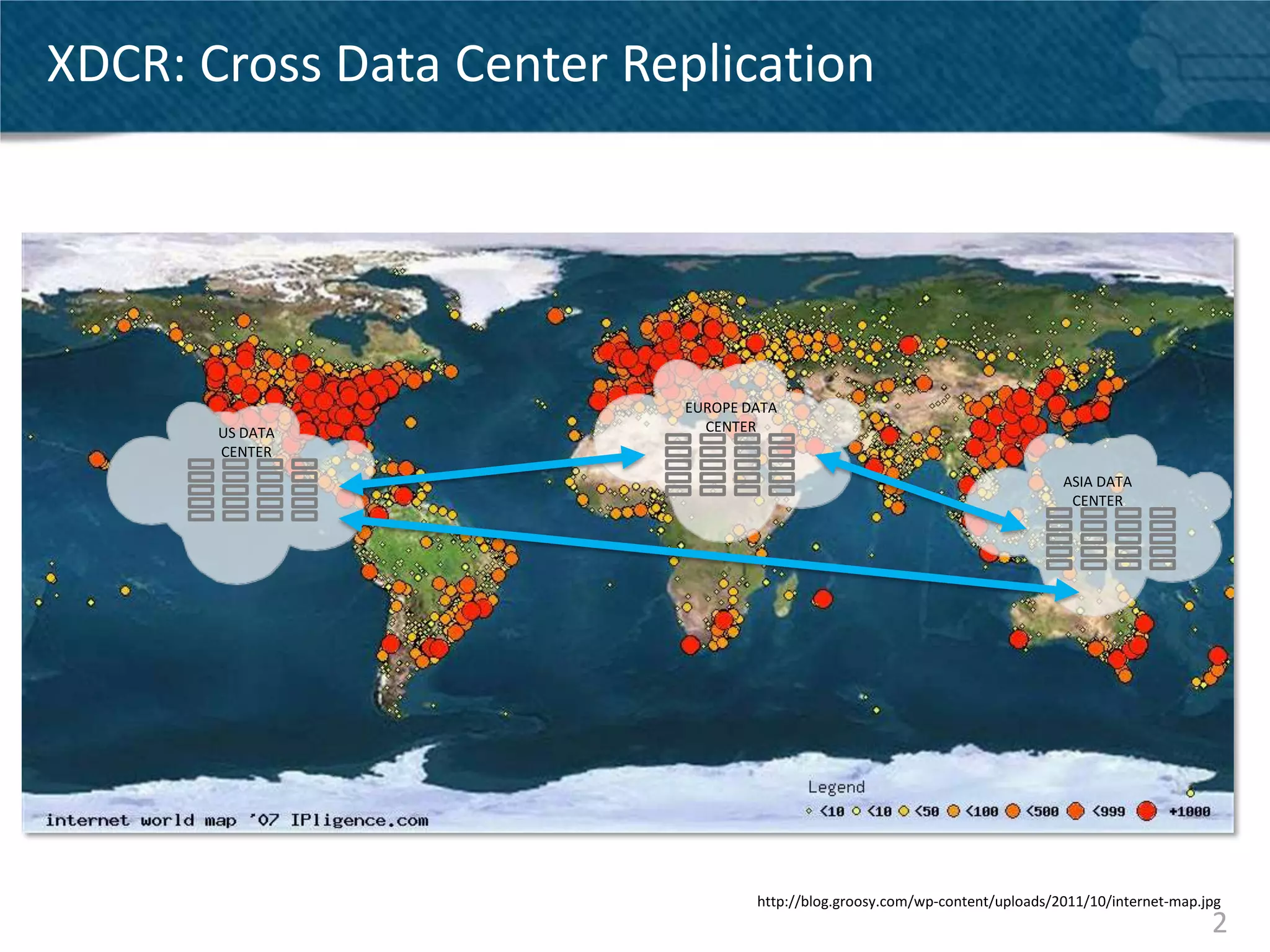
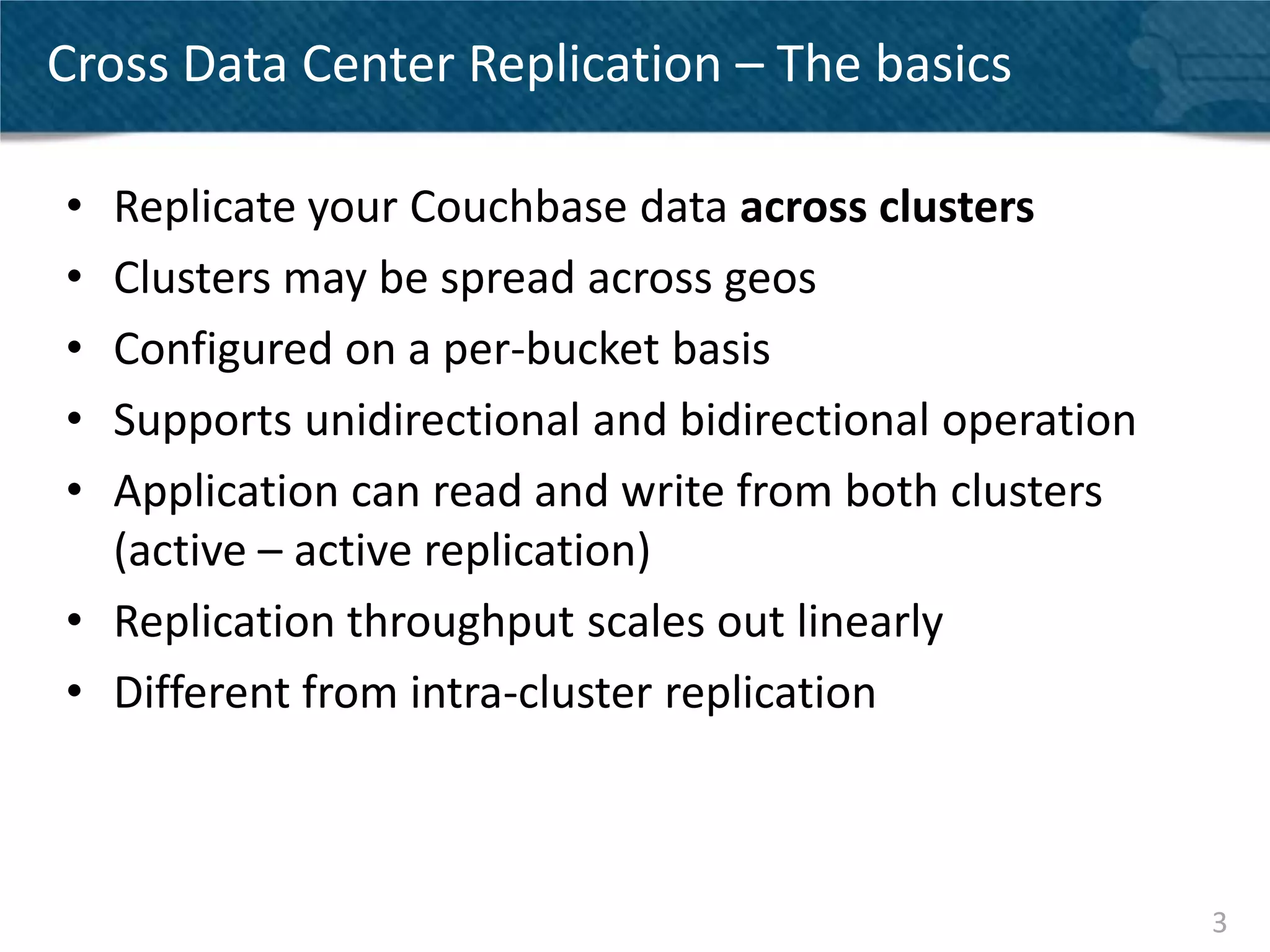
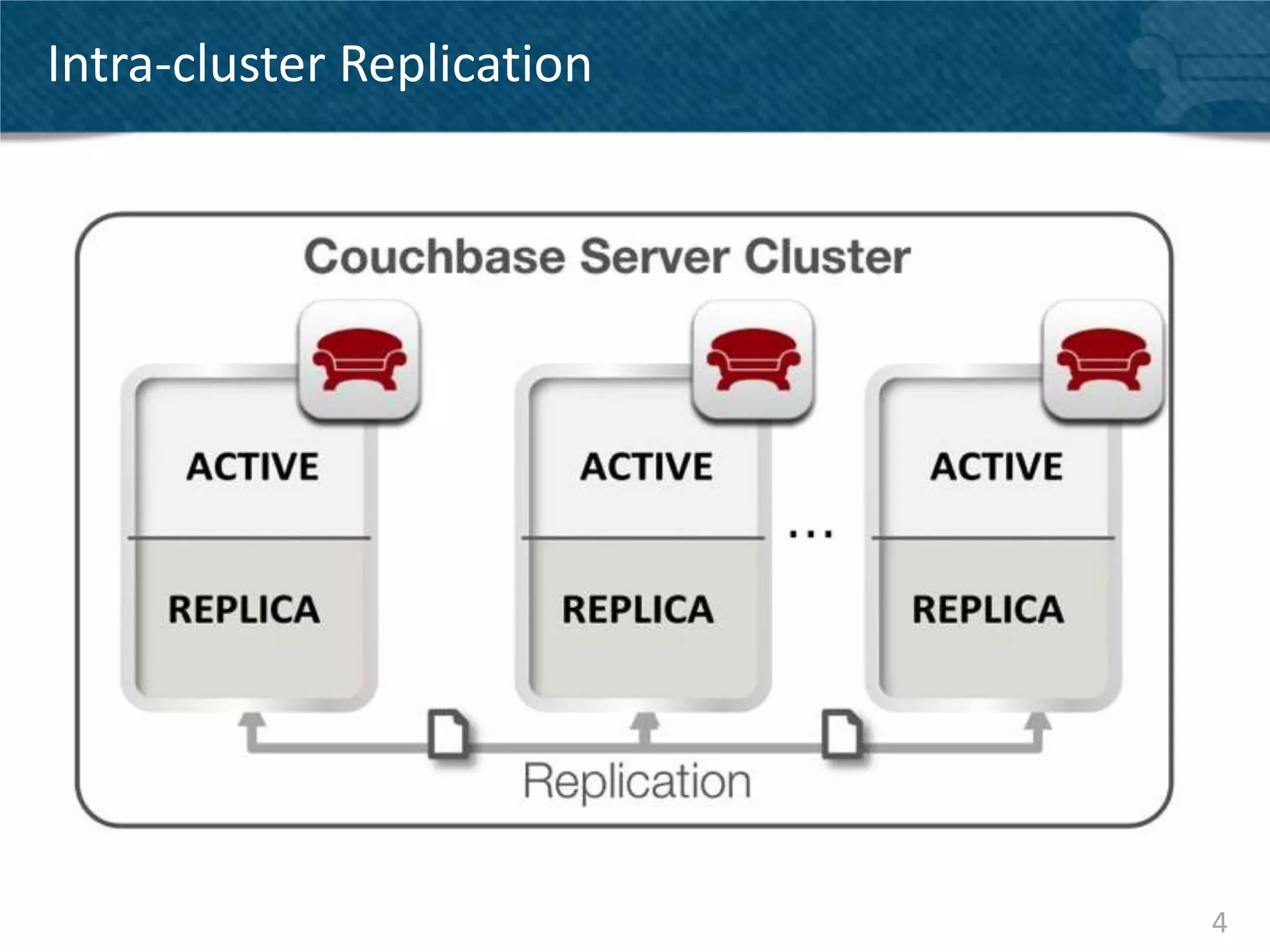
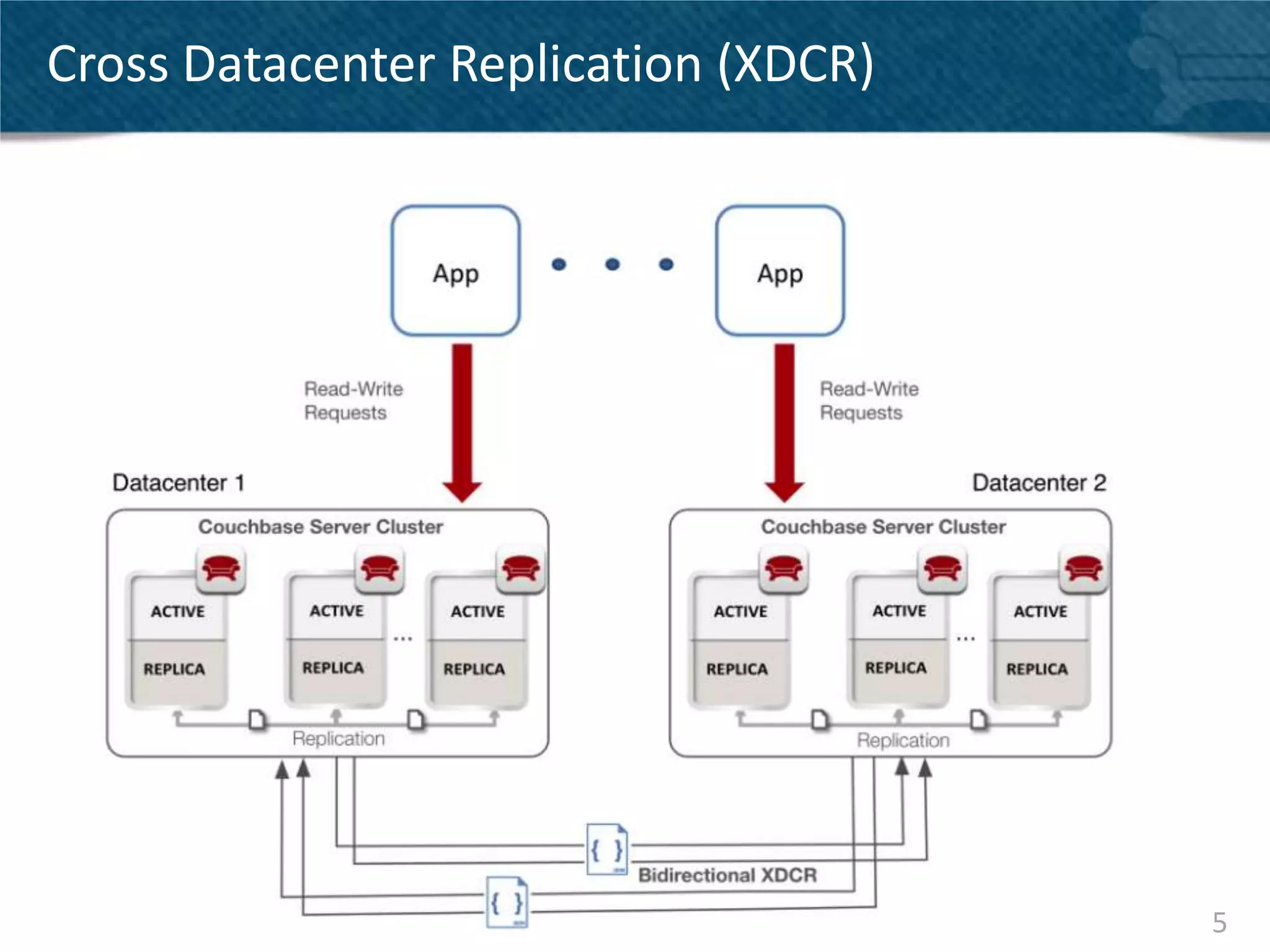
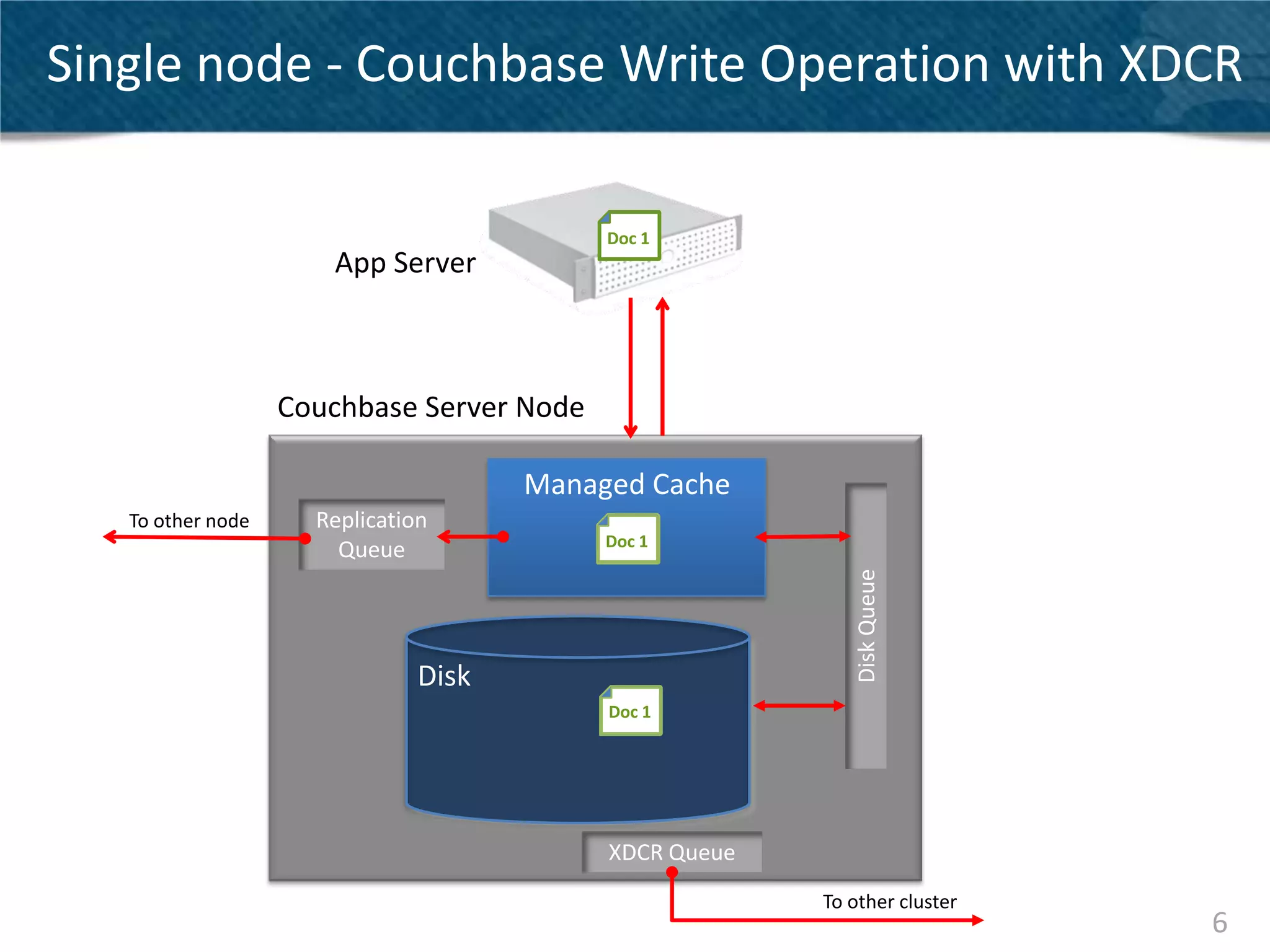
