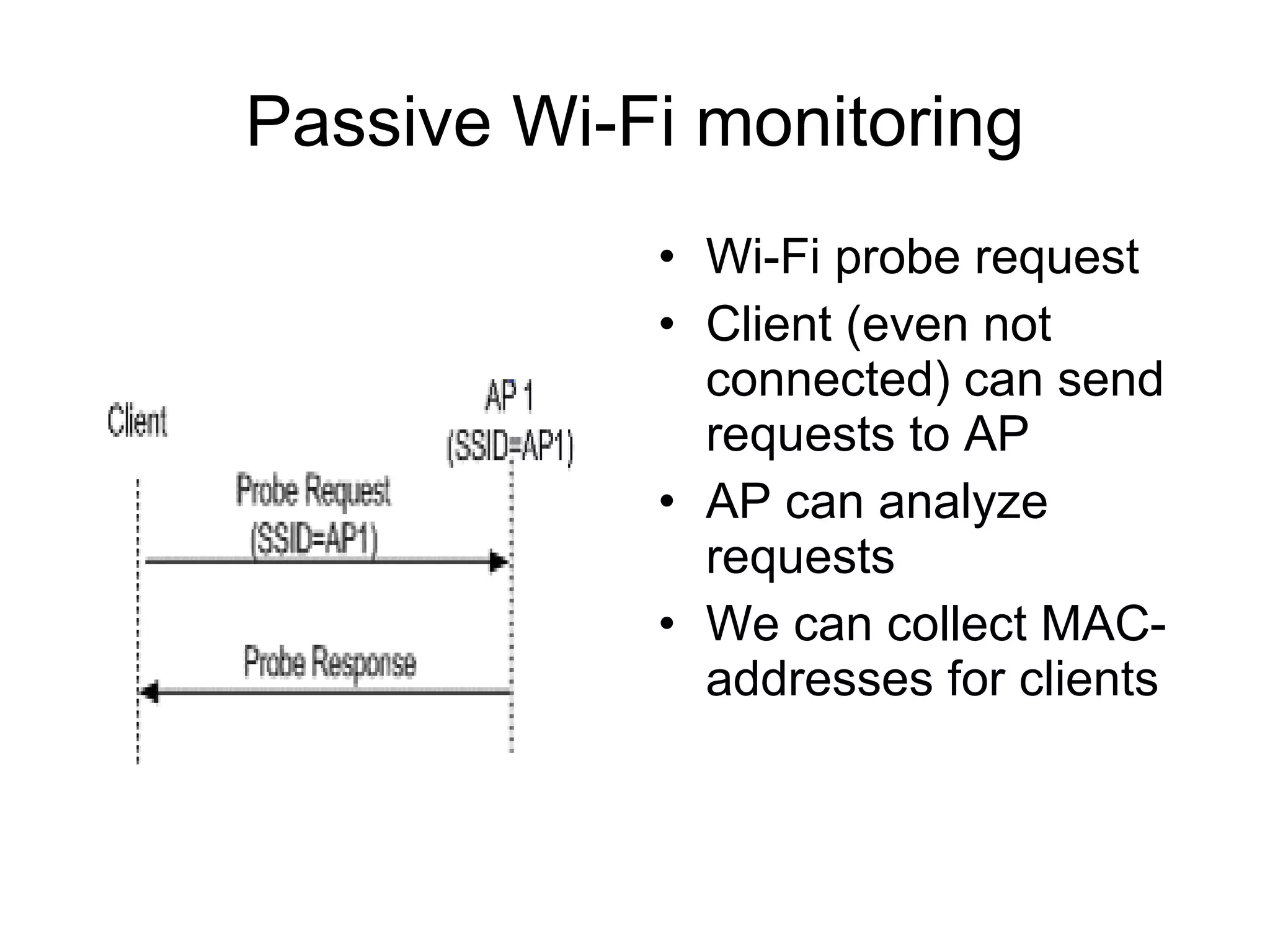
