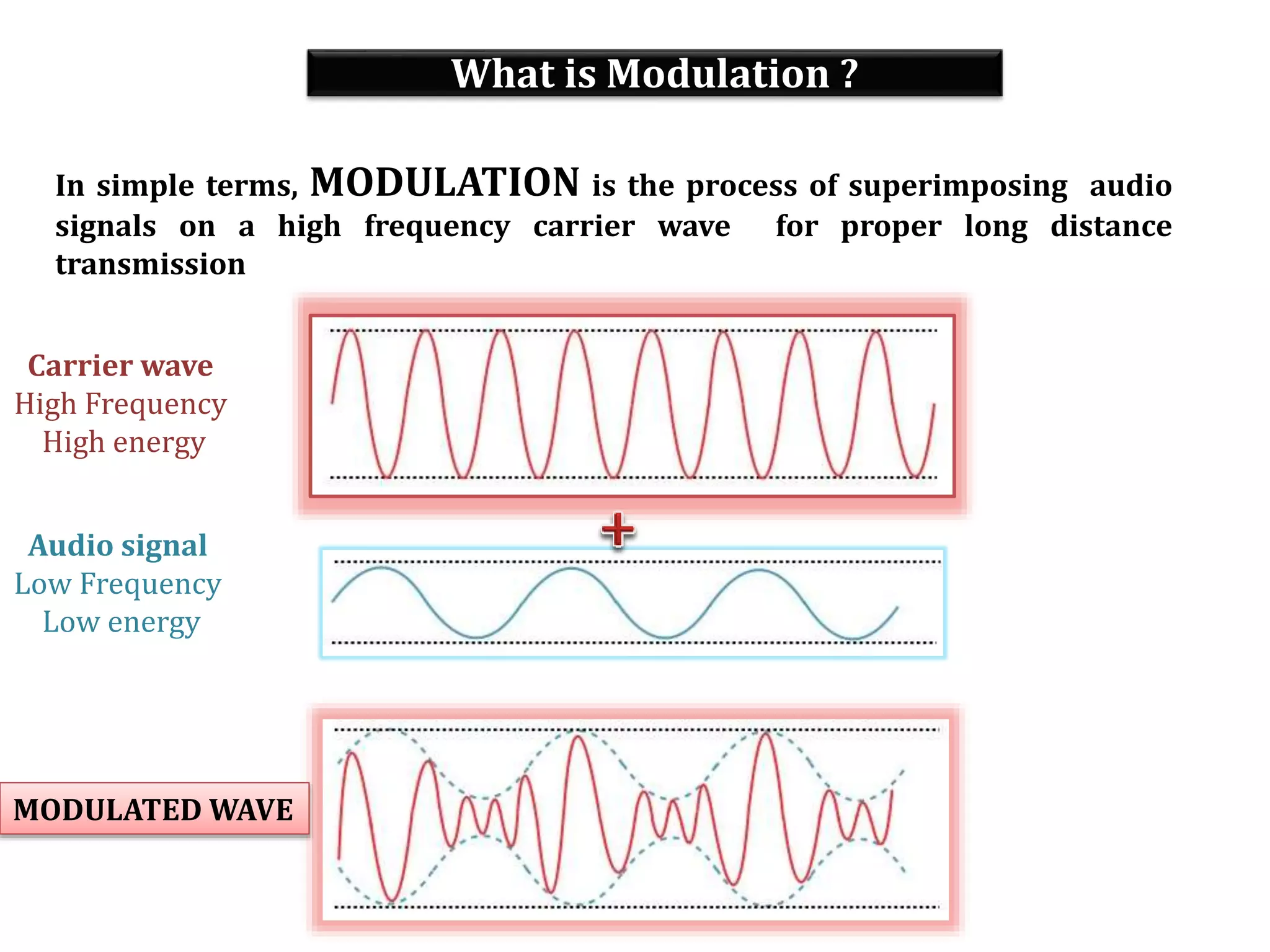
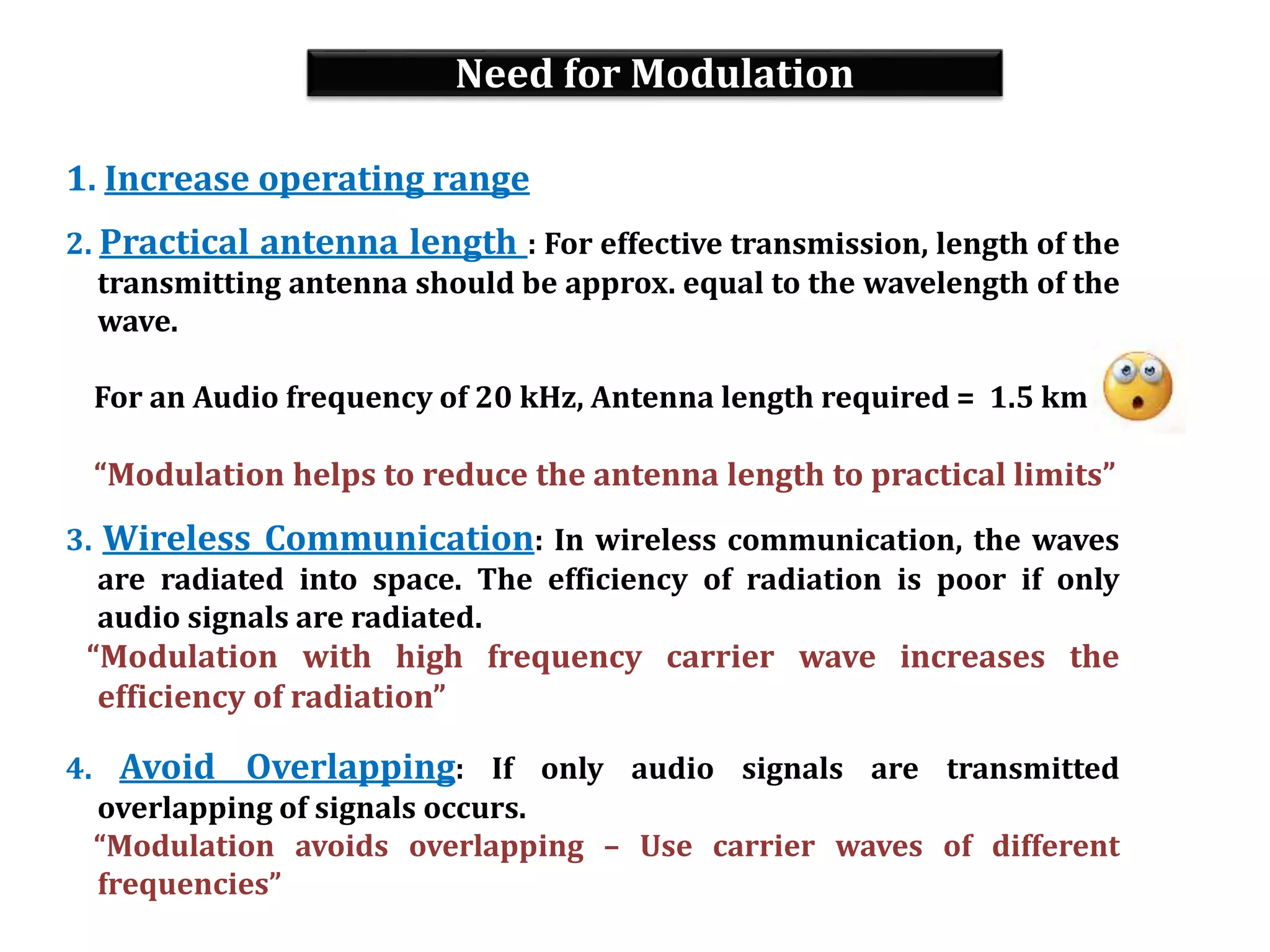
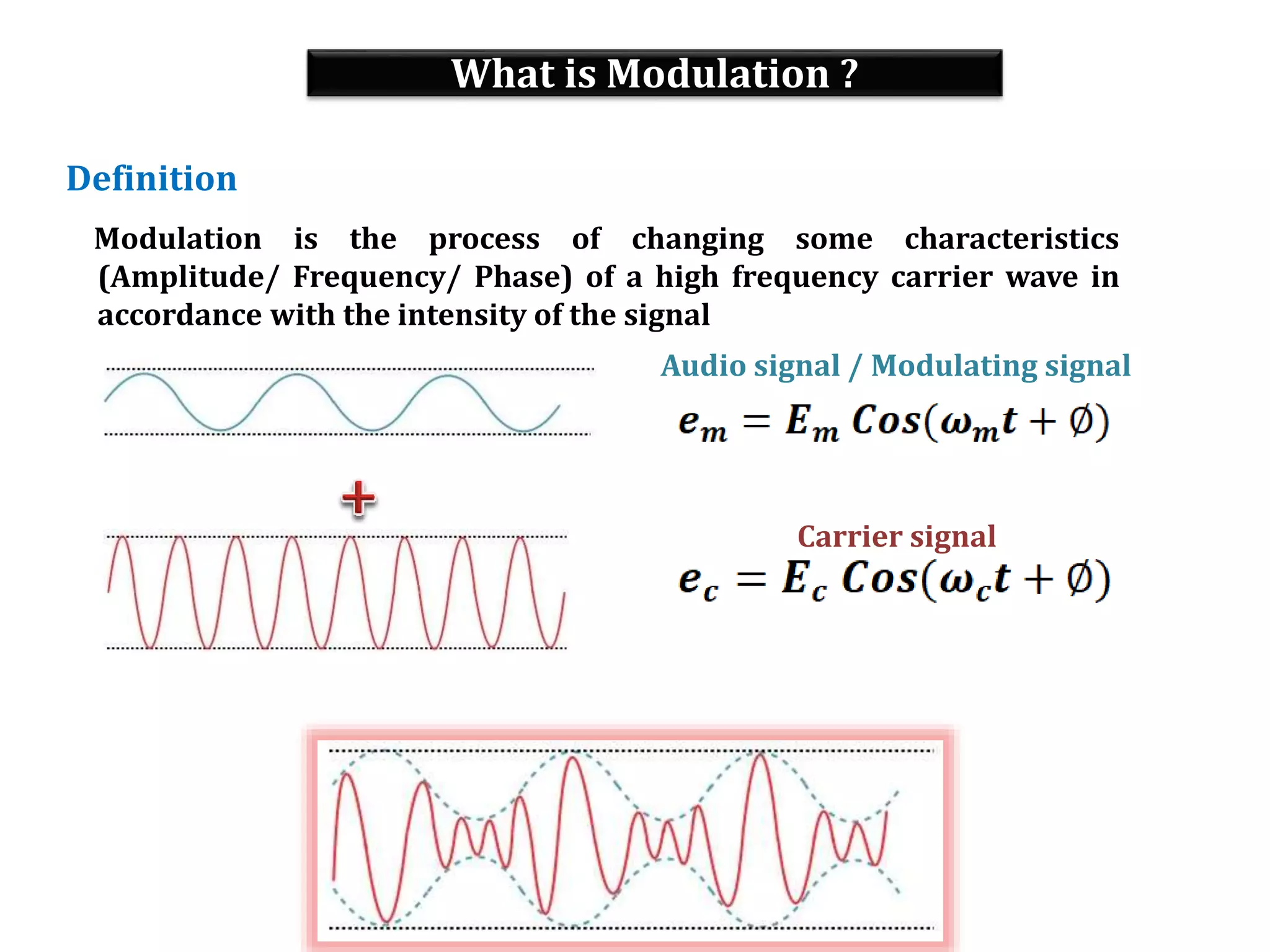
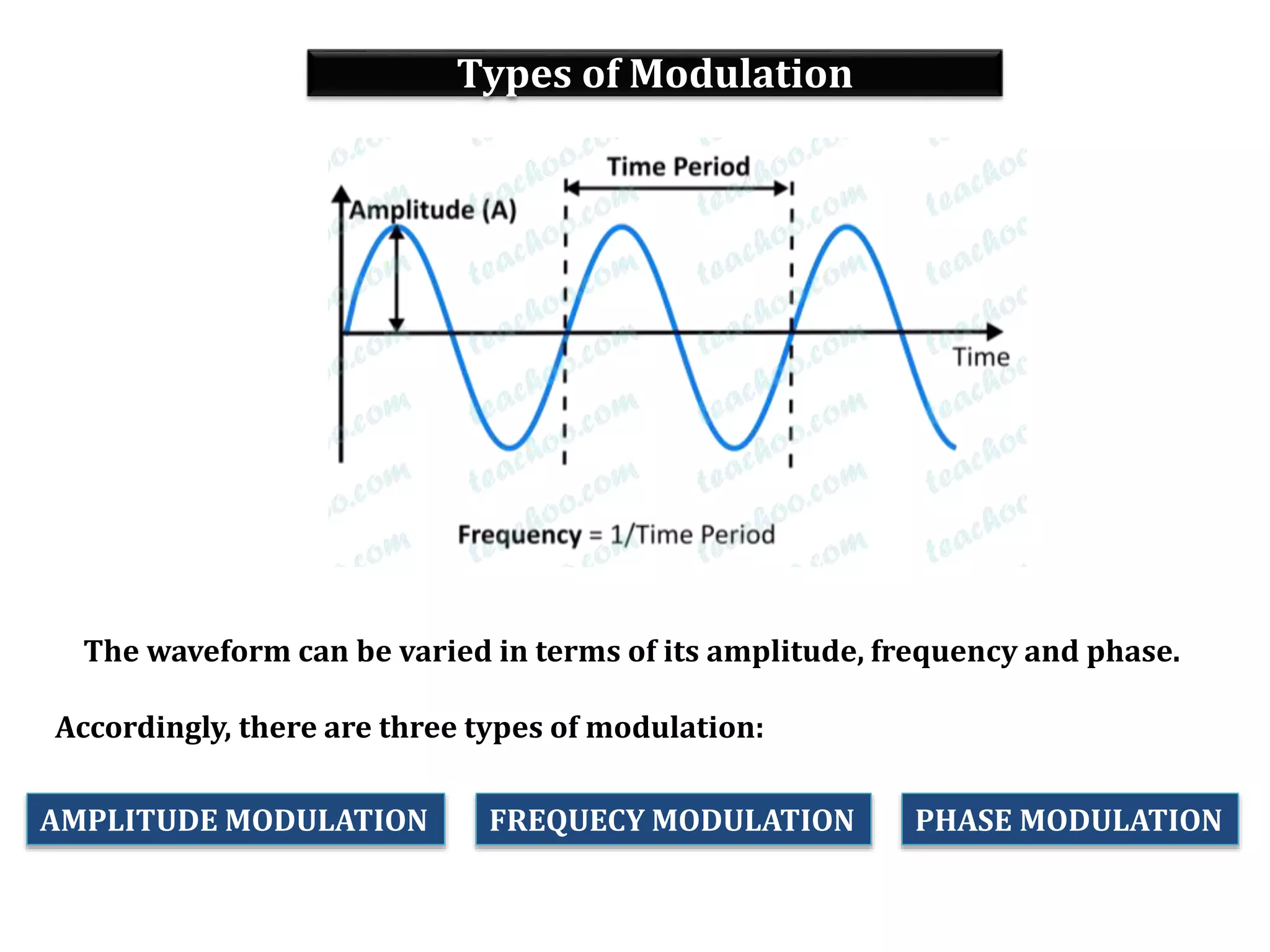