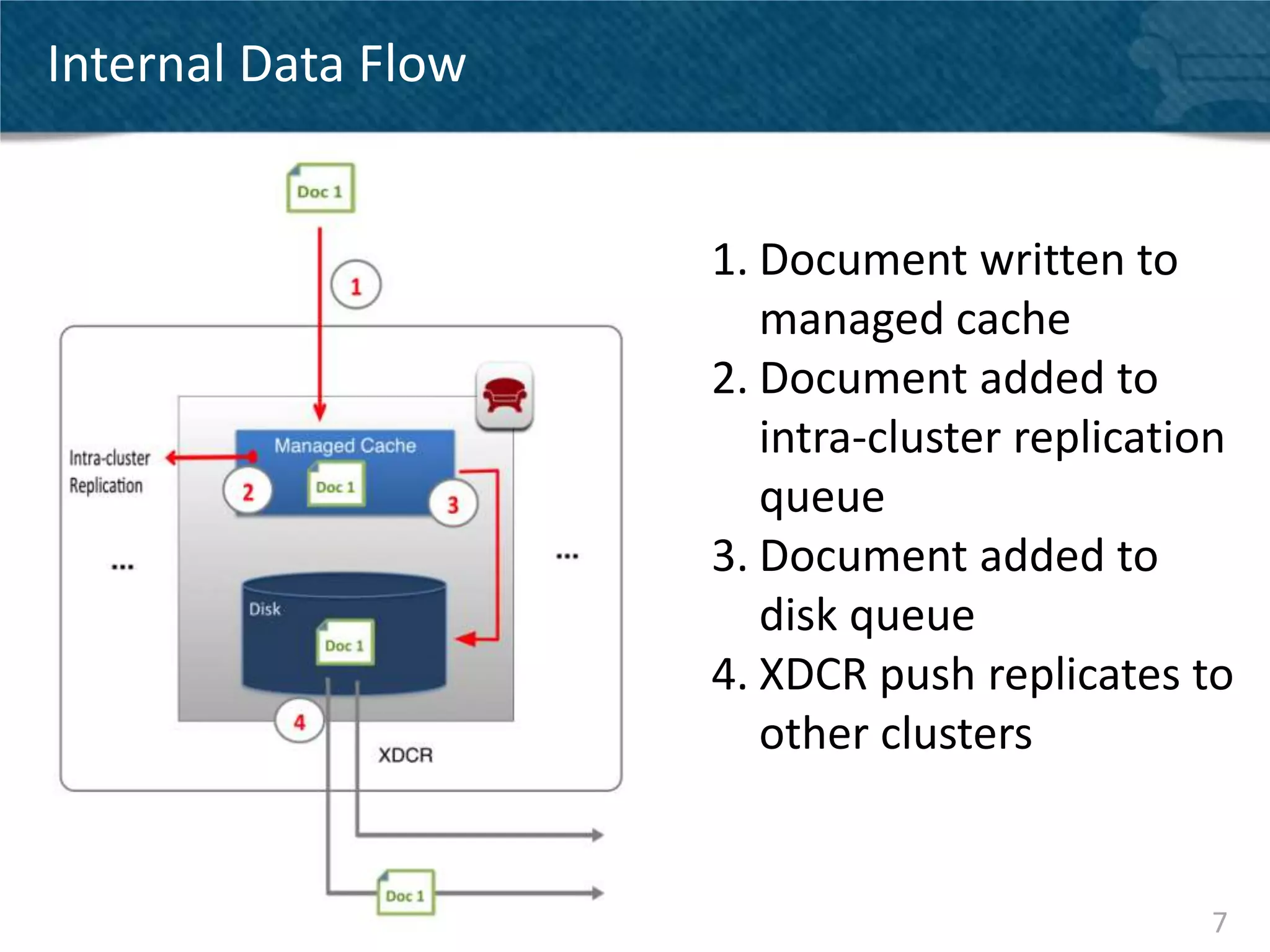
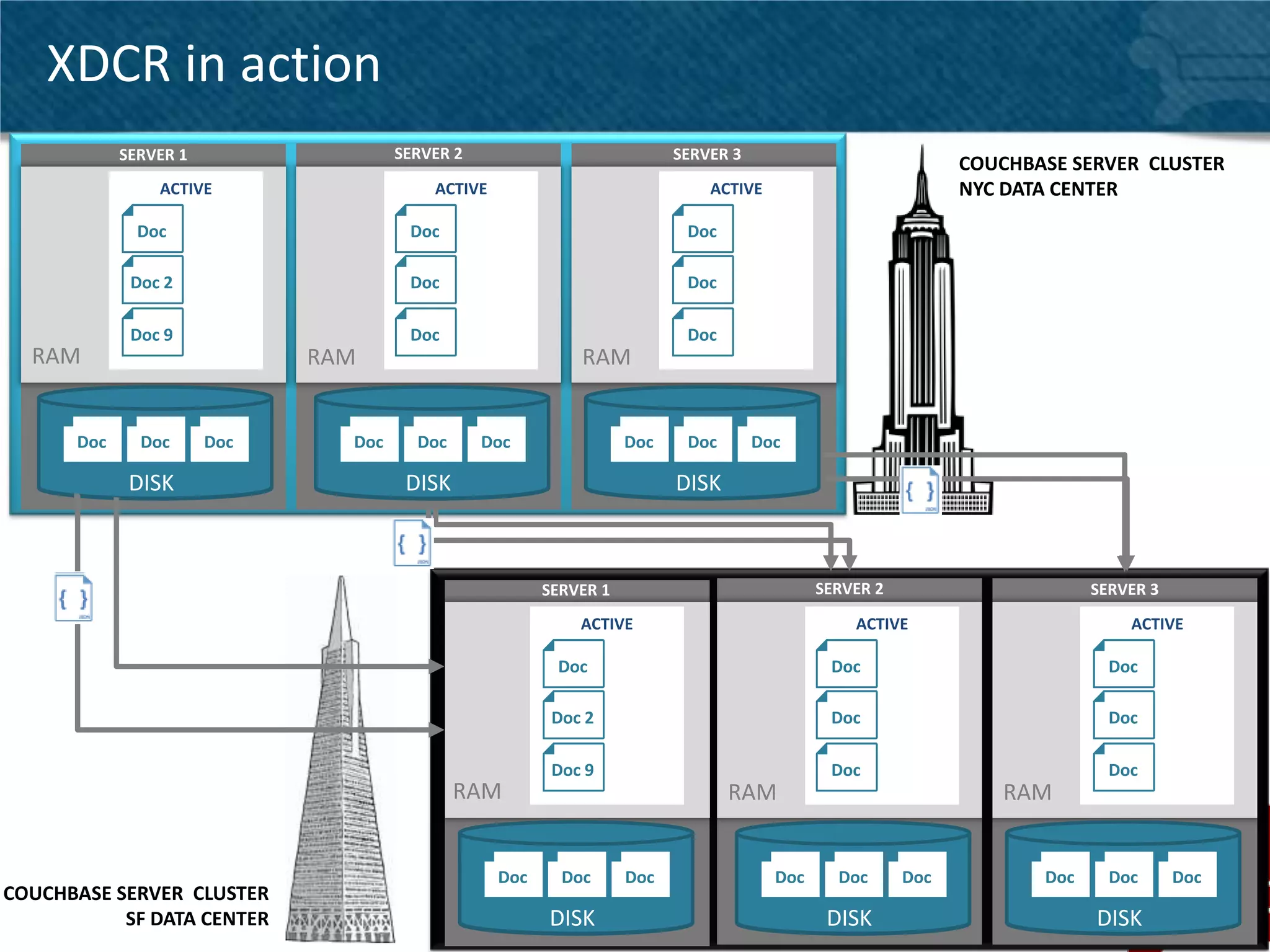
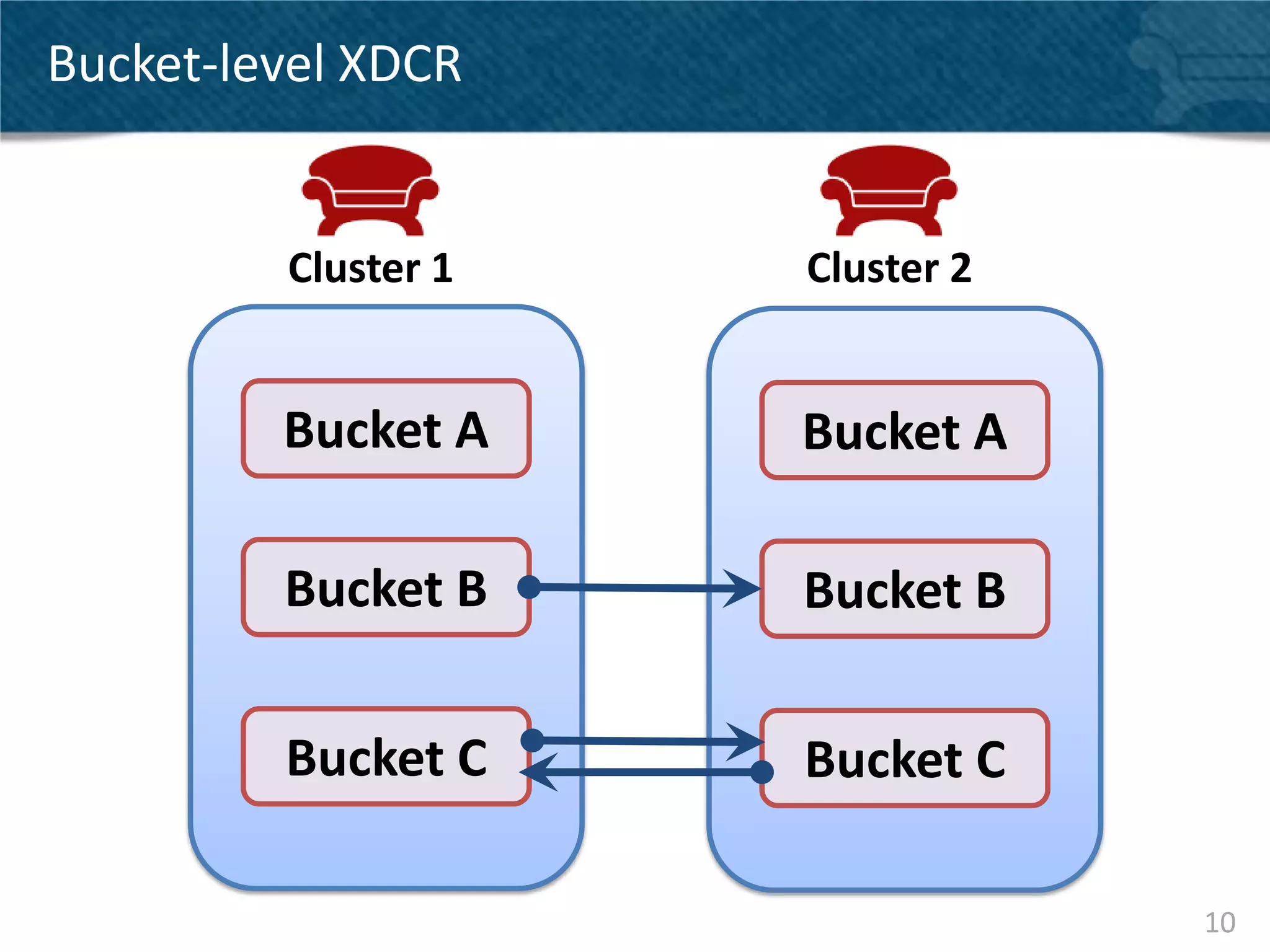
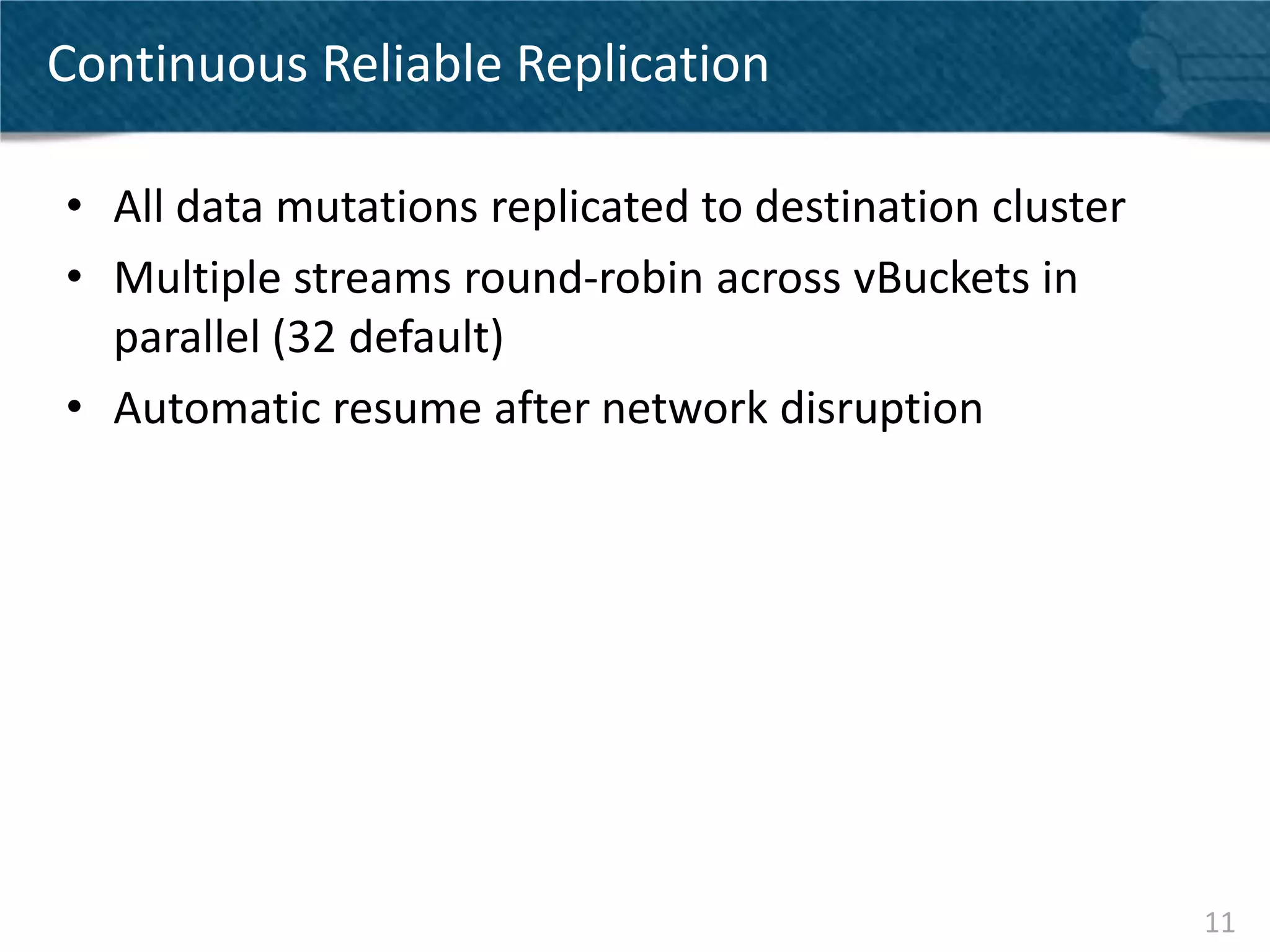
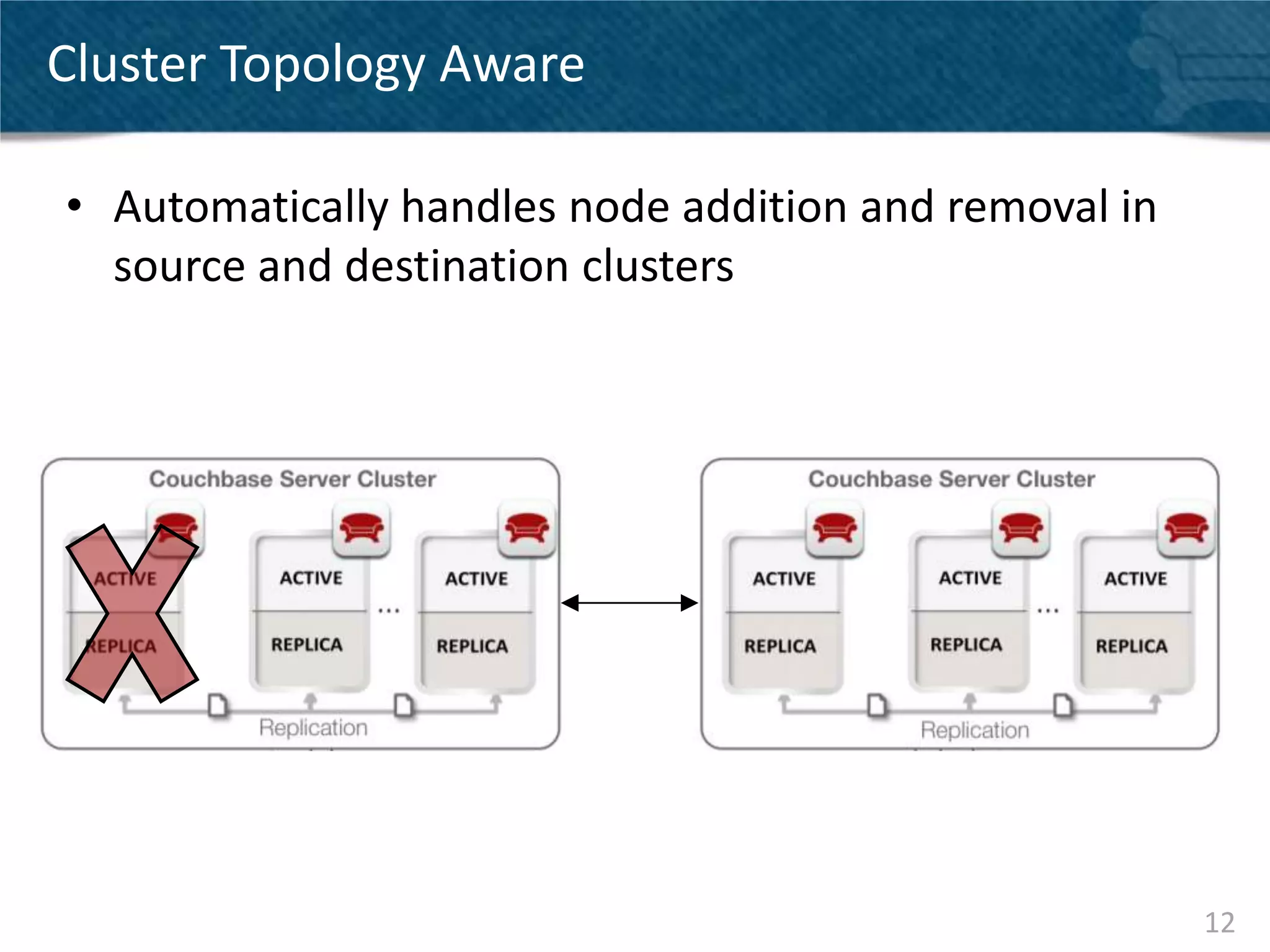
