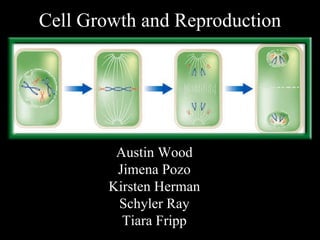
The document summarizes the process of cell growth and reproduction through cell division. It describes that cells come from pre-existing cells and undergo cell division to produce two identical daughter cells. The cell cycle is explained, including interphase where the cell grows and duplicates its chromosomes, and mitosis where the cell divides into two identical copies through the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then separates the cytoplasm to complete cell division.