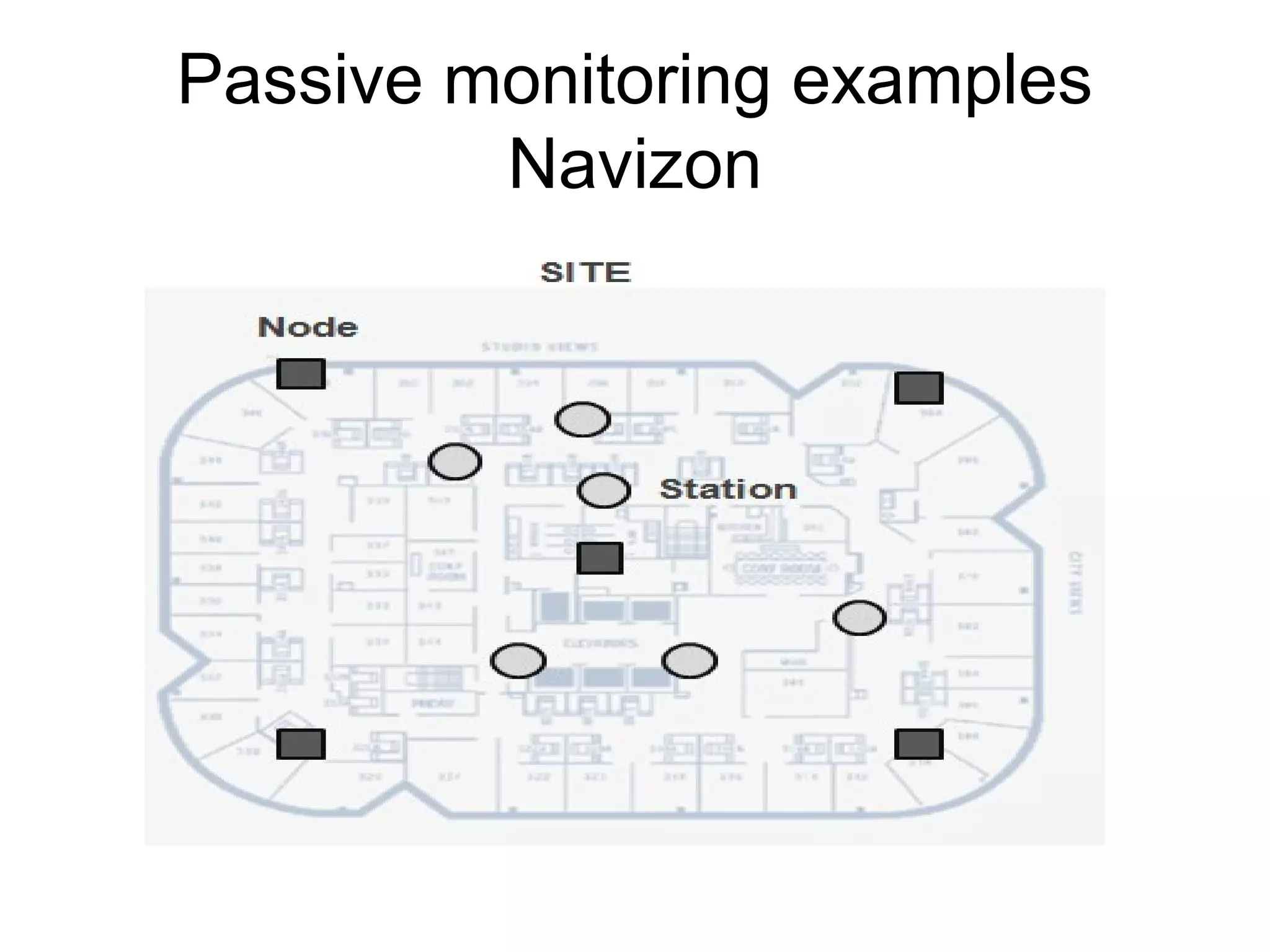
