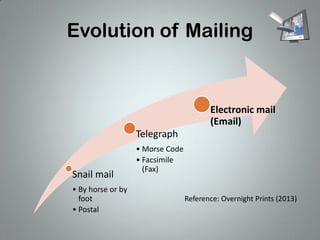
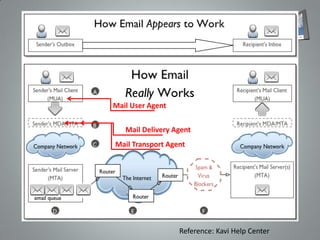
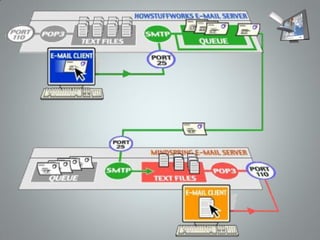
Electronic mail (email) evolved from traditional postal systems and telegraph communication. Ray Tomlinson is credited with inventing email in 1971 when he sent the first message containing the text "QWERTYUIOP" between two computers. Email works through an interaction between mail user agents, mail delivery agents, and mail transport agents that allow users to send and receive messages via protocols like SMTP, POP3, and IMAP running on port numbers 25, 110, and 143, respectively.