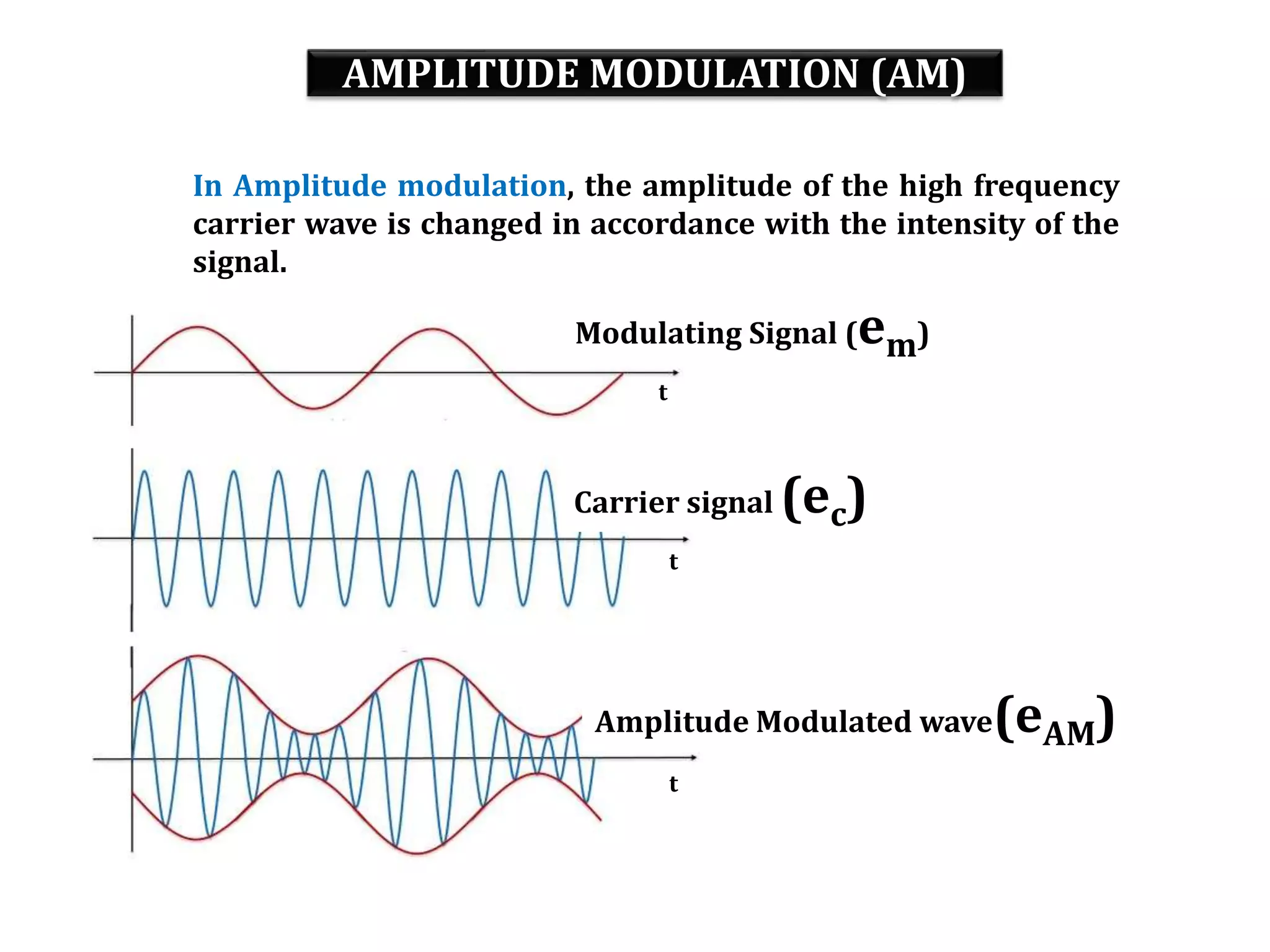
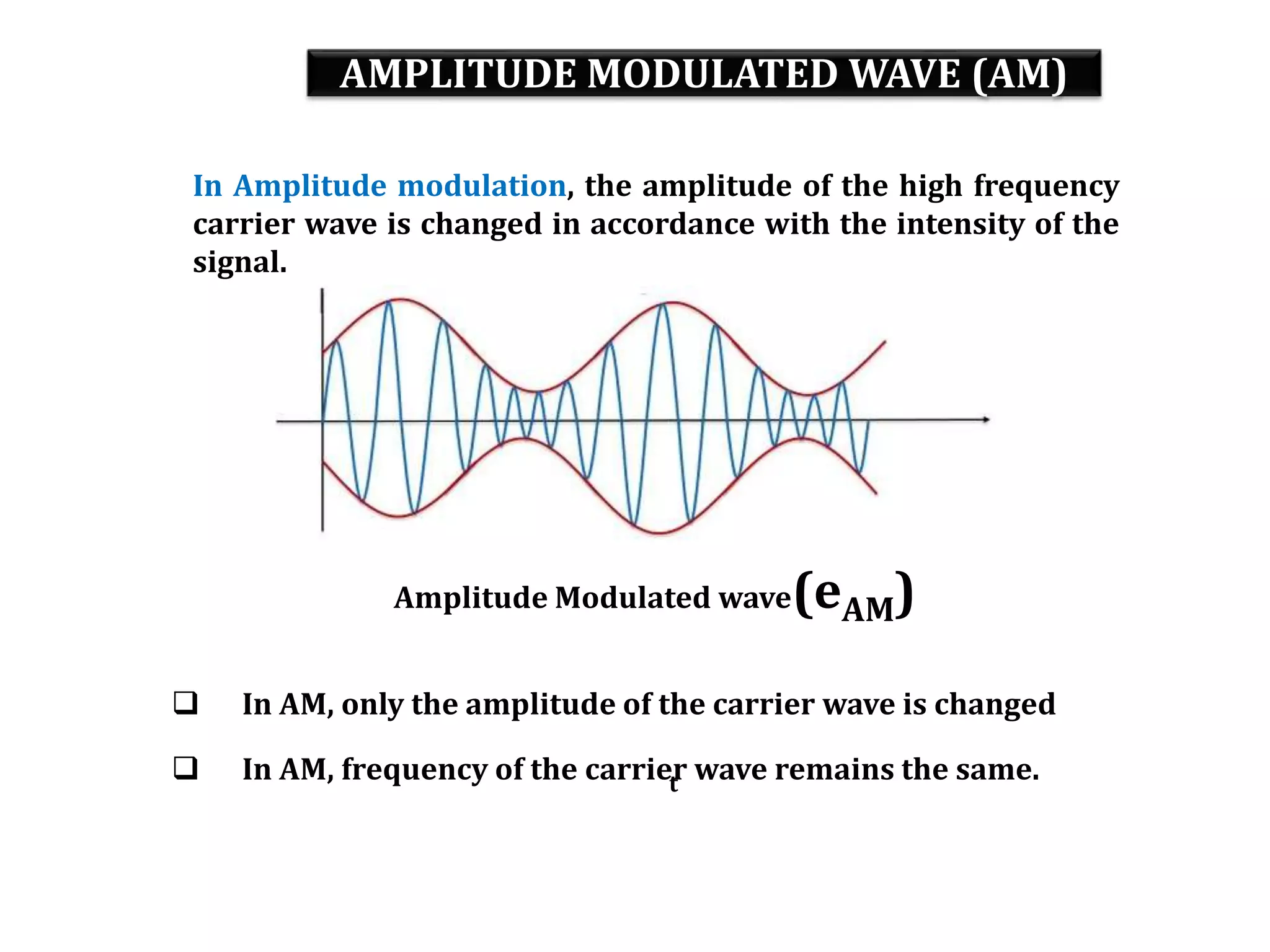
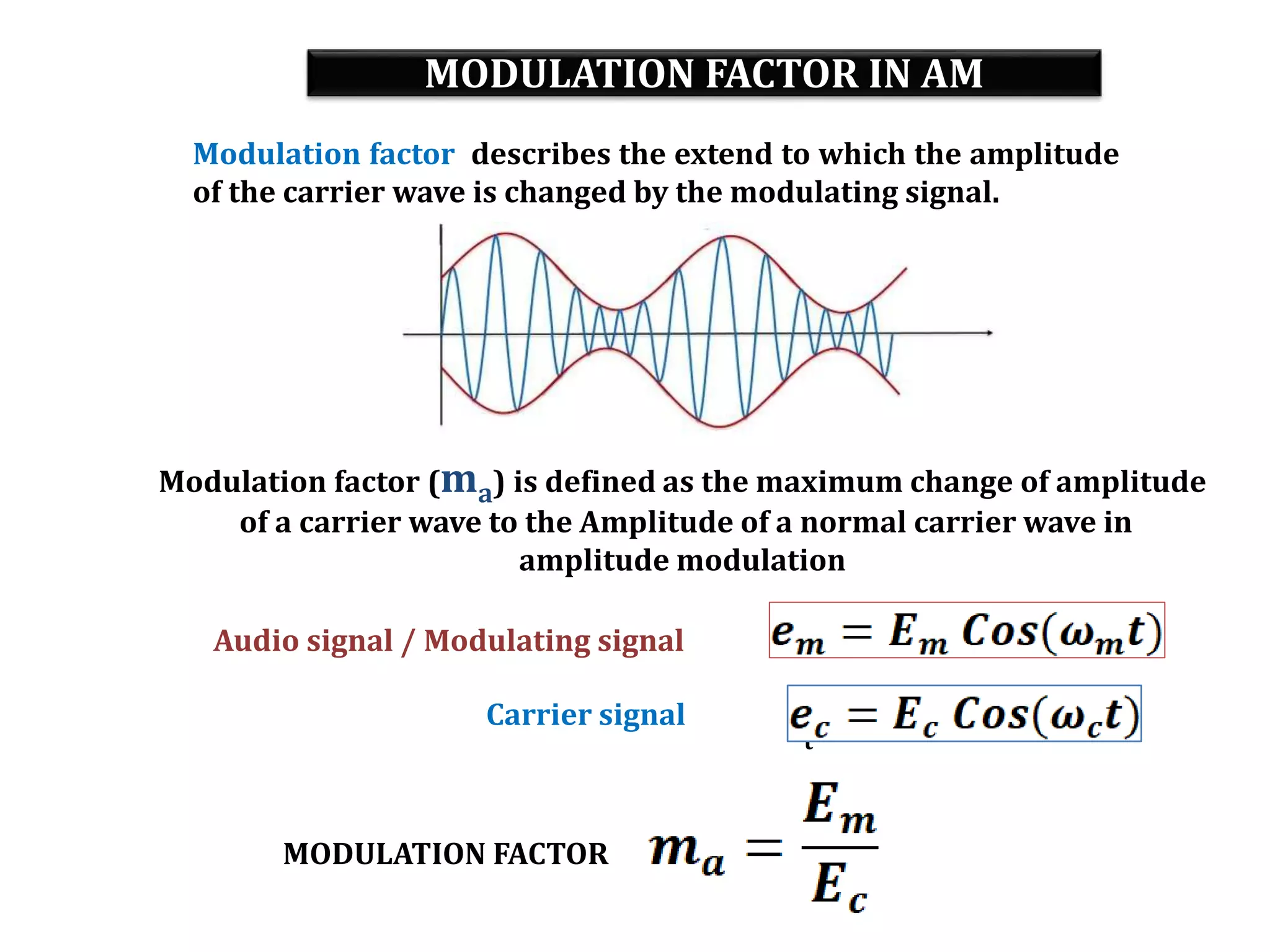
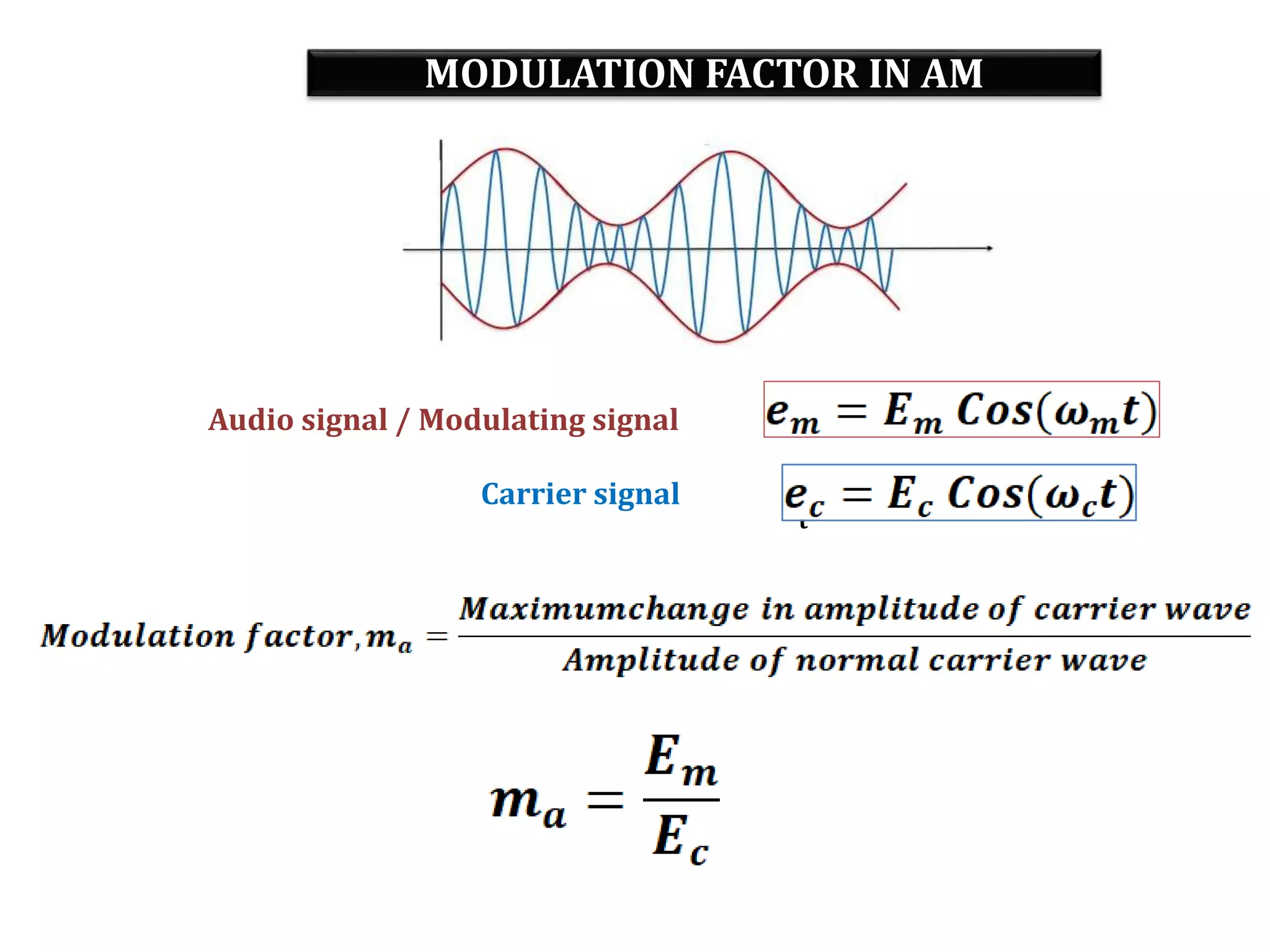