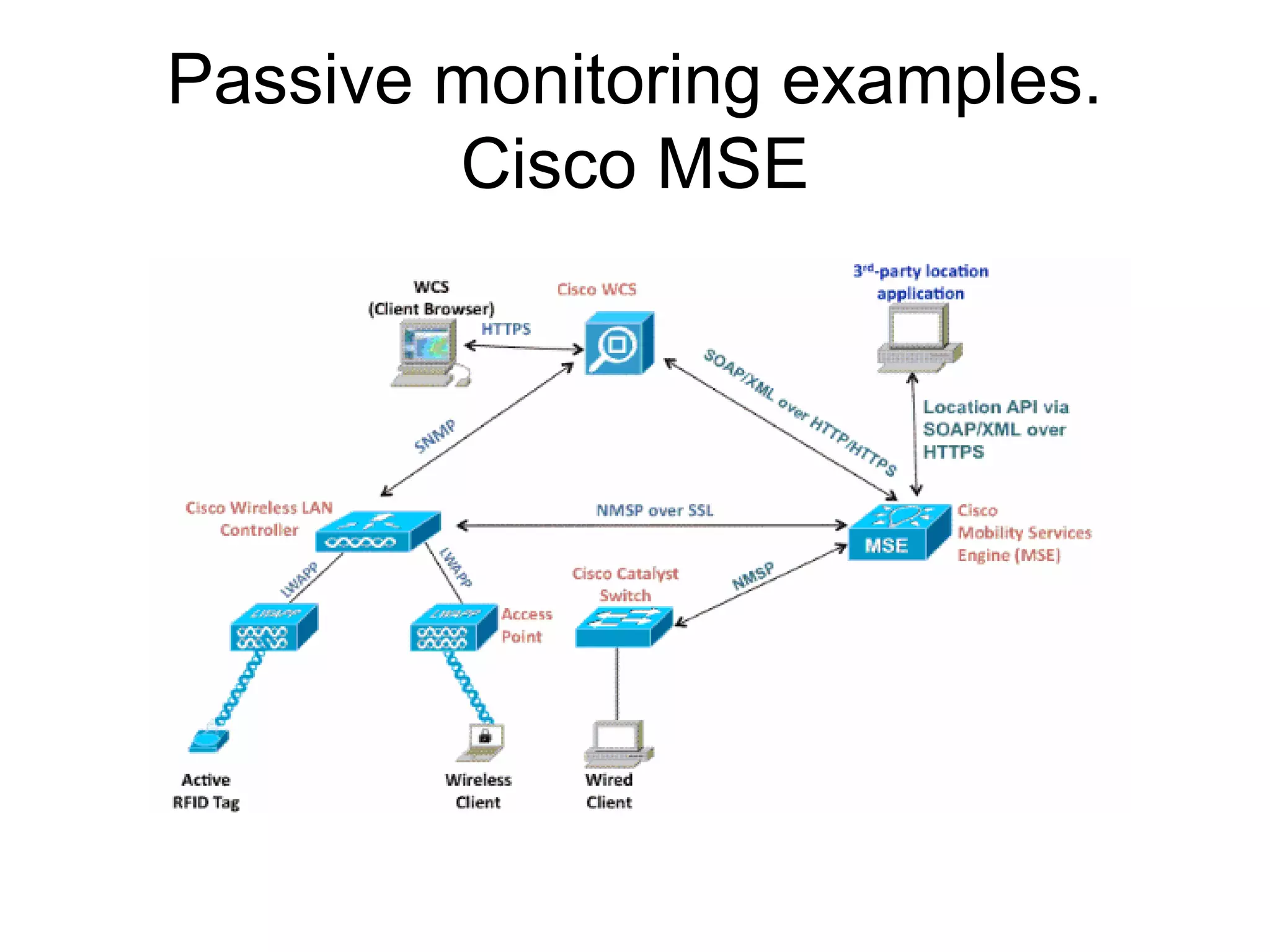
