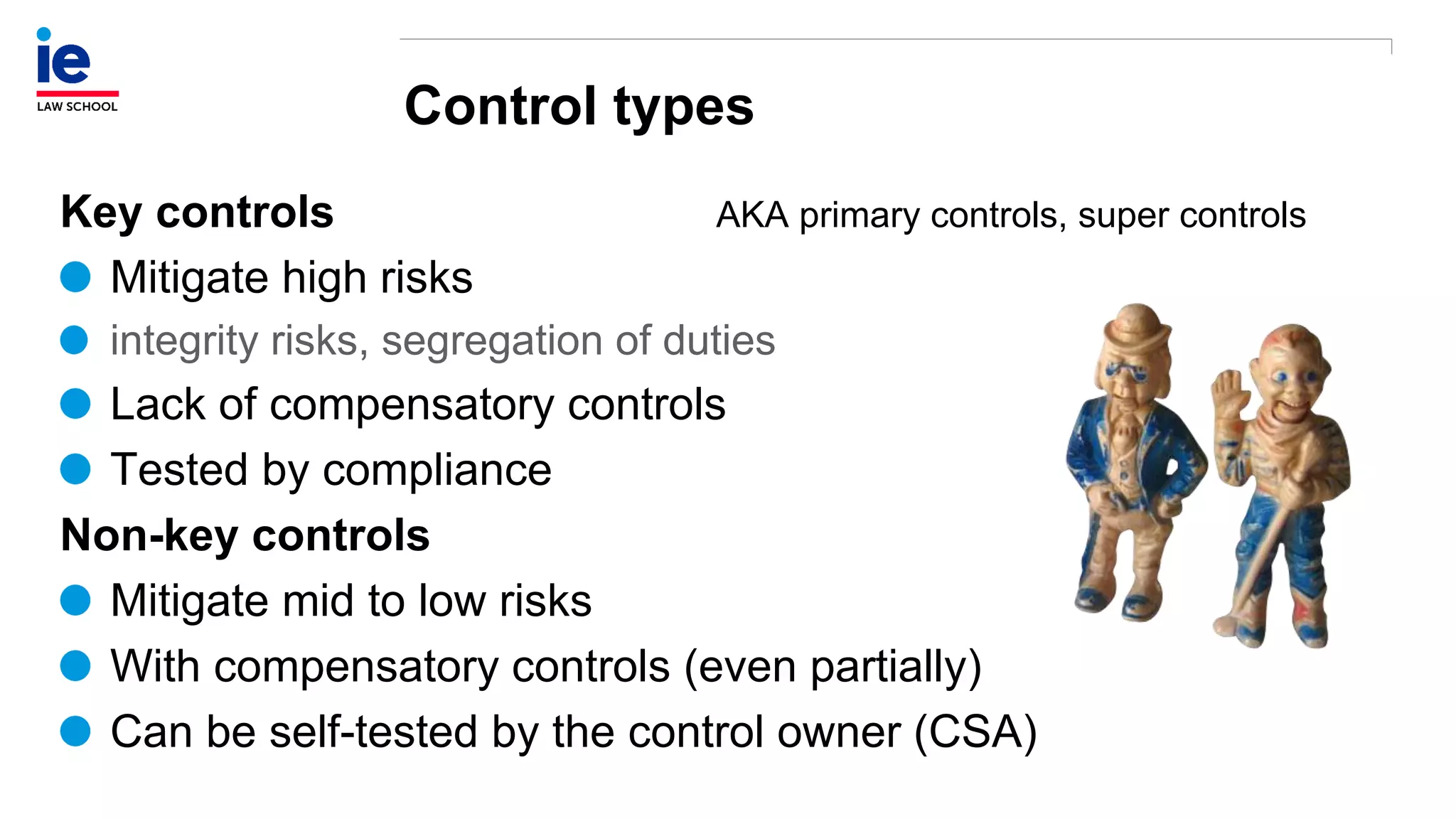
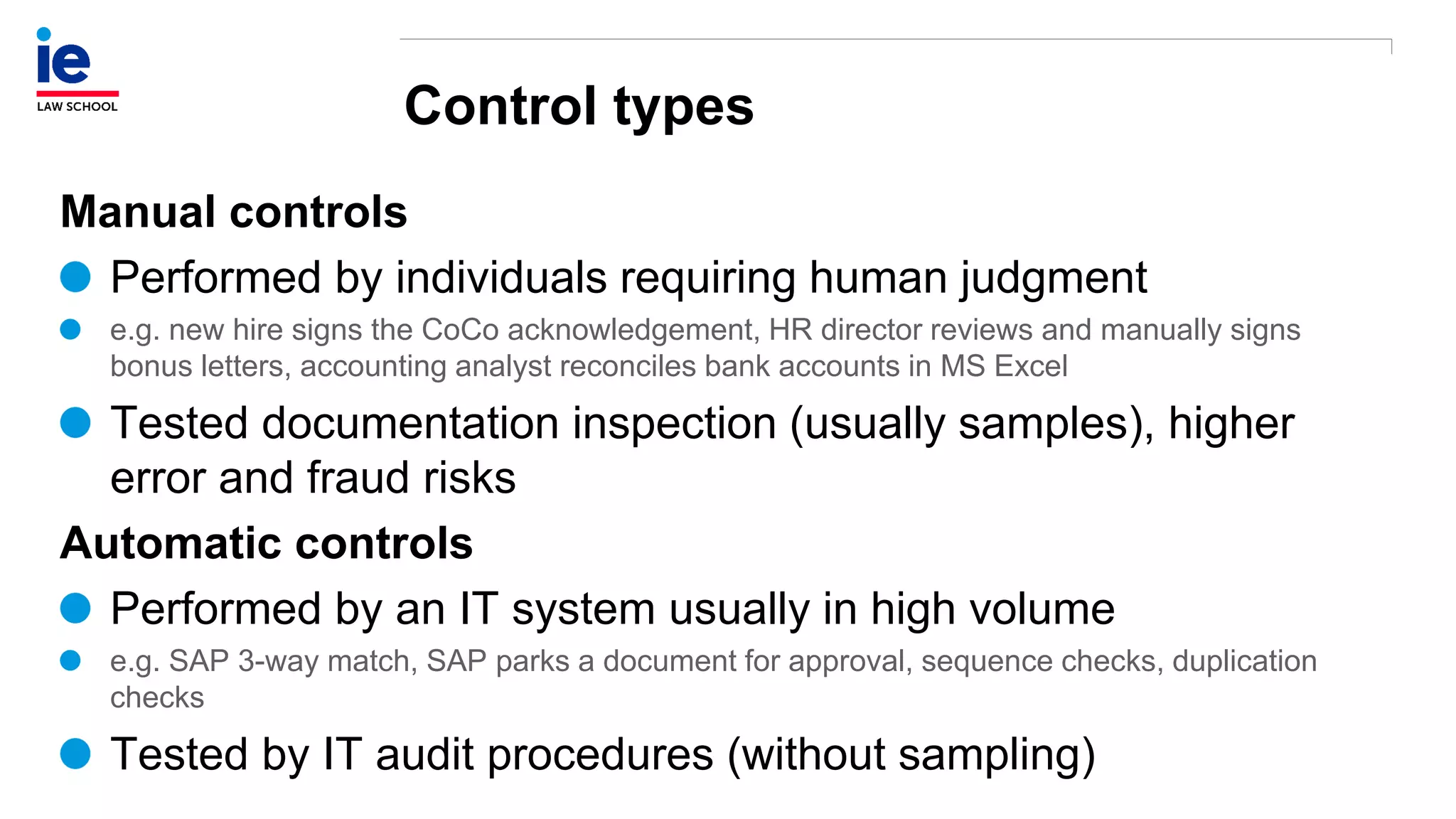
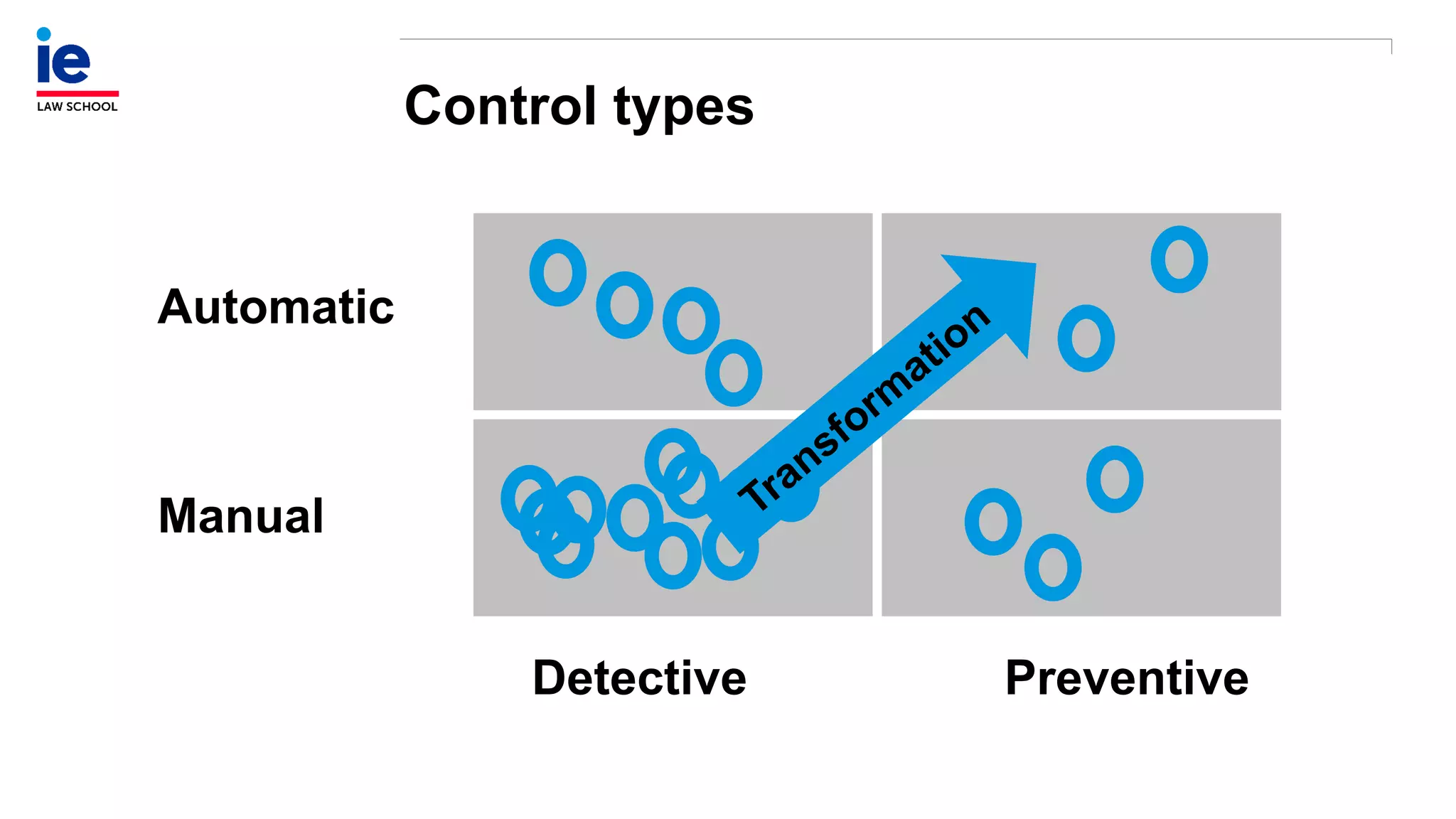