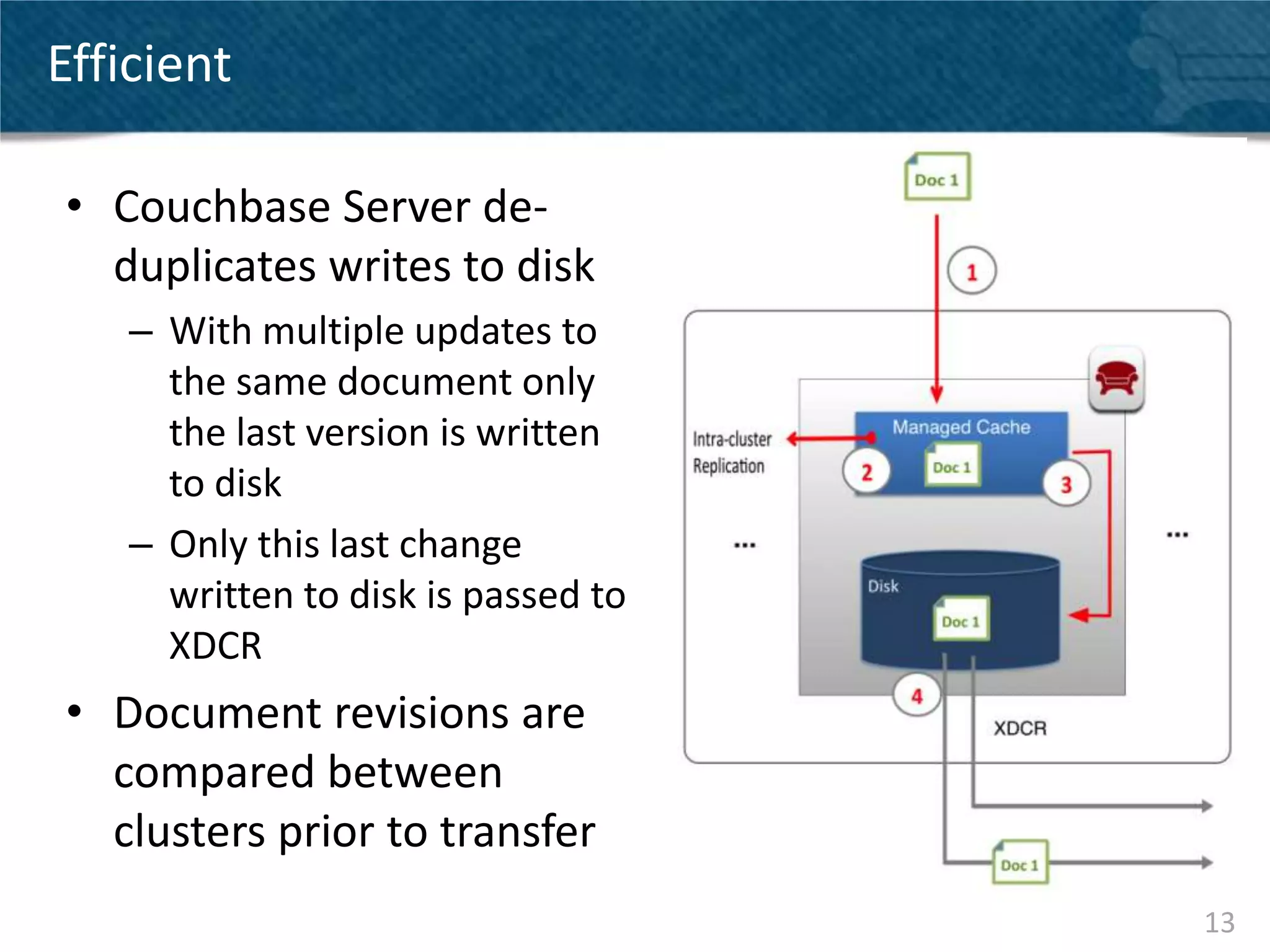
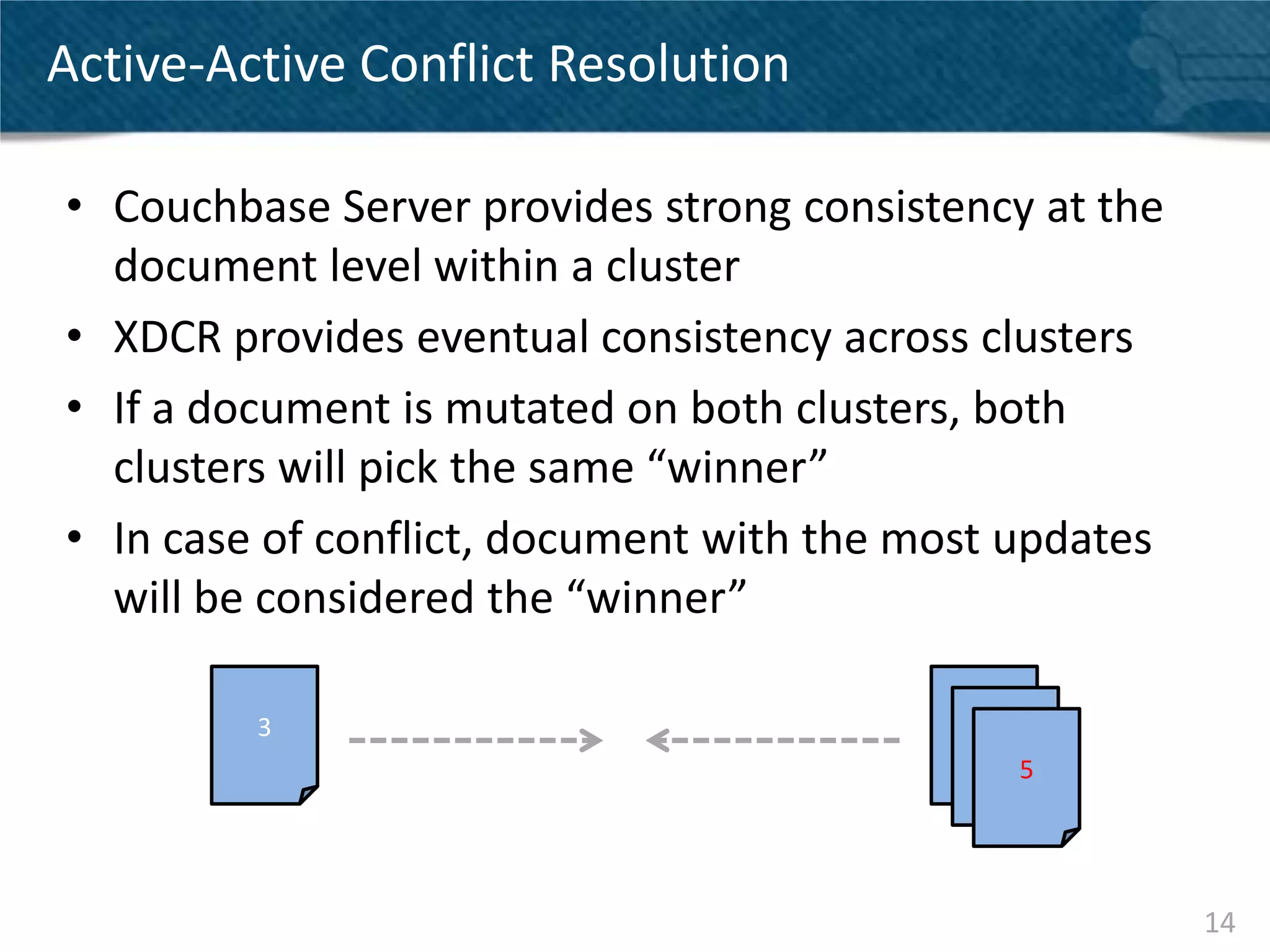
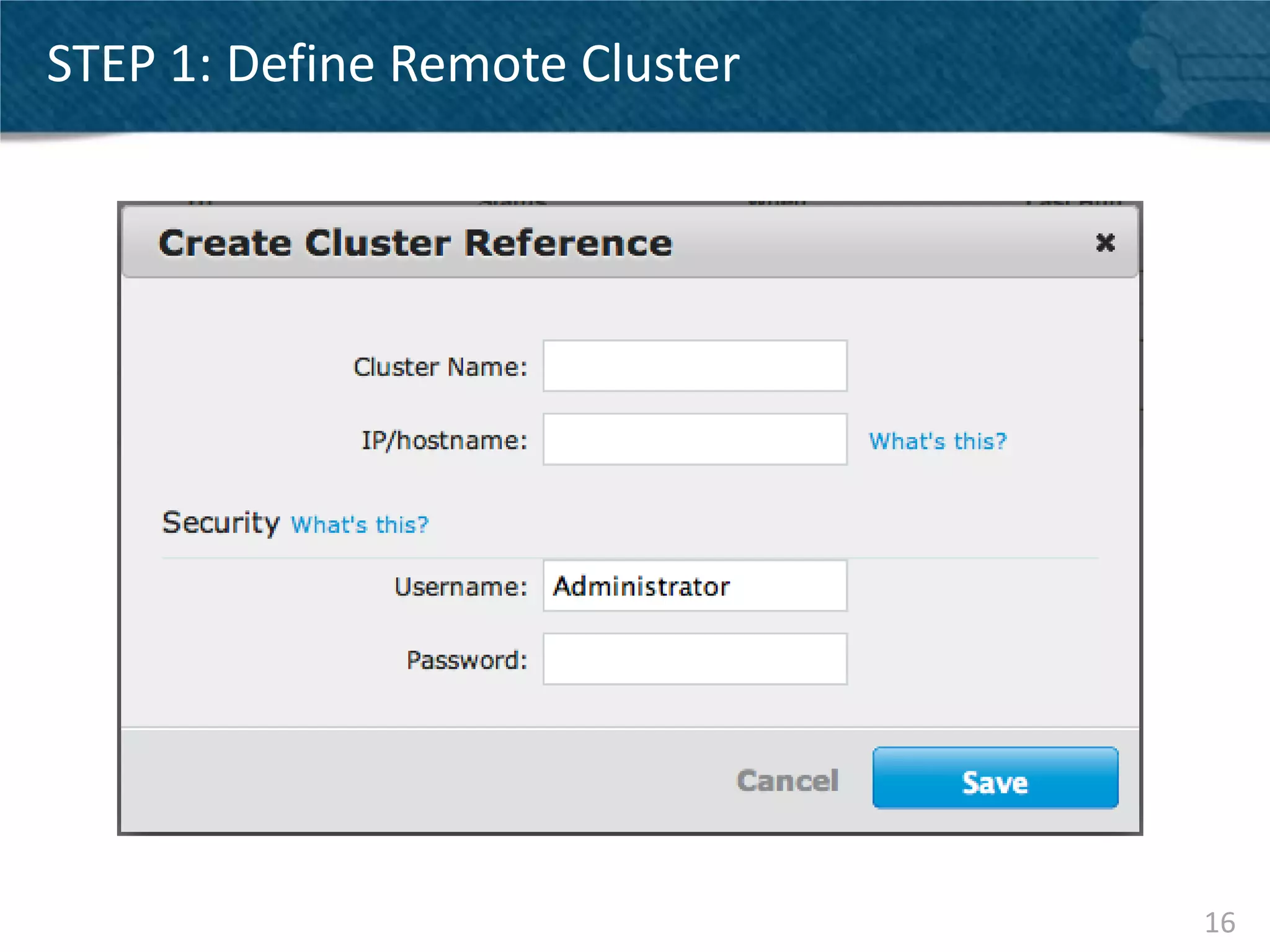
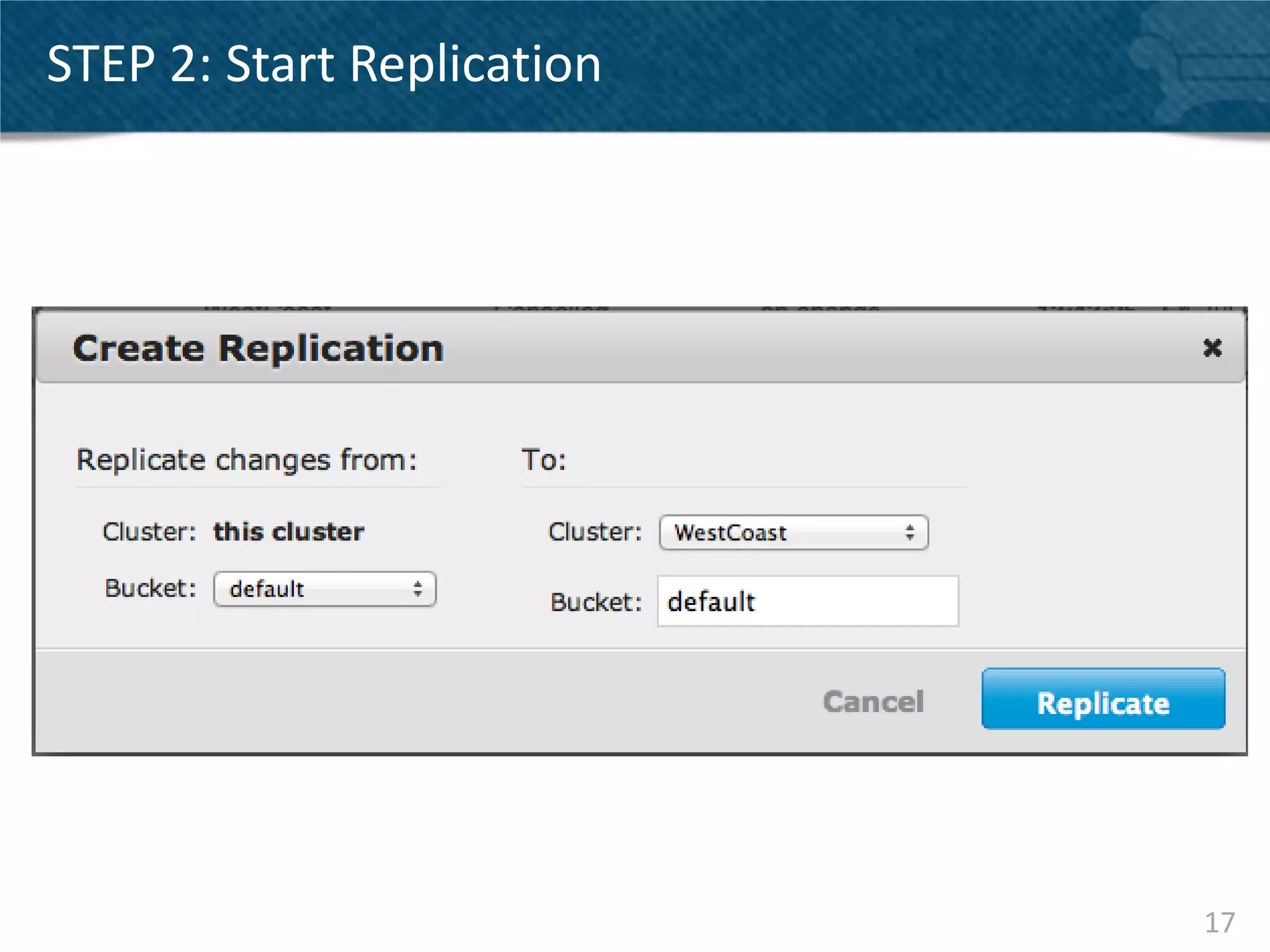