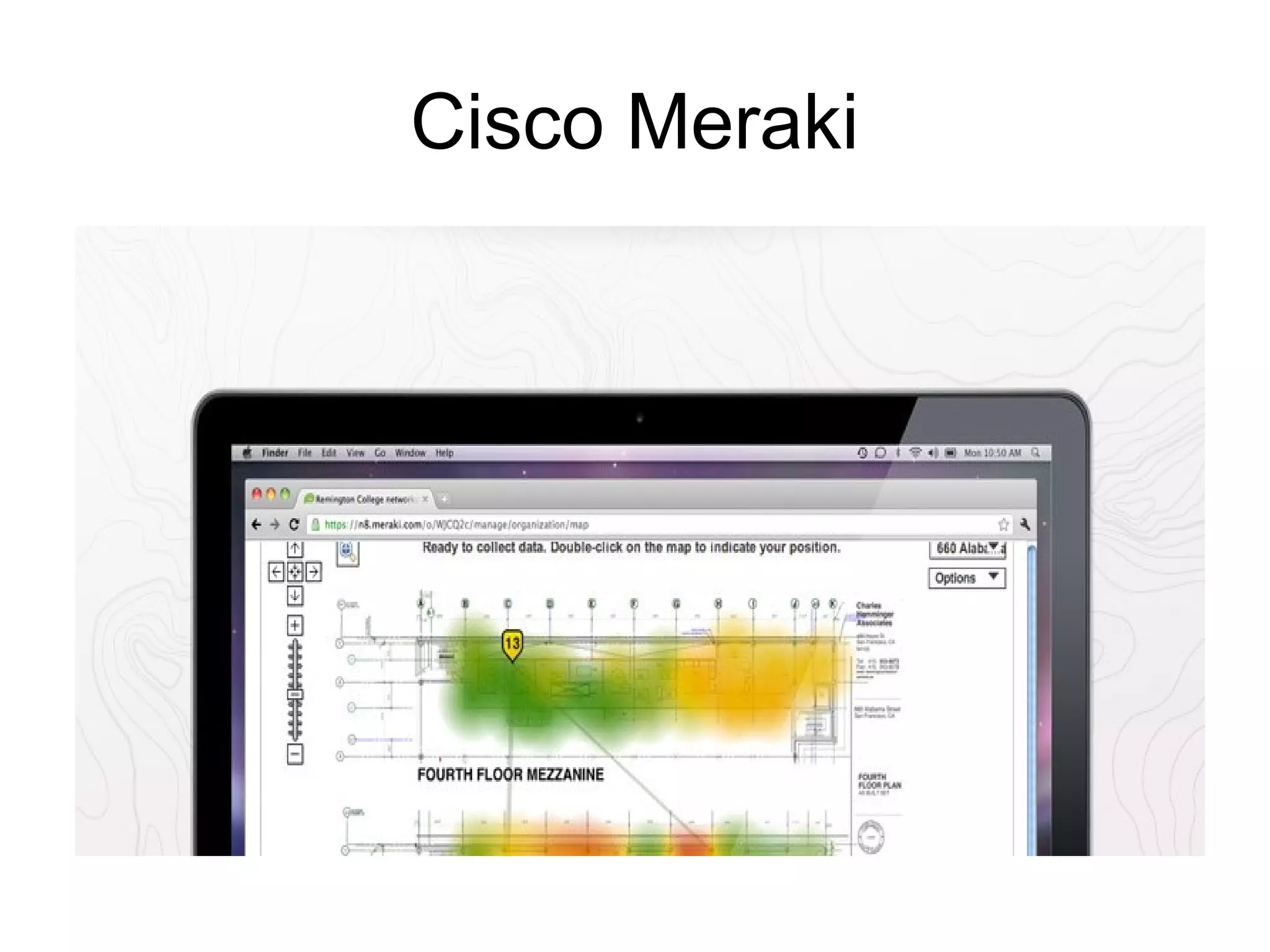
