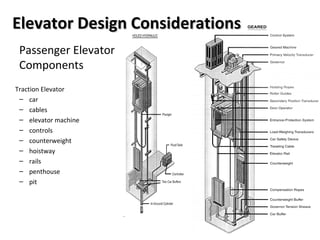
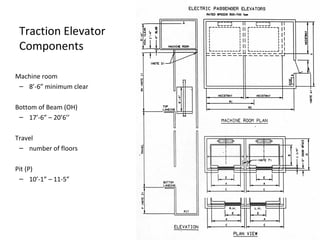
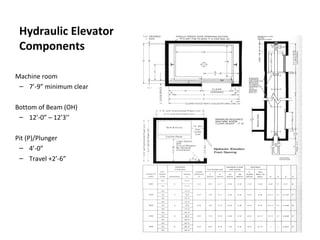
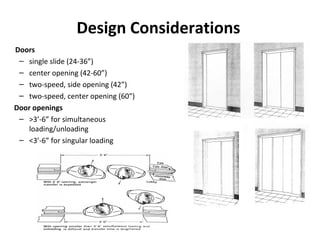
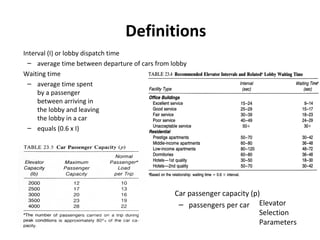
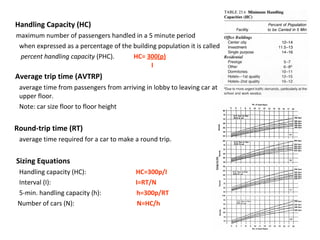
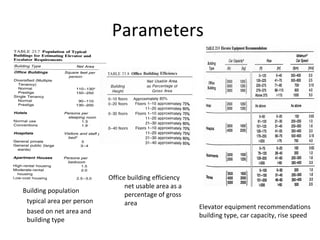
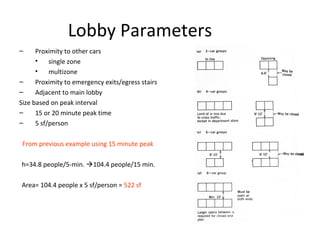
This document discusses lifts (elevators) and their importance in buildings. It covers the basic components and types of lifts, including traction and hydraulic elevators. It describes performance criteria for ideal lift operation and categories of lifts according to their function, such as for trade, hospitals, residences and stores. Key lift components are outlined for both traction and hydraulic systems. Design considerations for lift installation and sizing are also summarized.