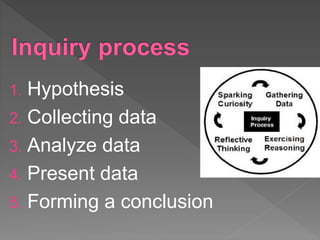
1. The document outlines the steps of conducting a geographic inquiry (GI) including forming a hypothesis, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting a conclusion.
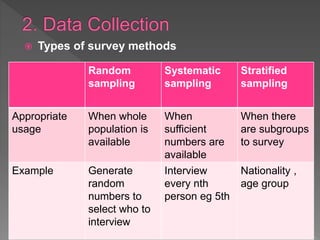
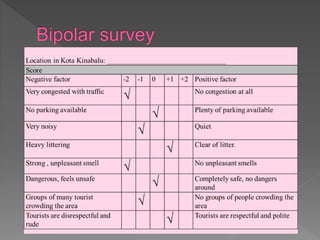
2. It discusses methods for collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, and observation and includes tips for effective survey design and administration.
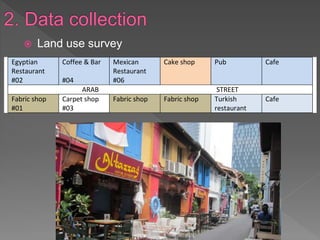
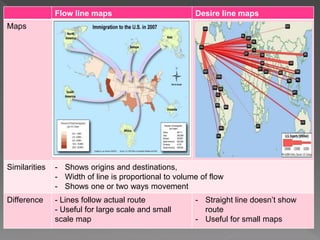
3. The document also presents different sampling methods and examples of ways to organize and present collected data including tables, flow maps, and desire line maps.