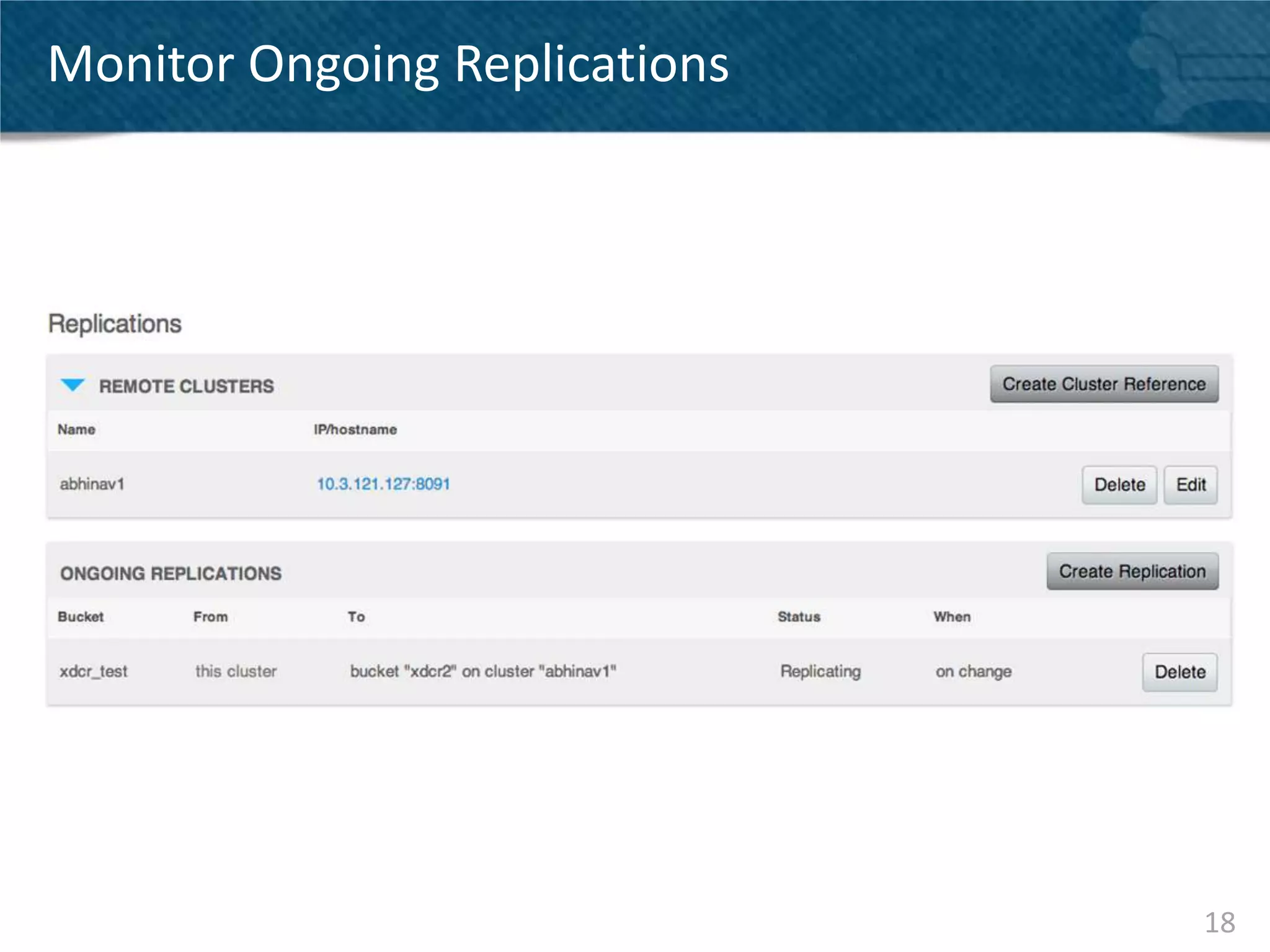
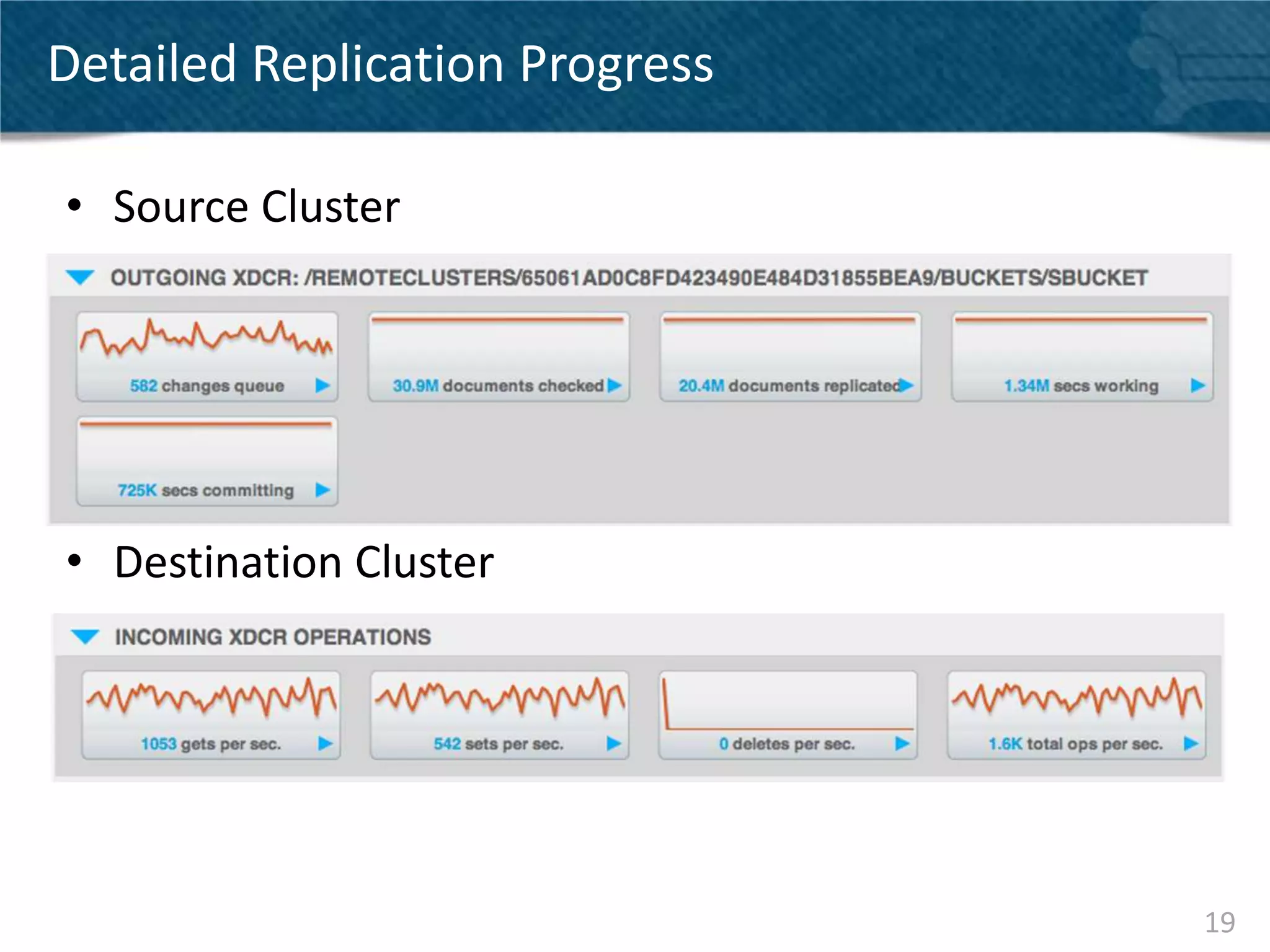
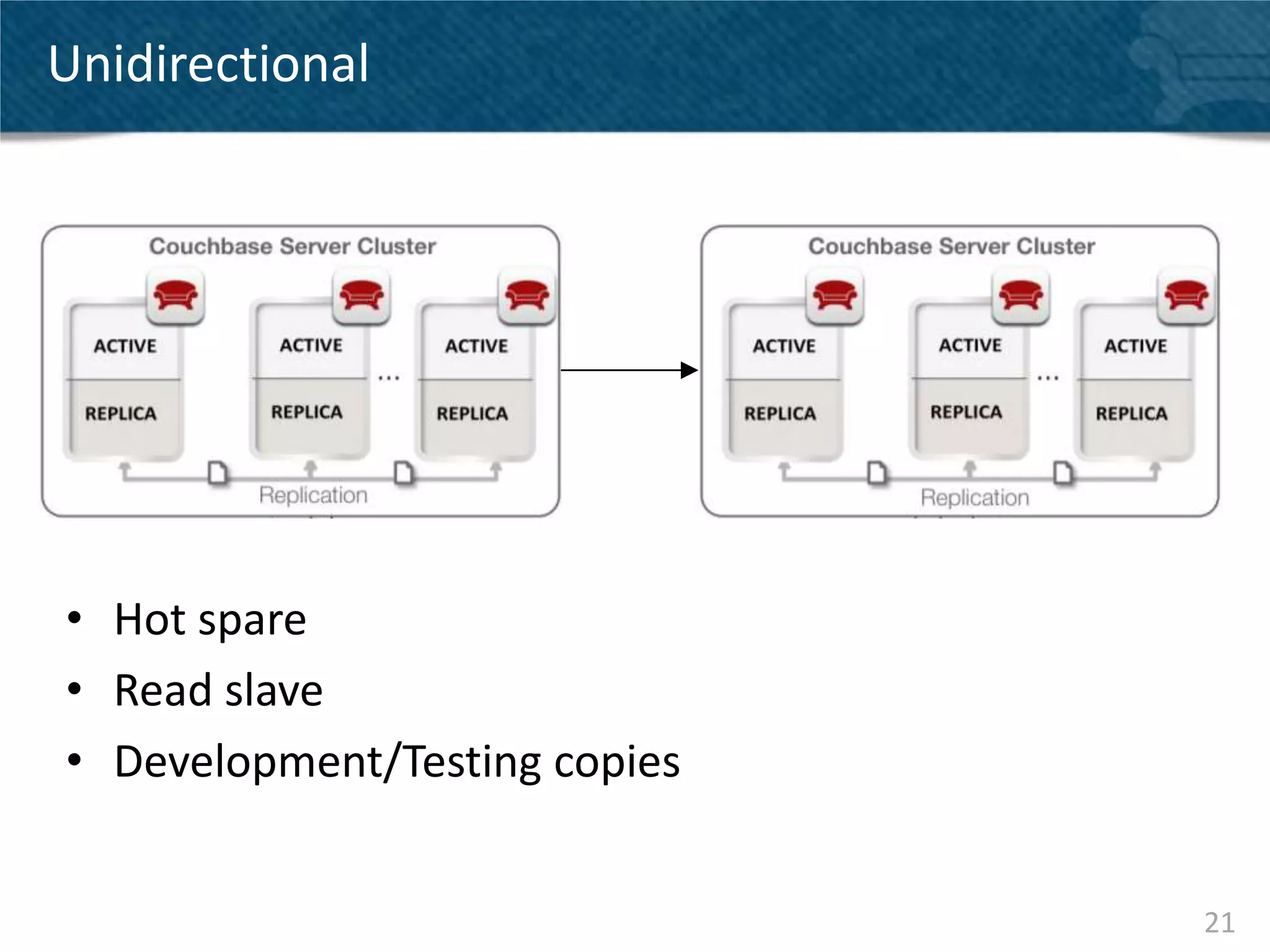
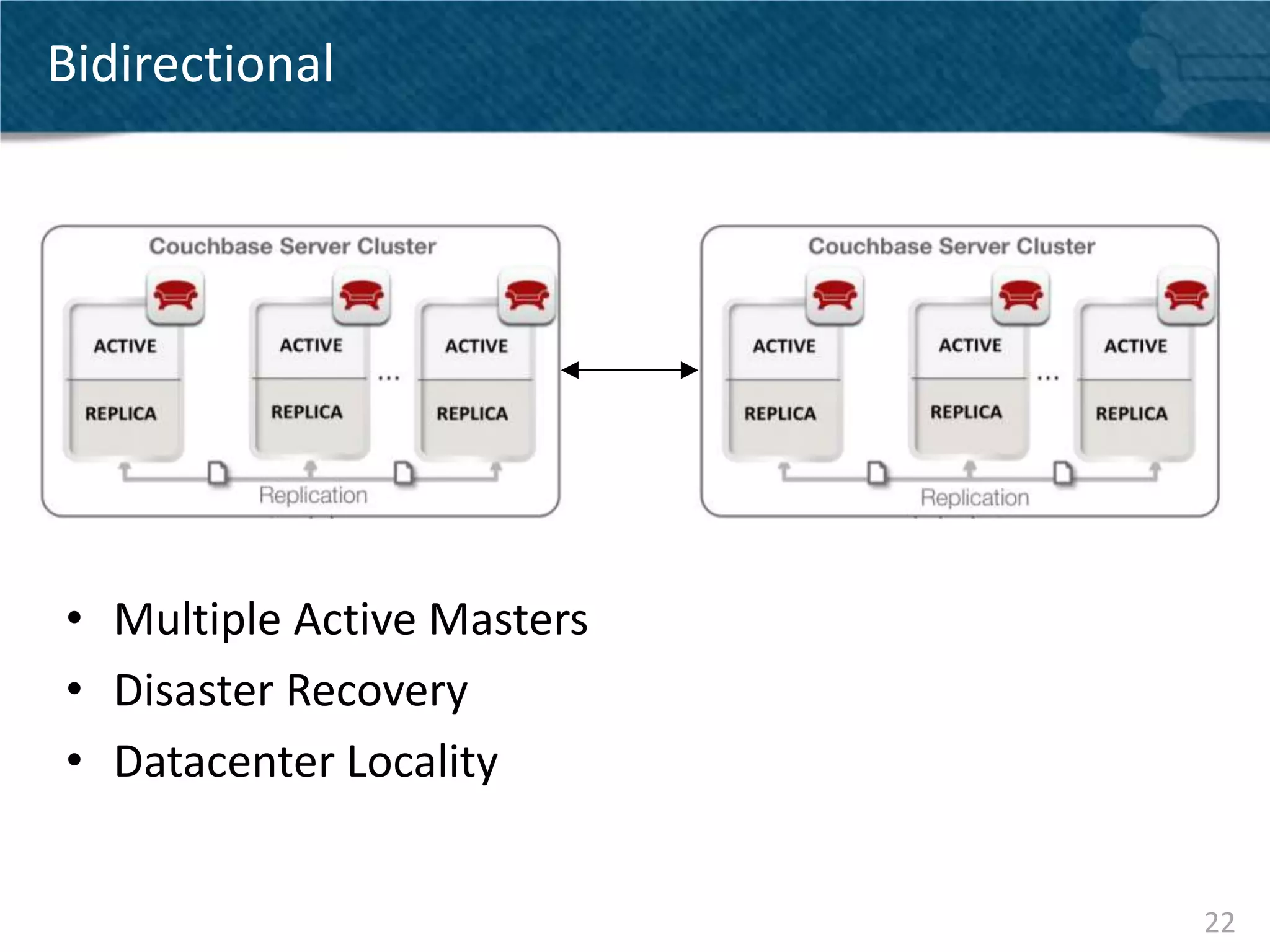
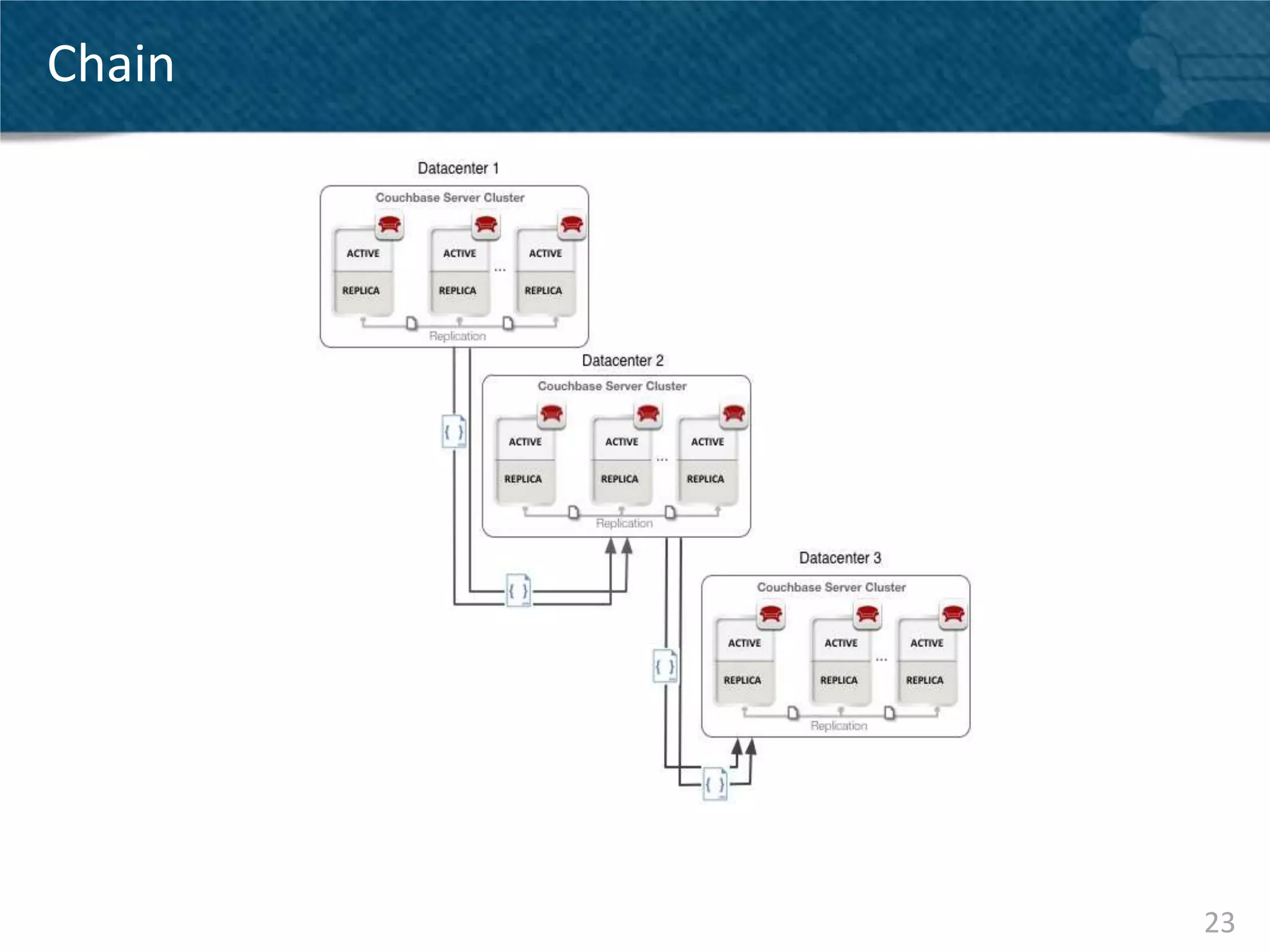