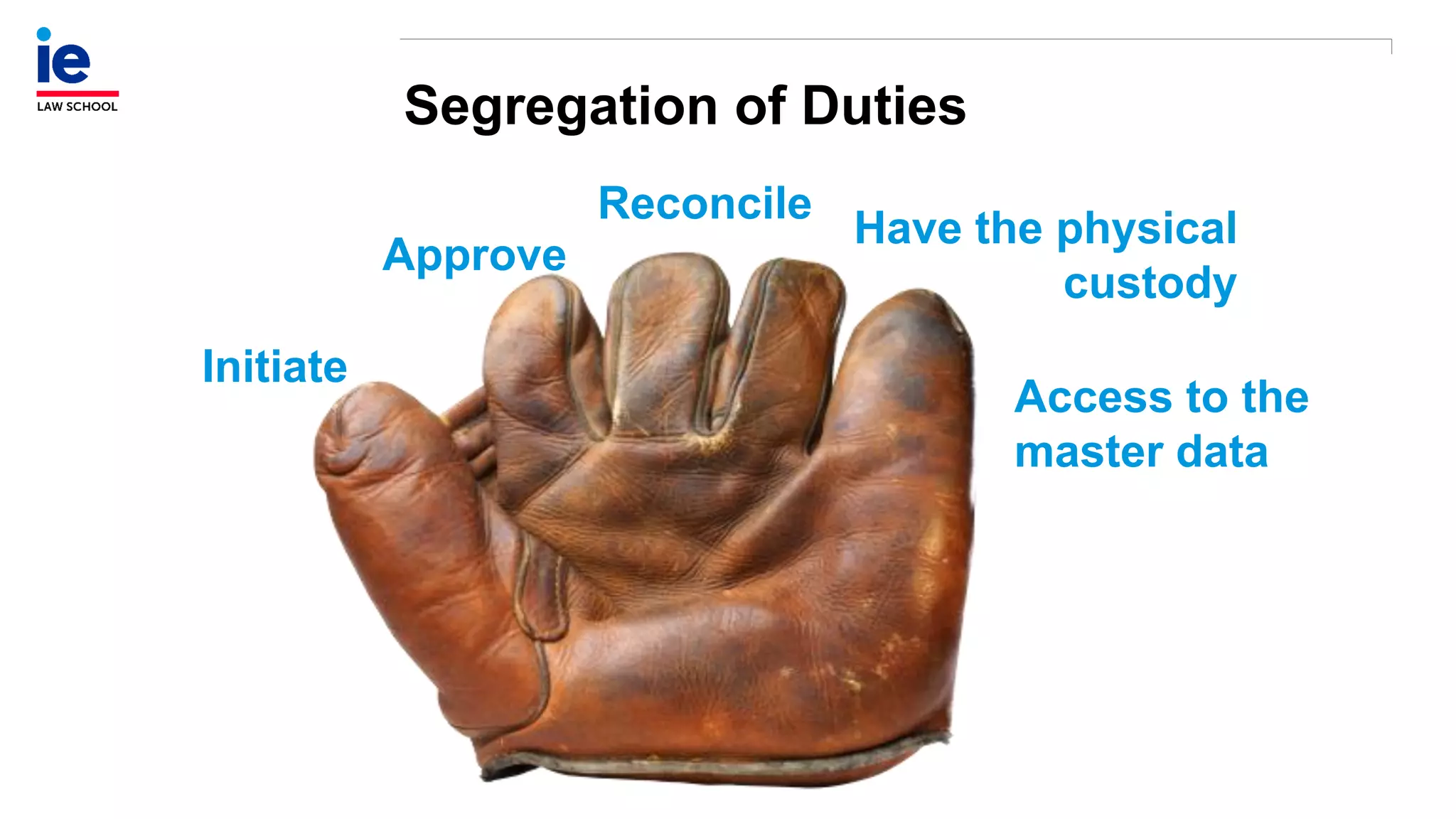
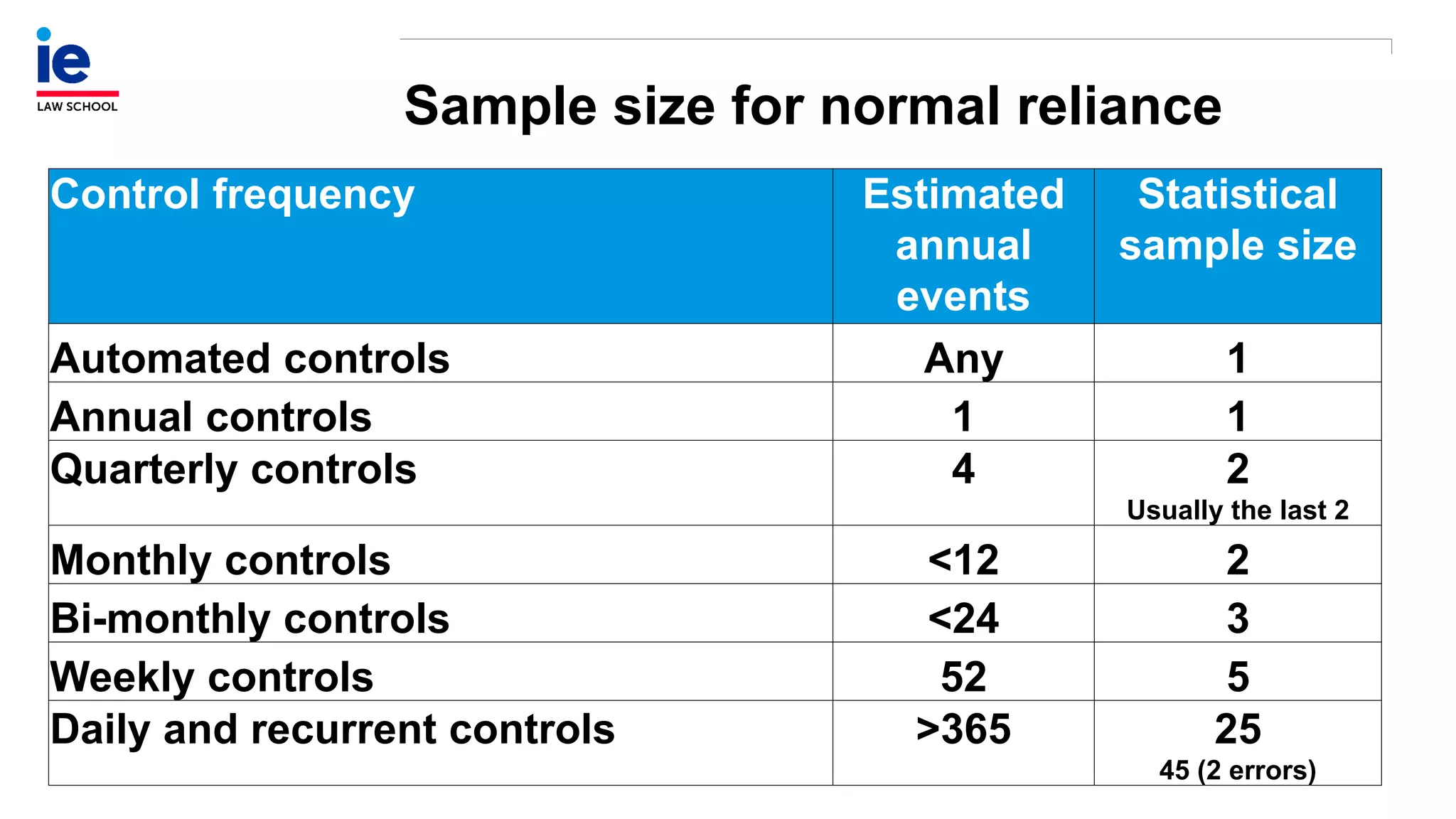
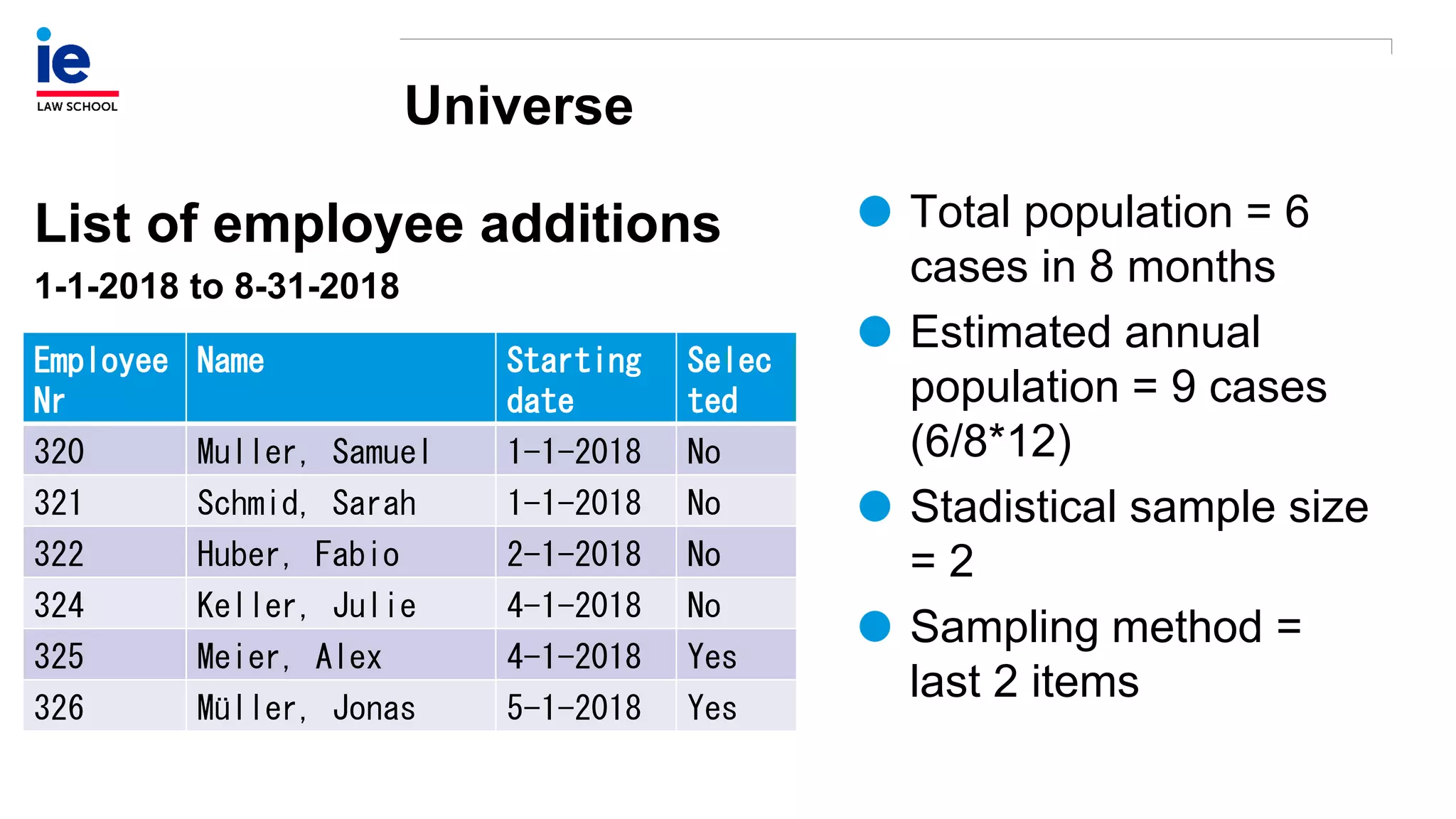
