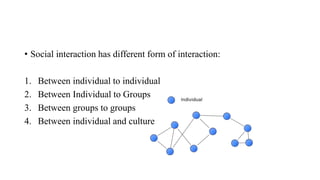
Social geography examines how social relationships, identities, and inequalities form and are influenced by space. Social interaction is the foundation of society, taking various forms from individual to individual or group interactions. Social groups are characterized by regular interaction between members who develop roles and agreed upon procedures. There are various types of social groups including primary groups based on family and friends and secondary groups based on shared occupations or locations. A community is defined by geographic location while a society includes people in different places connected through direct and indirect social ties.