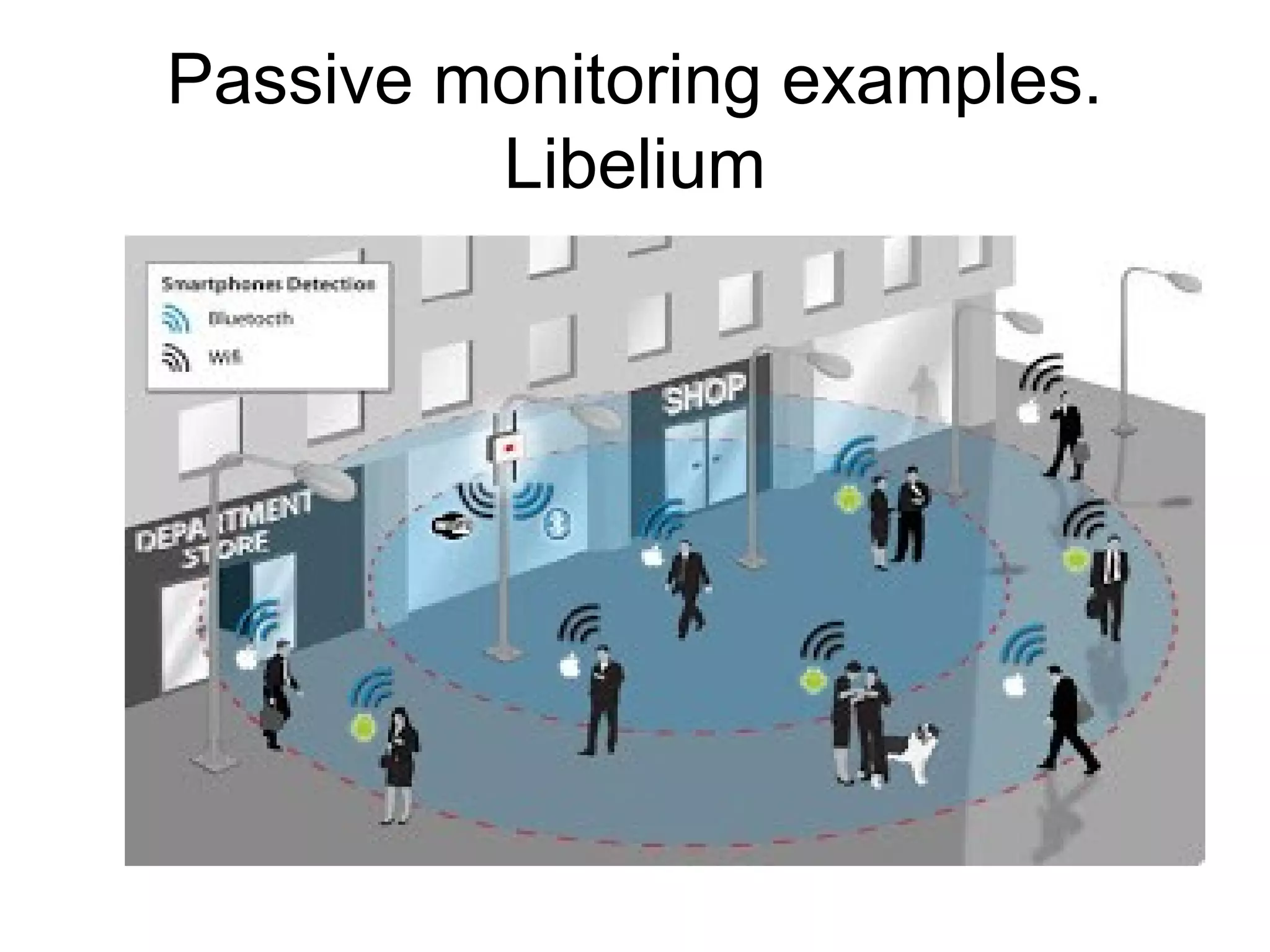
