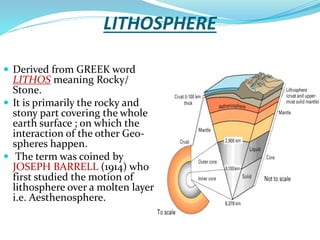
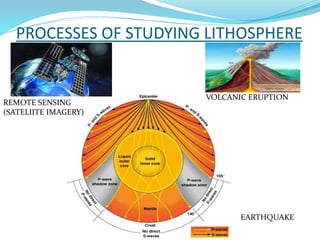
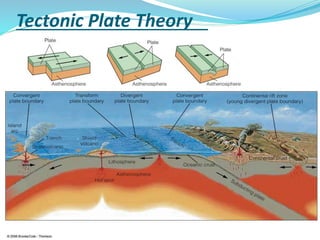
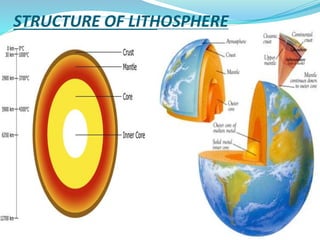
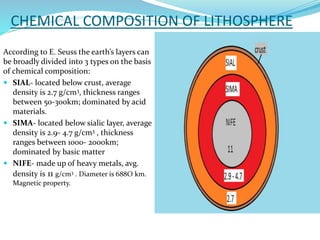
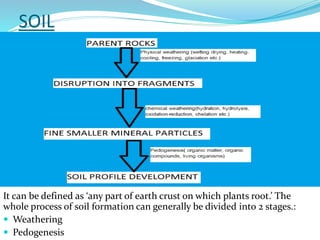
The document discusses the lithosphere, which is the outermost solid shell of the Earth composed of the crust and upper mantle. It is divided into three main sections. The first section introduces the lithosphere and describes its composition and structure. The lithosphere consists of oceanic and continental crust and the upper mantle. The second section discusses various geological processes that affect the lithosphere like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and plate tectonics. The third section describes the chemical composition and types of rocks found in the lithosphere.