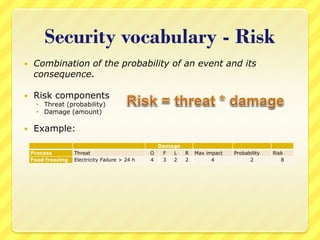
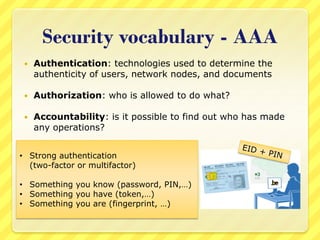
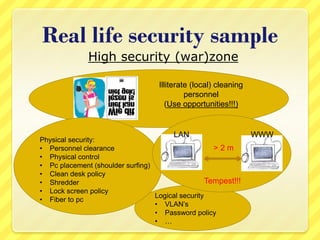
The document provides an overview of information security concepts including definitions of security attributes like confidentiality, integrity and availability. It discusses why security is important for compliance, protecting assets and reputation. The document recommends a layered security approach using best practices and standards like ISO 27002. Key security terms are defined such as threats, damages, risks, and authentication. It emphasizes the importance of managing risks and notes that personnel are often the weakest link for attackers who start with information gathering.