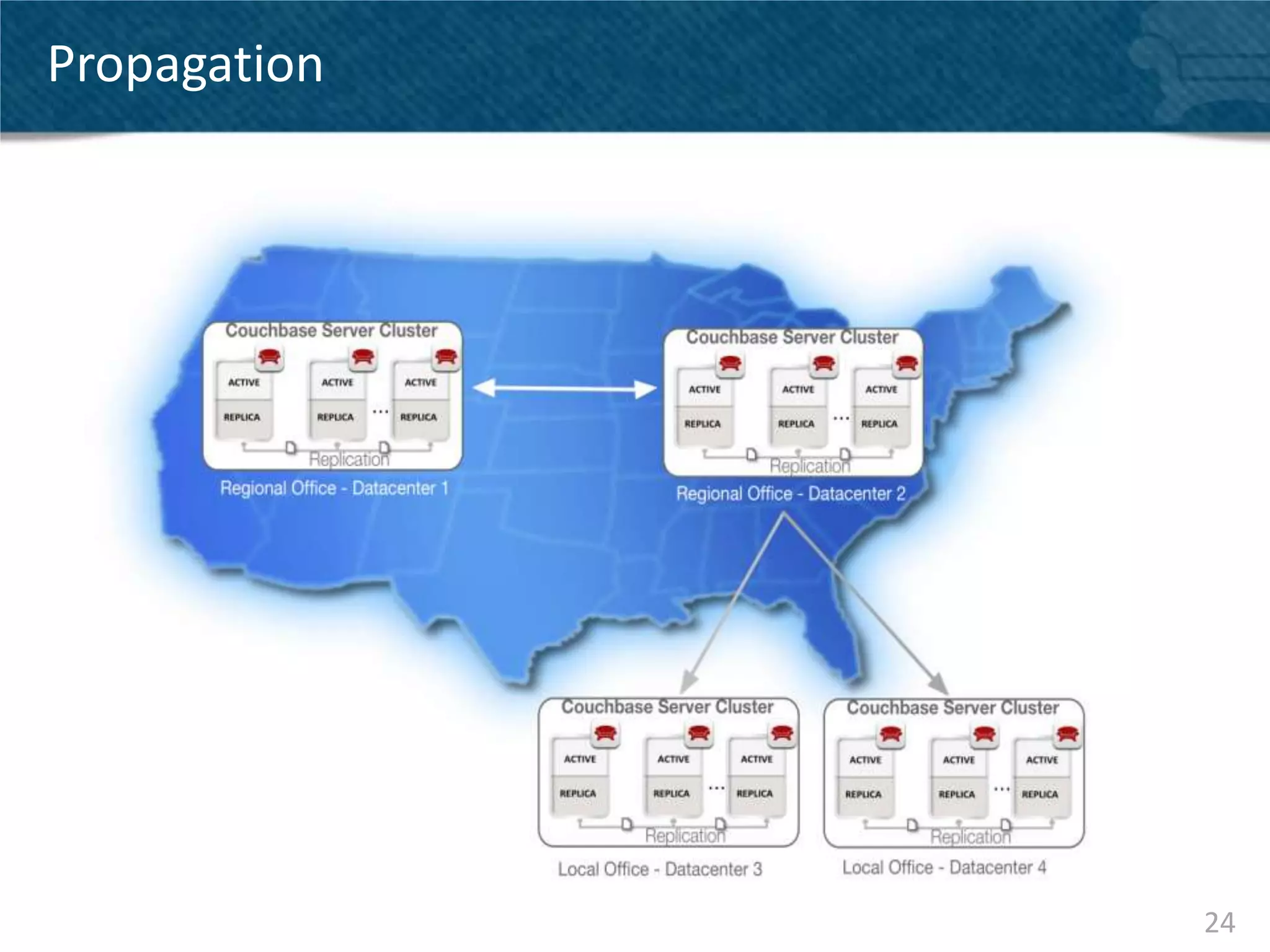
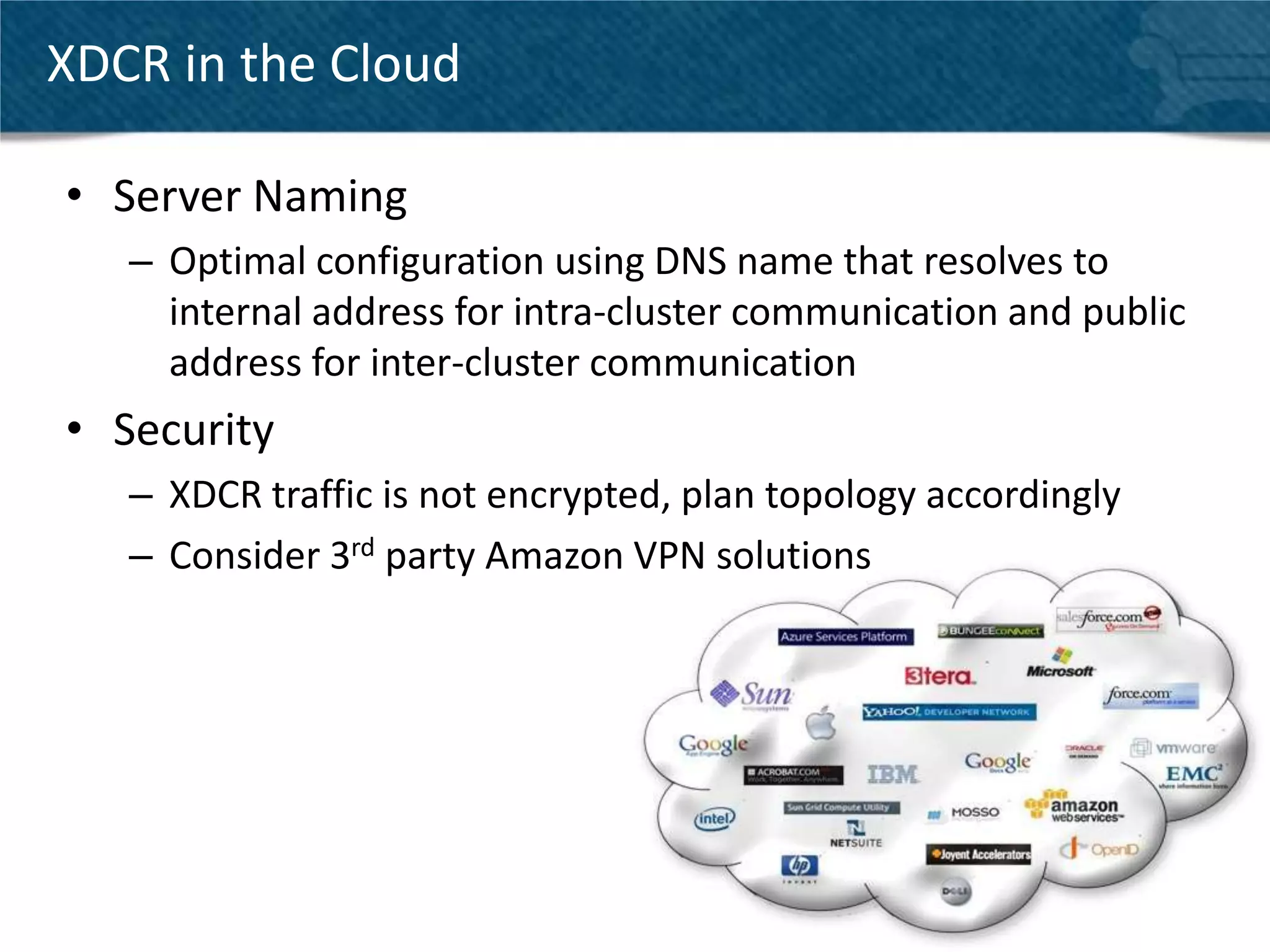
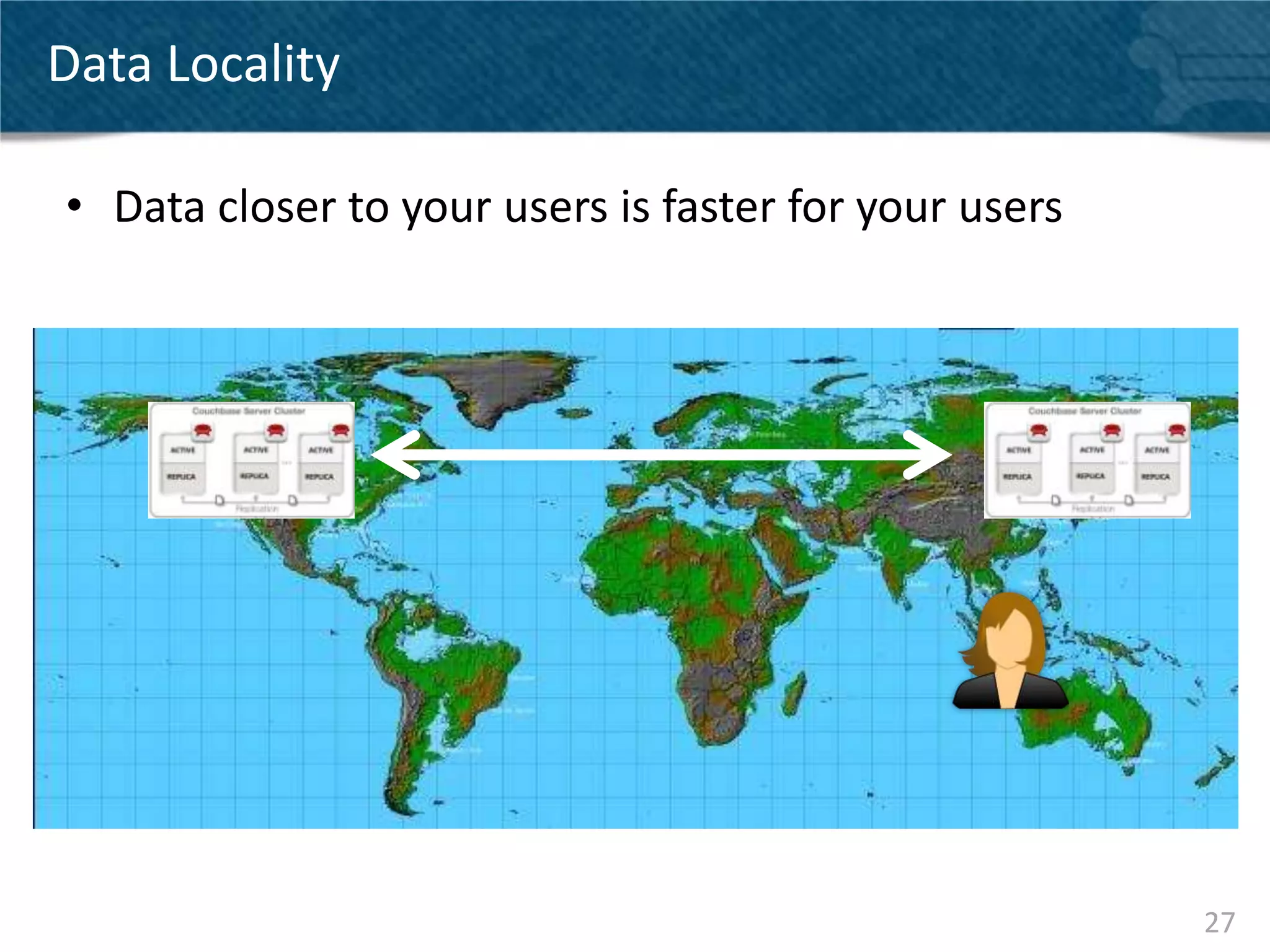
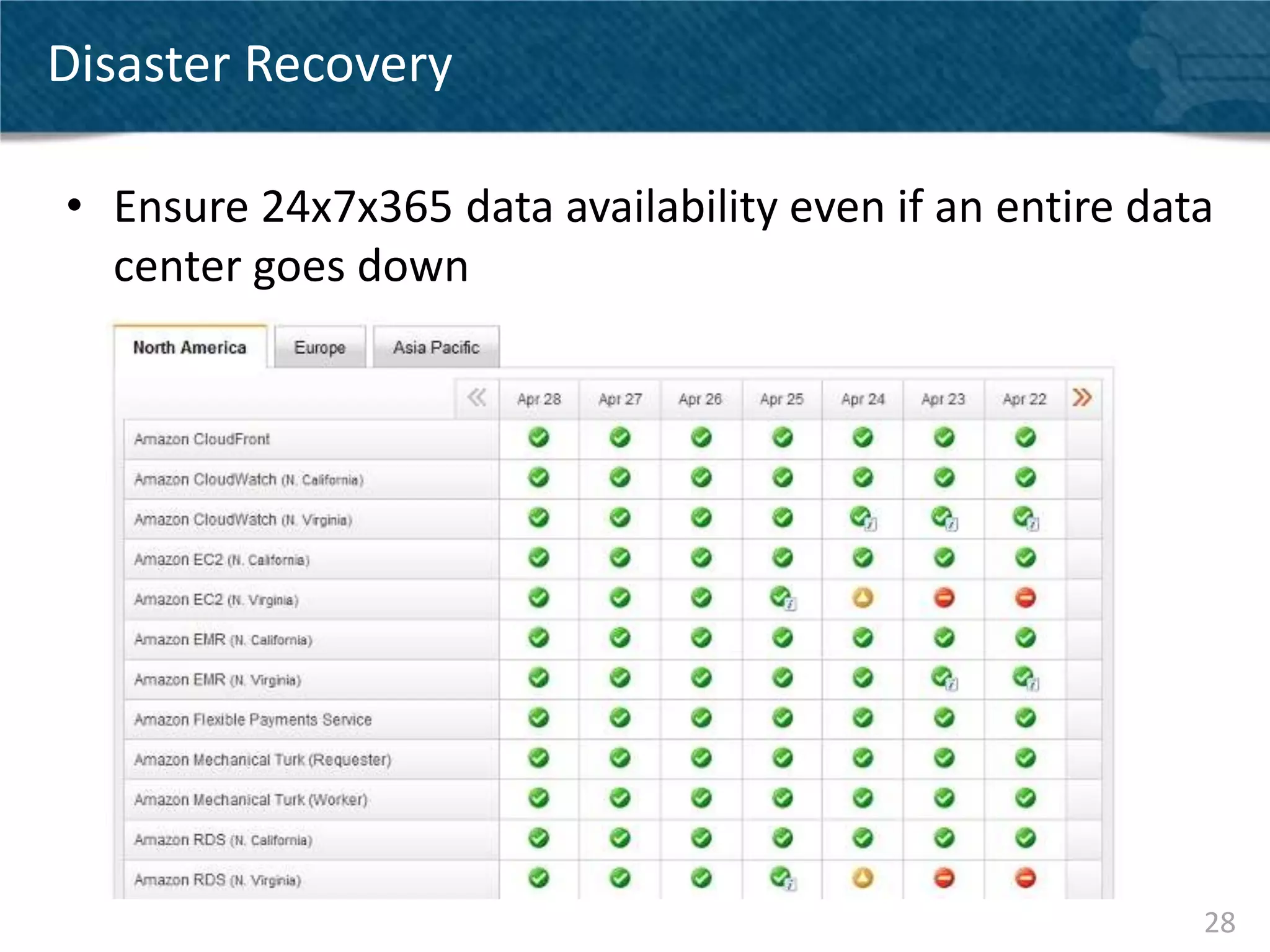
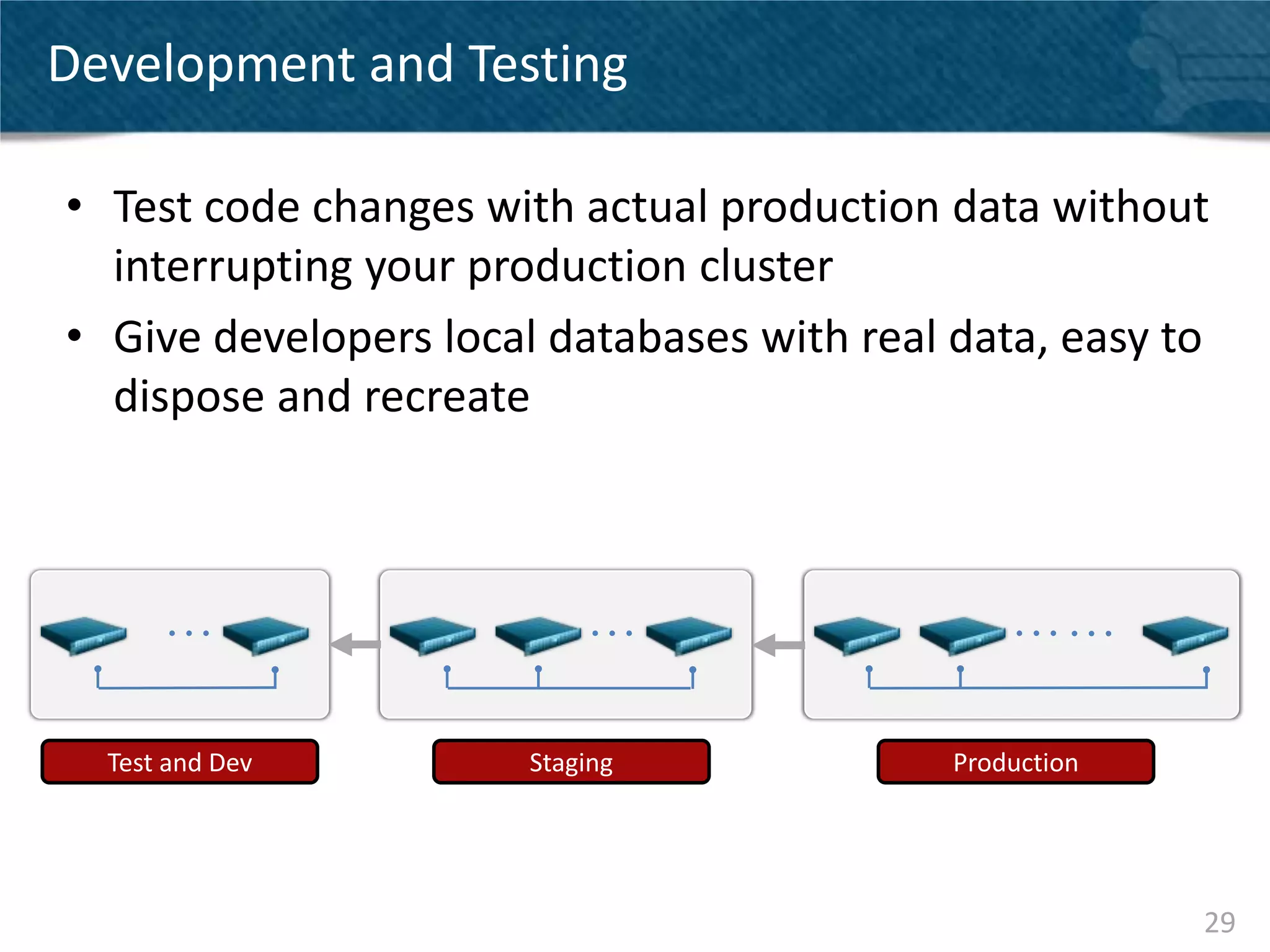
Couchbase Server 2.0 introduces Cross Data Center Replication (XDCR) which allows replication of data between Couchbase clusters across different data centers or regions. XDCR replicates data in real-time for high availability and disaster recovery. Replication is configured on a per-bucket basis and supports both unidirectional and bidirectional replication topologies. XDCR provides eventual consistency and conflict resolution when documents are modified in both clusters. Administrators can monitor ongoing replications and view detailed replication status and progress.