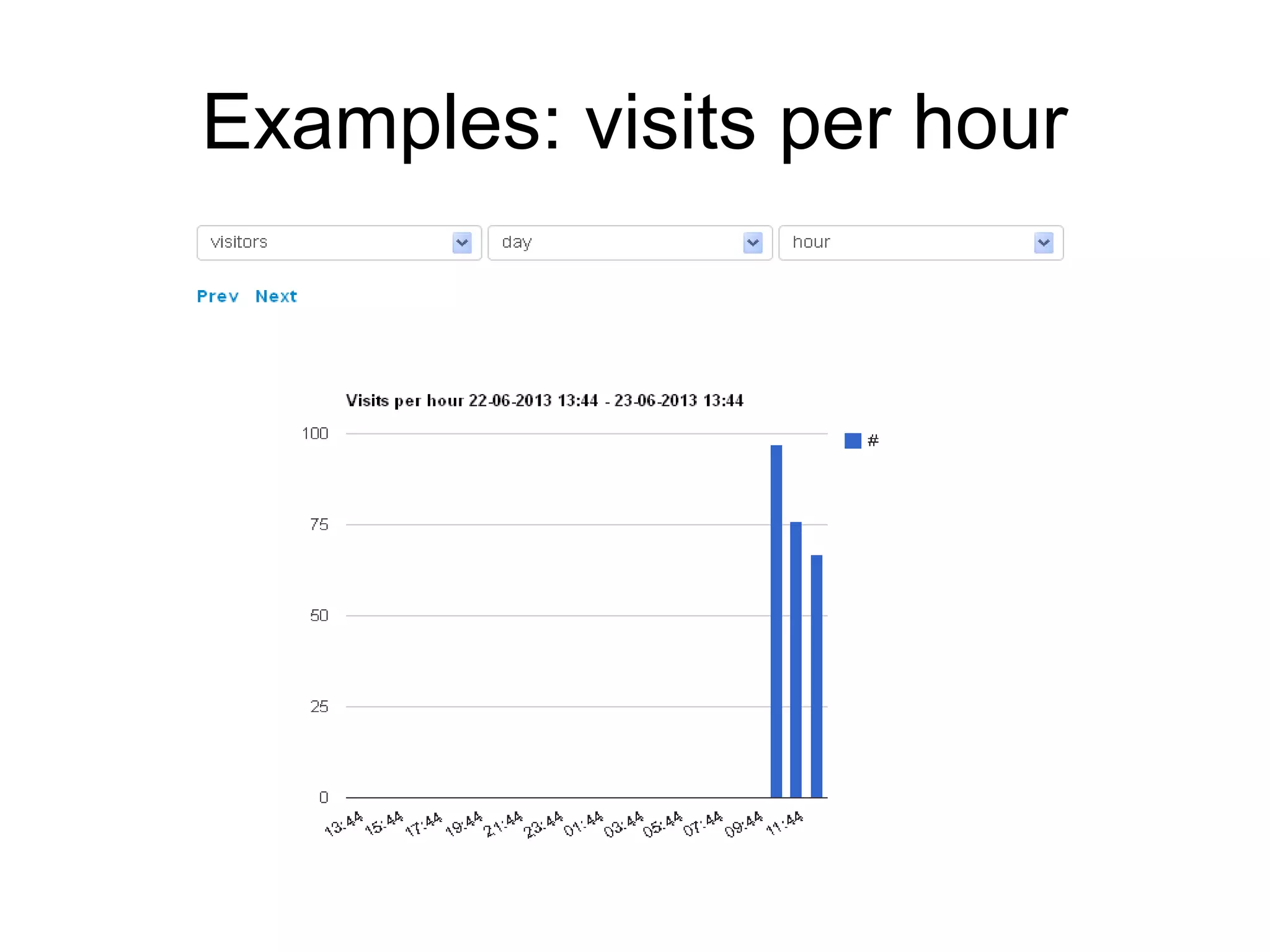