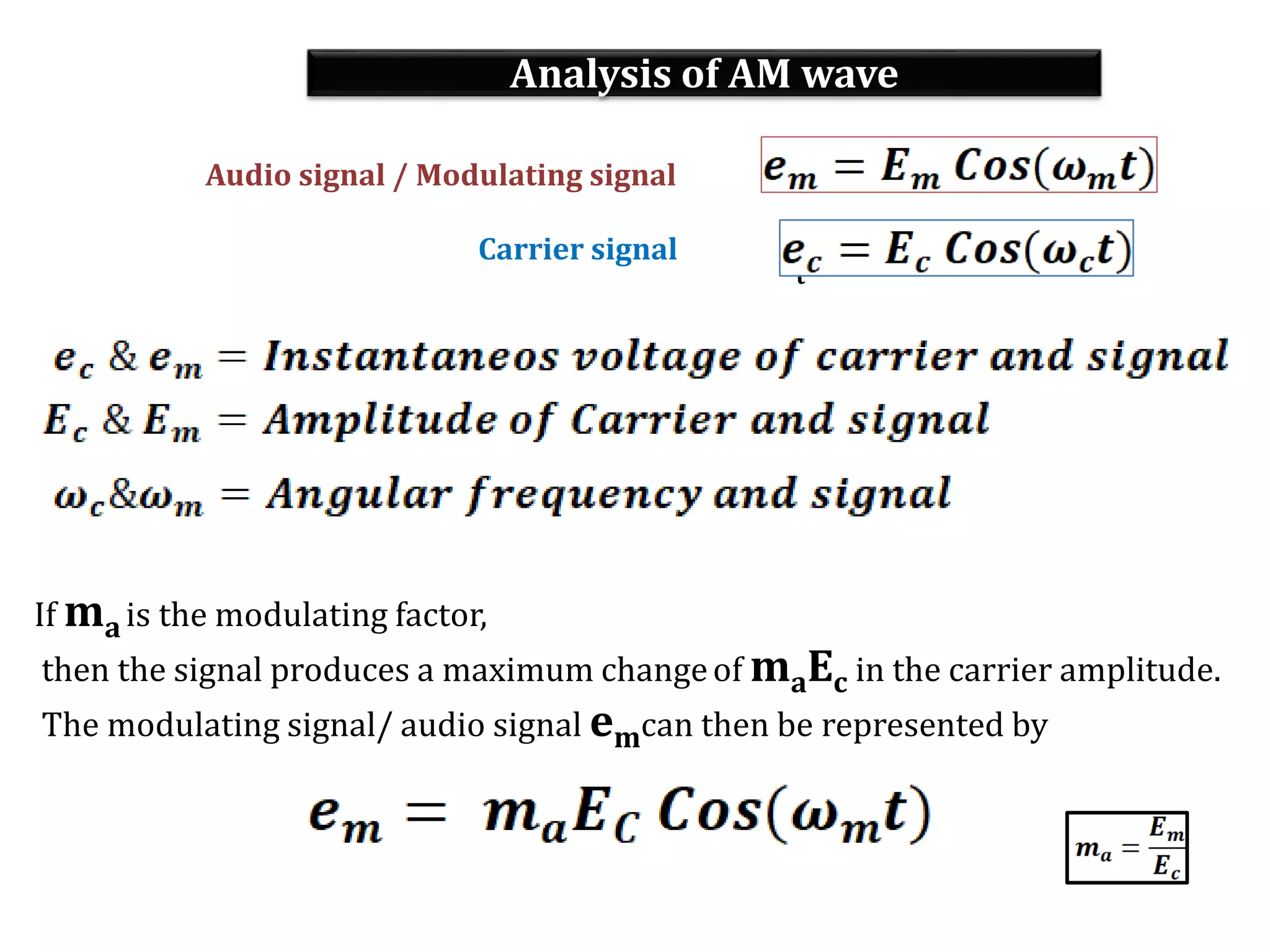
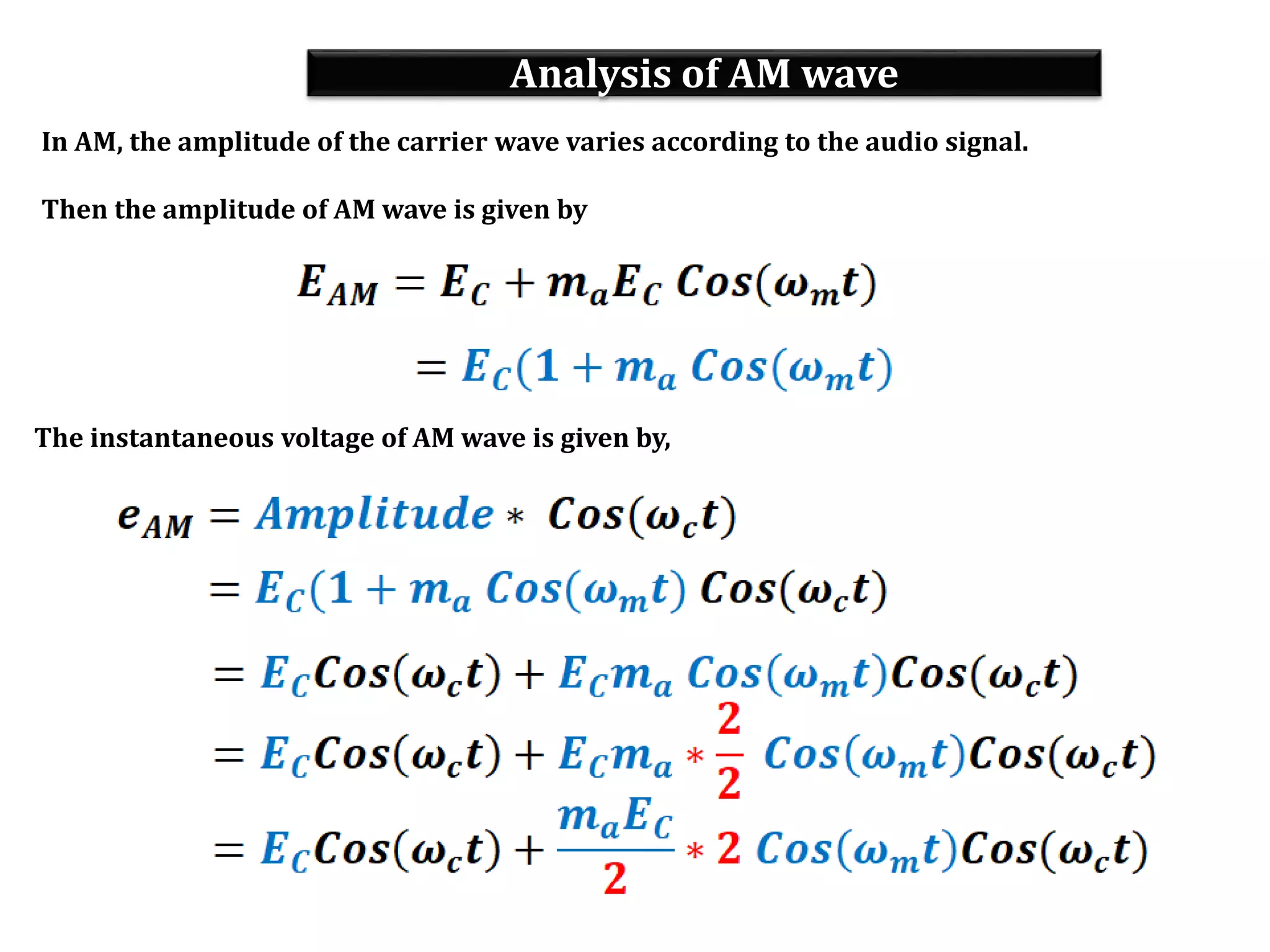
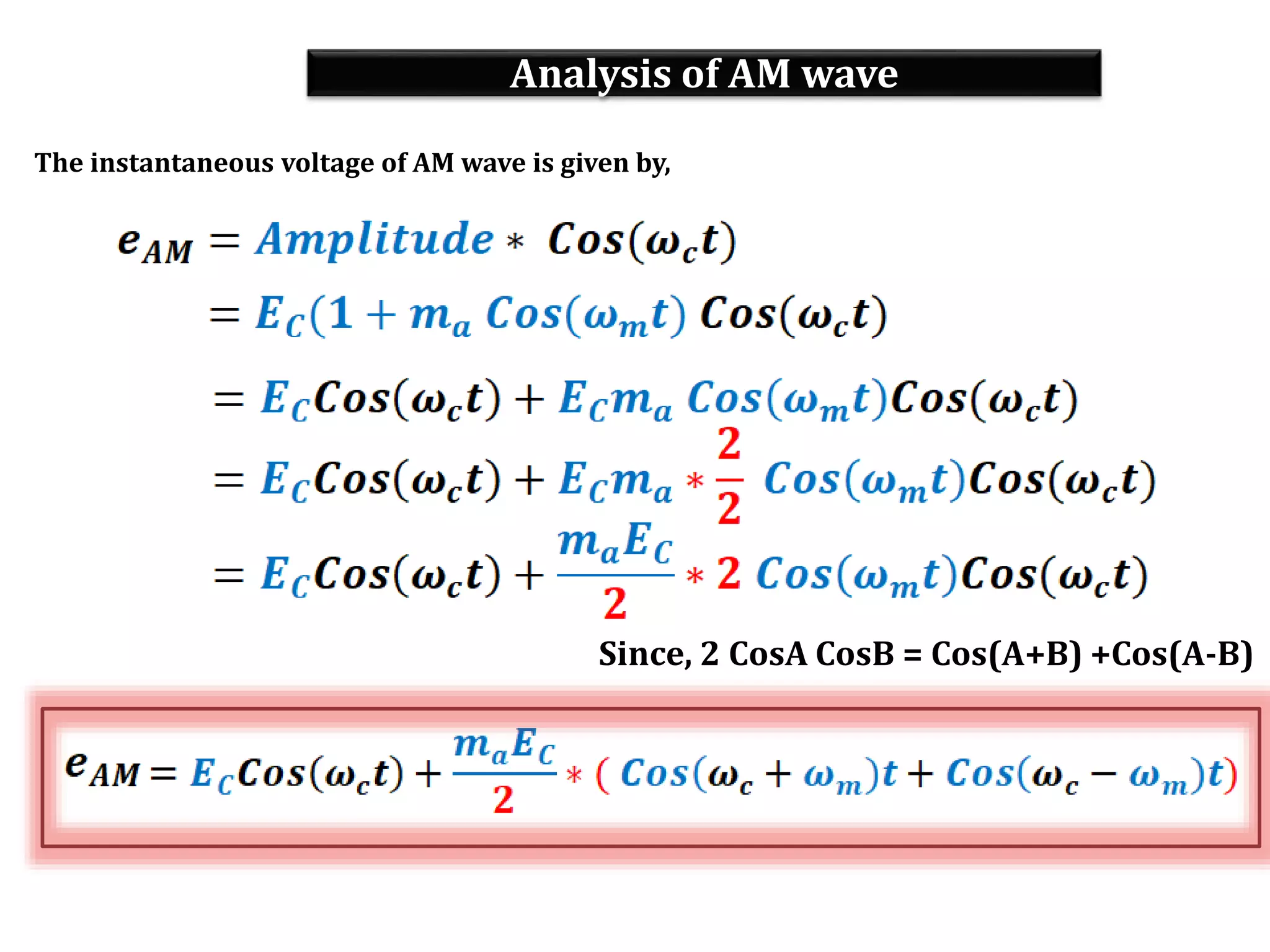
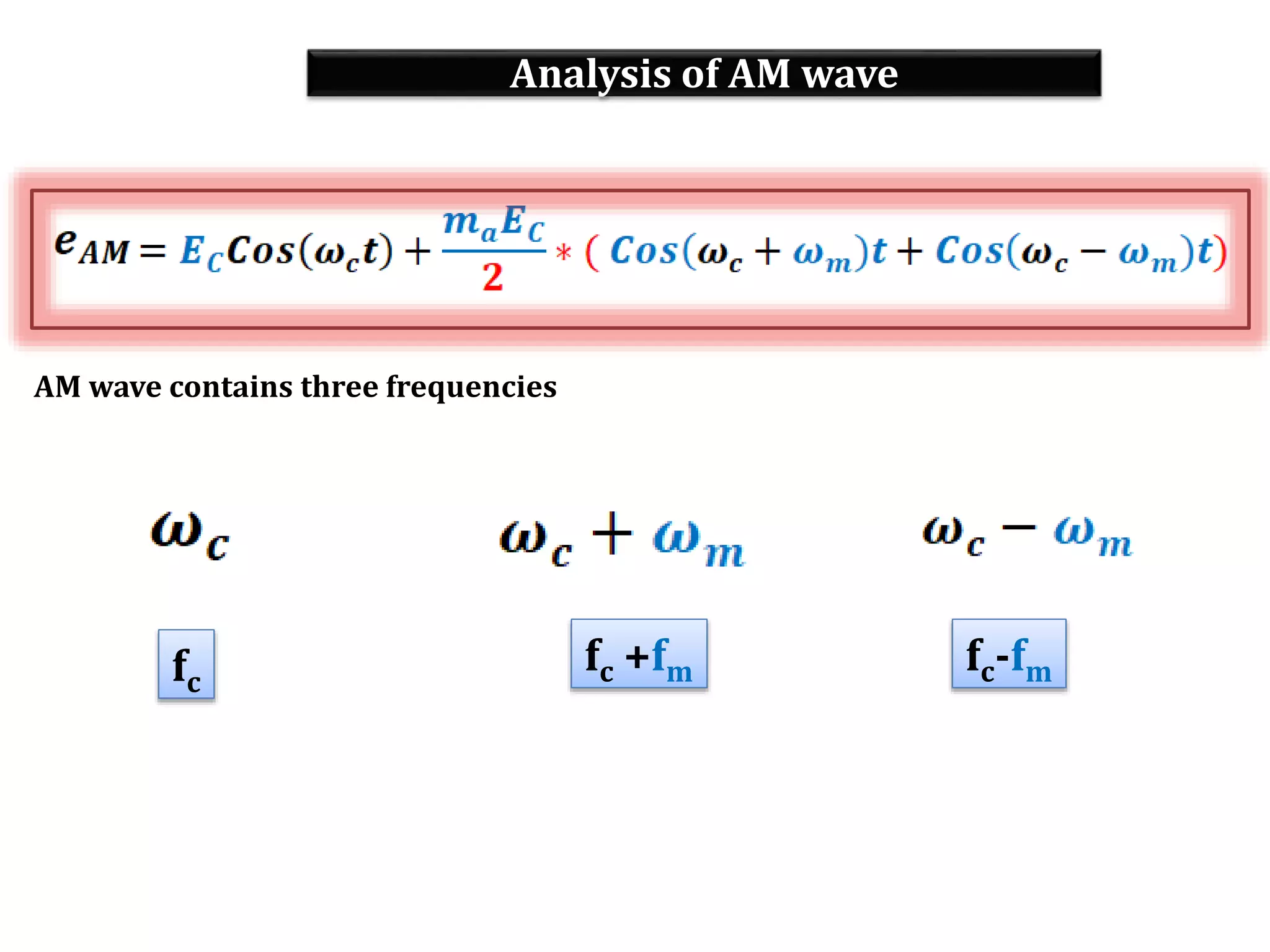