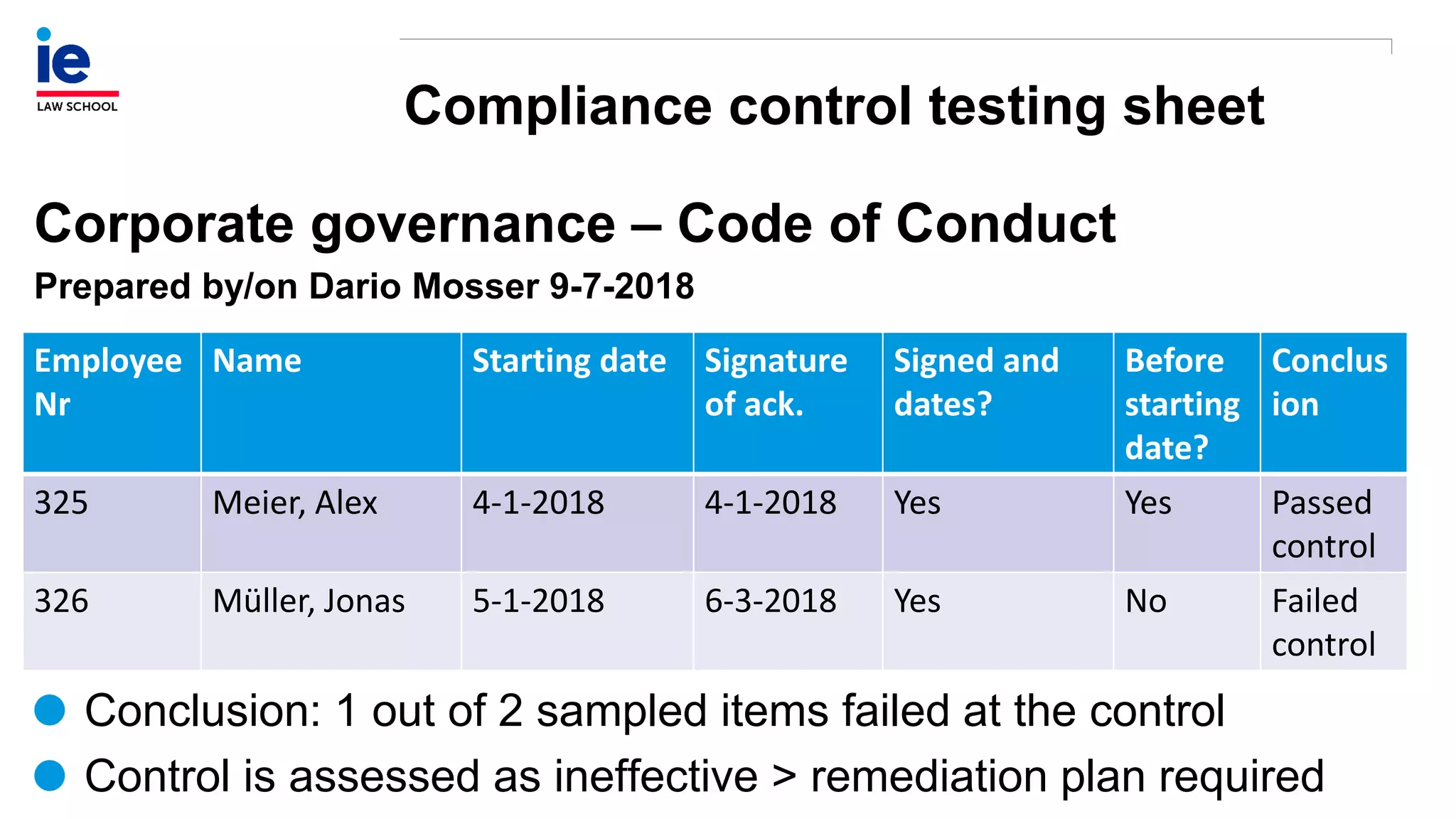
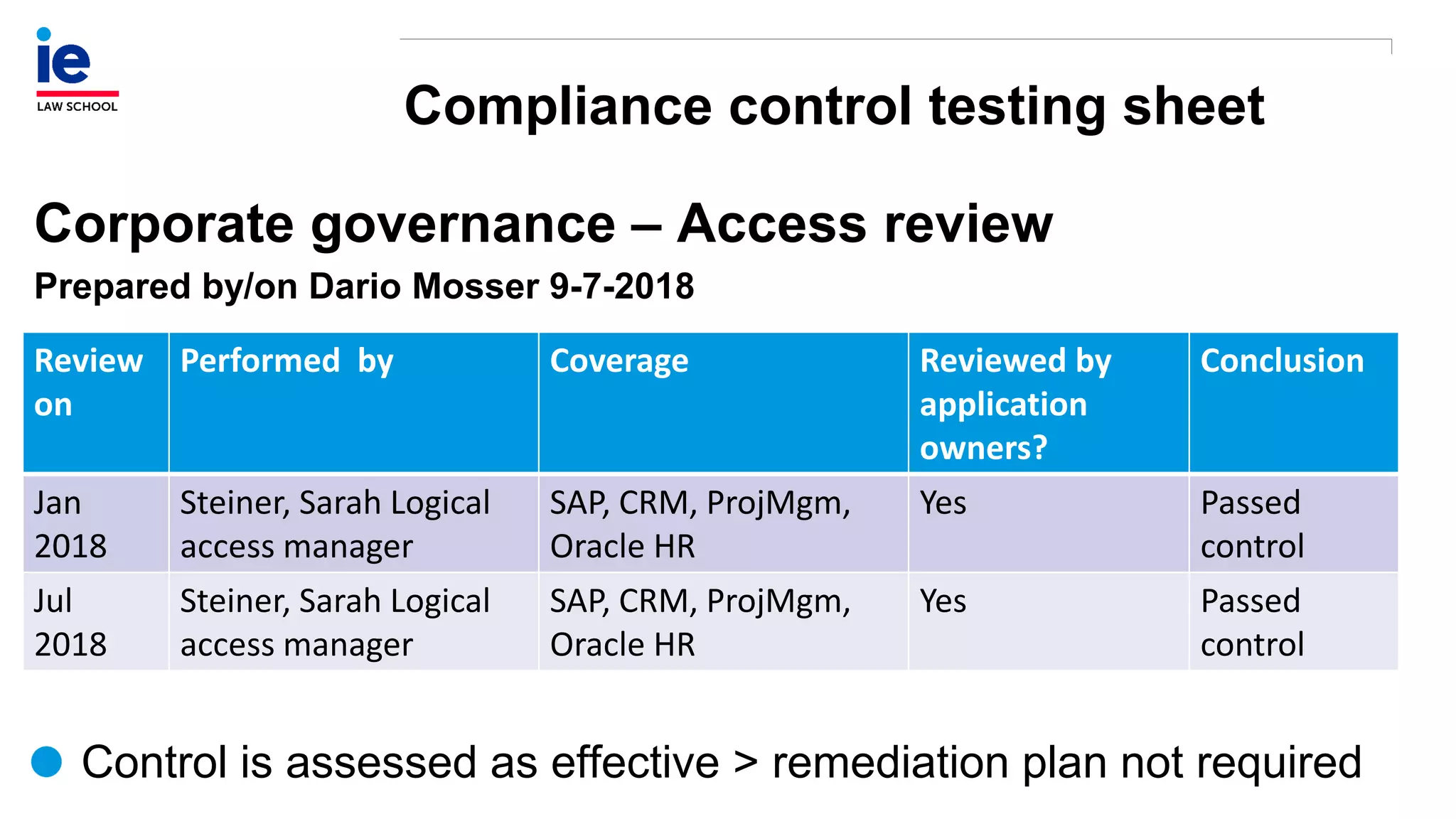
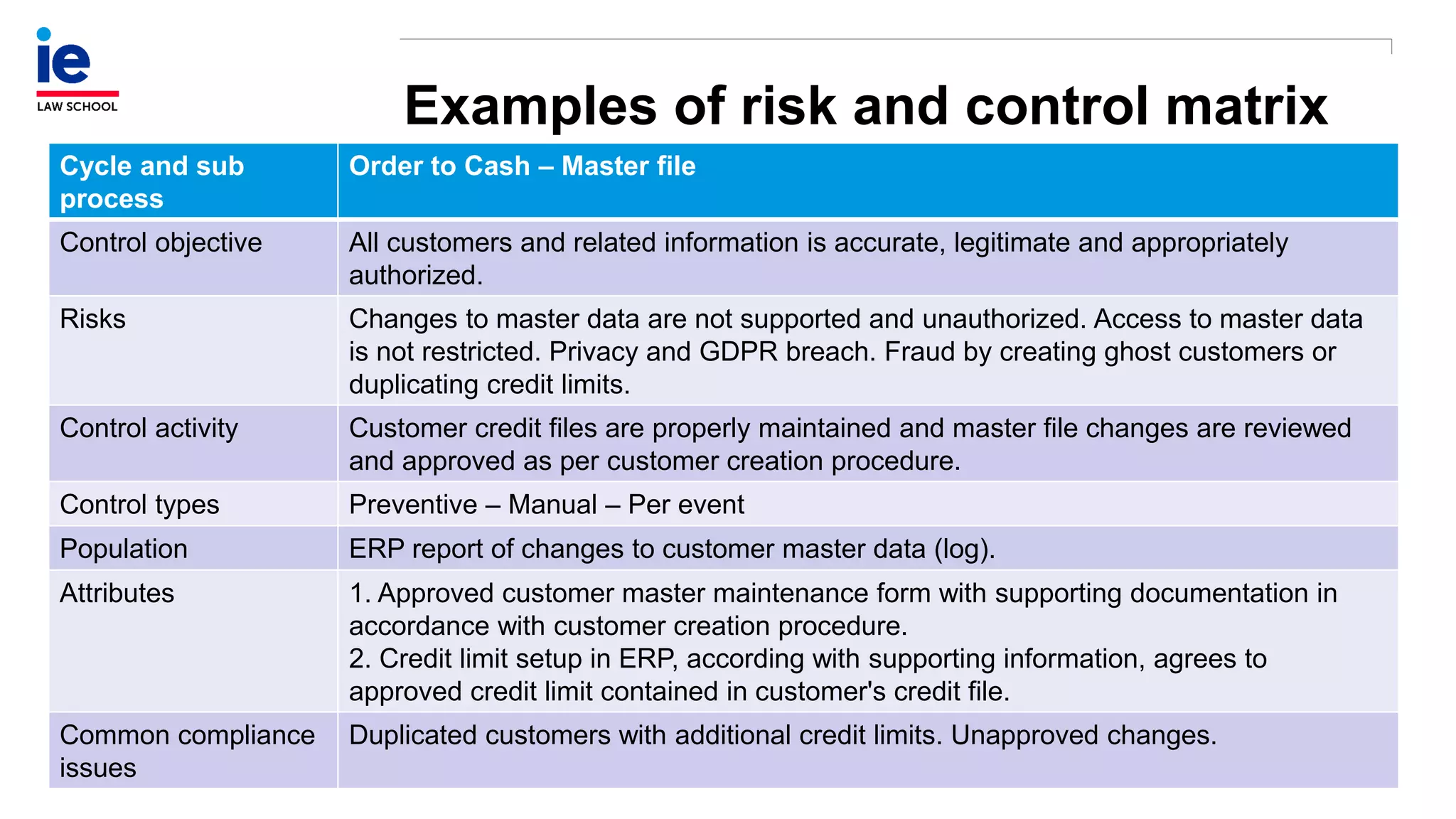
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to managing compliance risks through effective risk assessment, control consolidation, and continuous monitoring in organizations. It emphasizes the importance of tailored compliance programs based on organizational culture maturity, detailing practical implications for internal controls, remediation plans, and documentation of compliance processes. Additionally, it provides guidance on identifying emerging risks and coordinating with risk management and internal audit functions to ensure effective compliance frameworks.