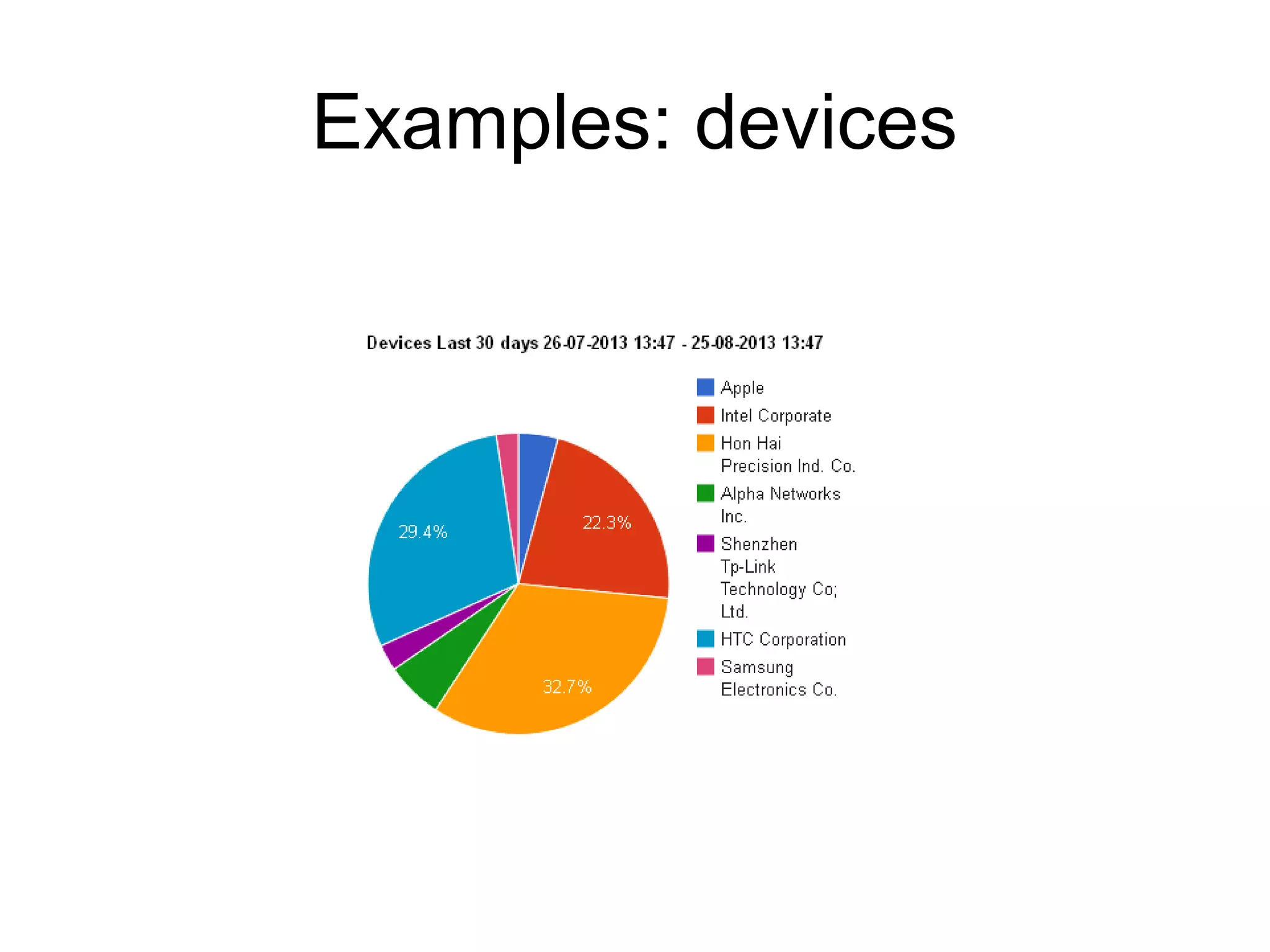