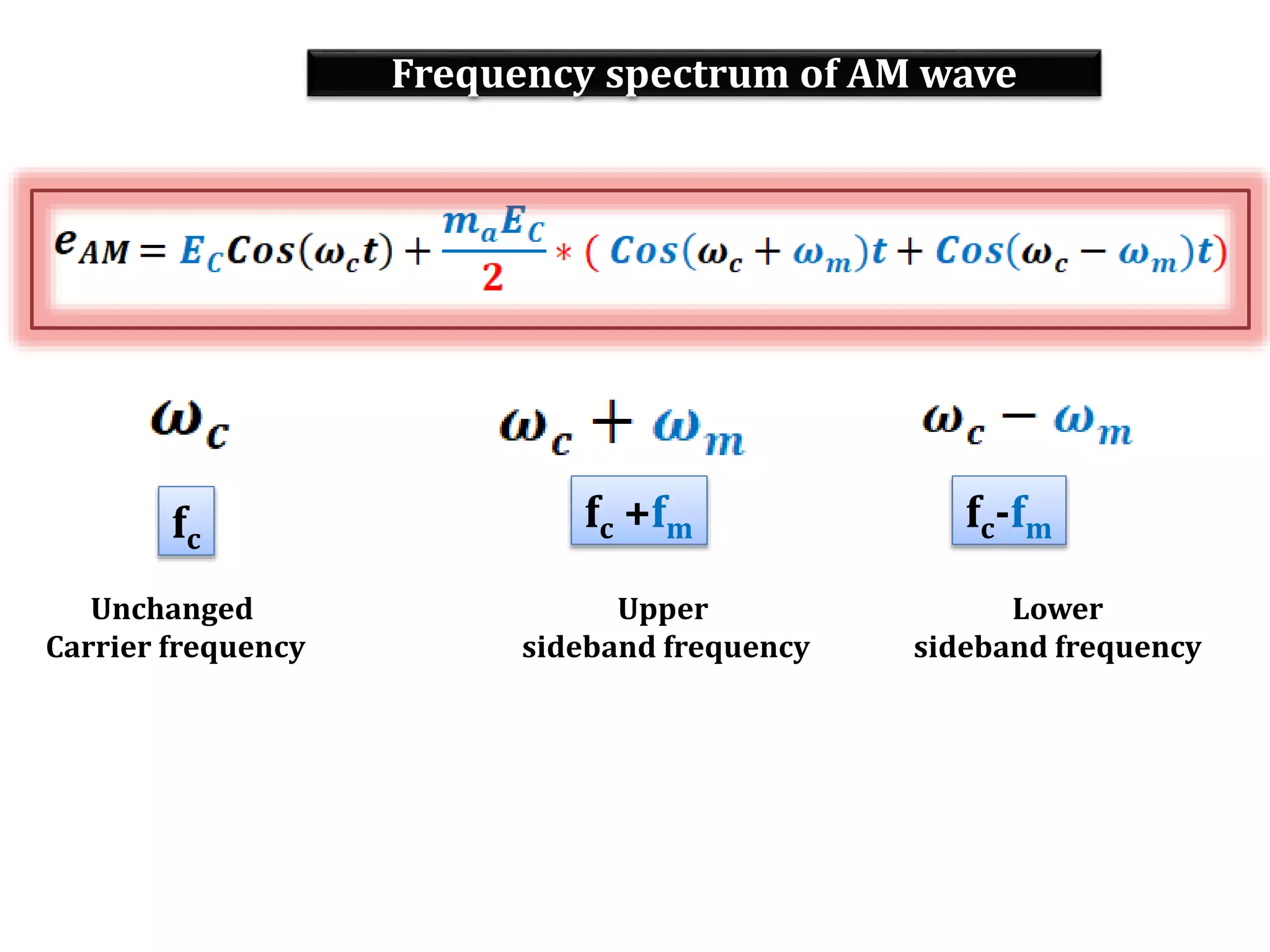
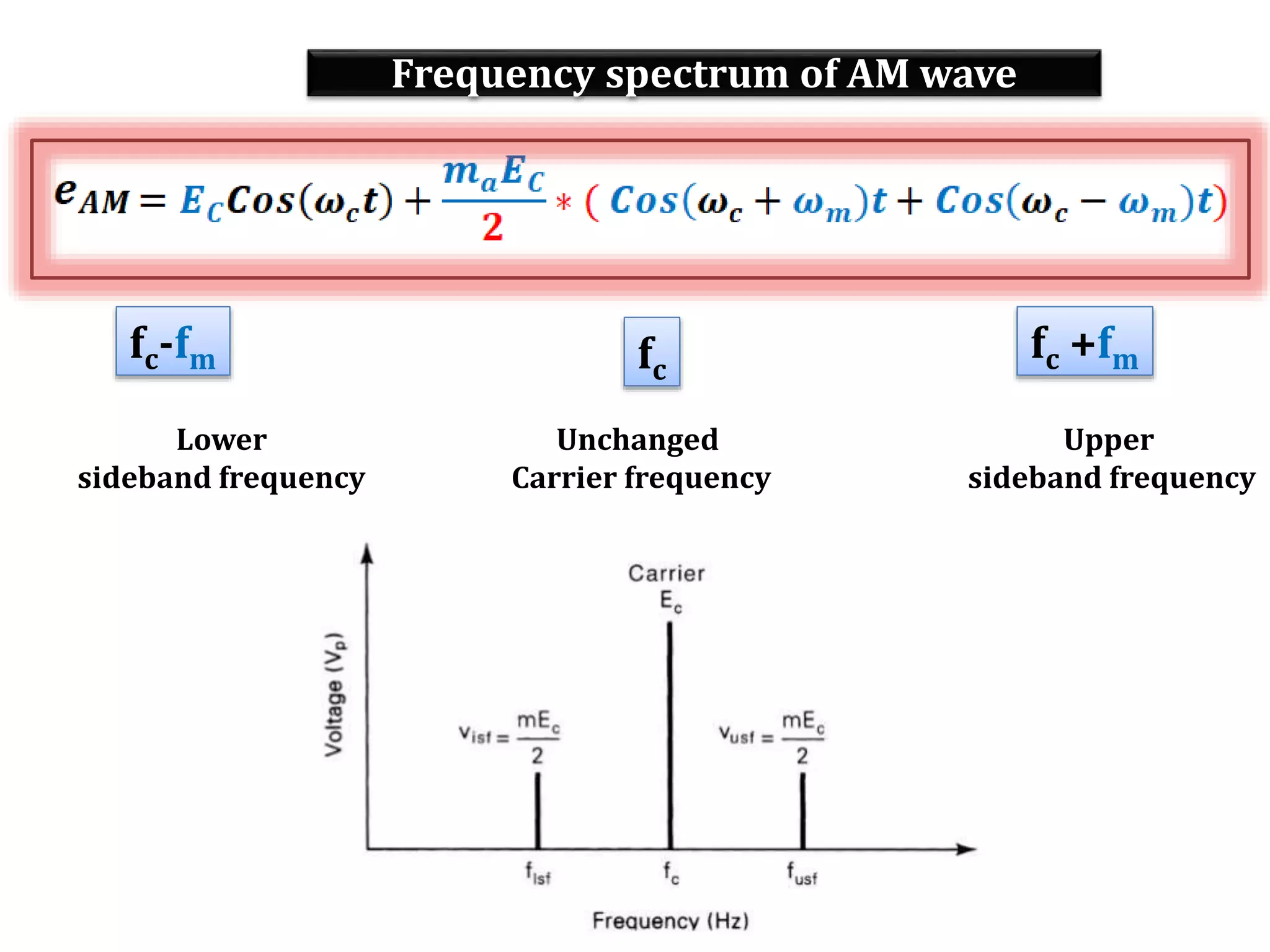
This document provides an outline for a lecture on electronics modulation. It begins with introductions for two professors teaching different units of the course. The bulk of the document then focuses on the topic of modulation, defining it as a process of superimposing audio signals on carrier waves to allow for long distance transmission. It describes the need for modulation to increase operating range, allow practical antenna lengths, and enable wireless communication. It outlines the main types of modulation as amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation. Finally, it provides details on amplitude modulation, including analyzing the amplitude modulated wave and its frequency spectrum.