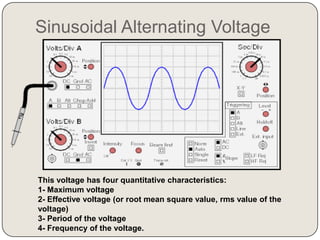
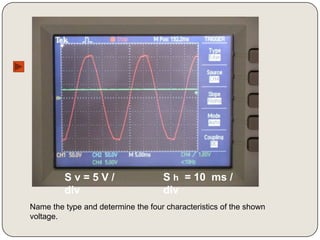
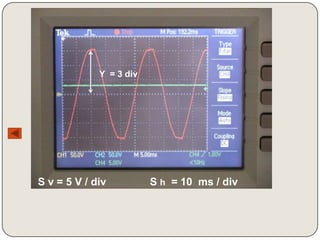
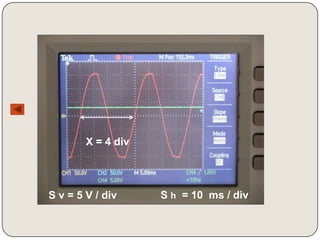
Here are the values of x and y for each oscillogram:
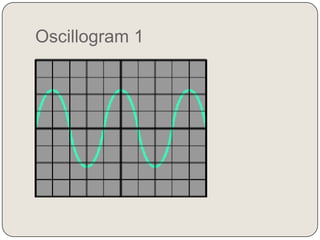
Oscillogram 1:
x = 2 div
y = 4 div
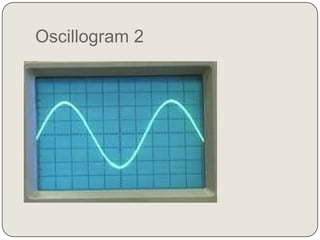
Oscillogram 2:
x = 3 div
y = 2 div
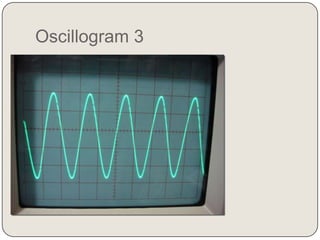
Oscillogram 3:
x = 5 div
y = 1 div
The effective voltage in display 1 is:
Ueff = Sv x y = 5V/div x 4 div = 20V
The frequency of the voltage in display 3 is:
T = Sh x X = 10ms/div x 5 div = 50ms
f = 1/T = 1/50ms = 20Hz
Let me know