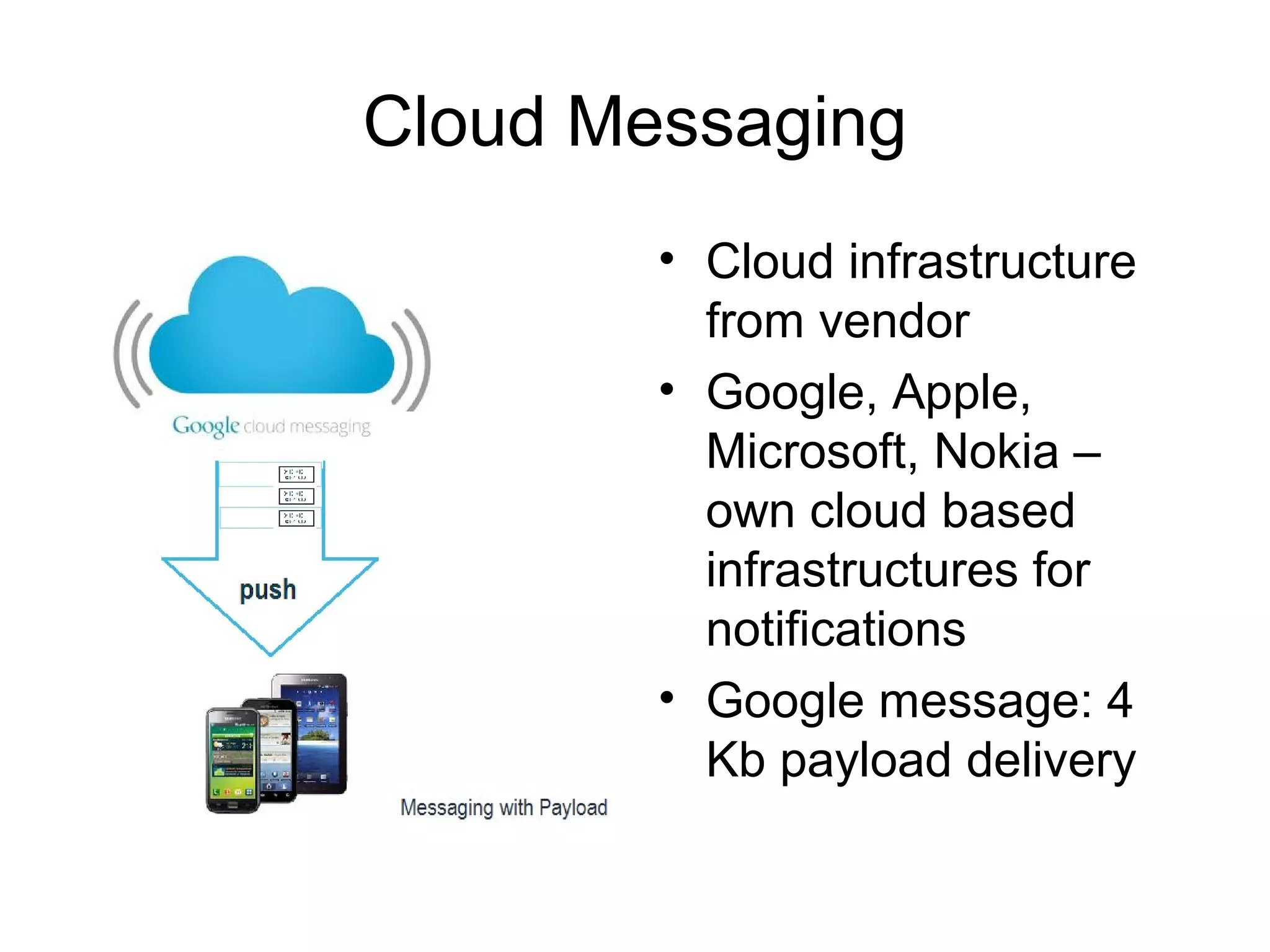
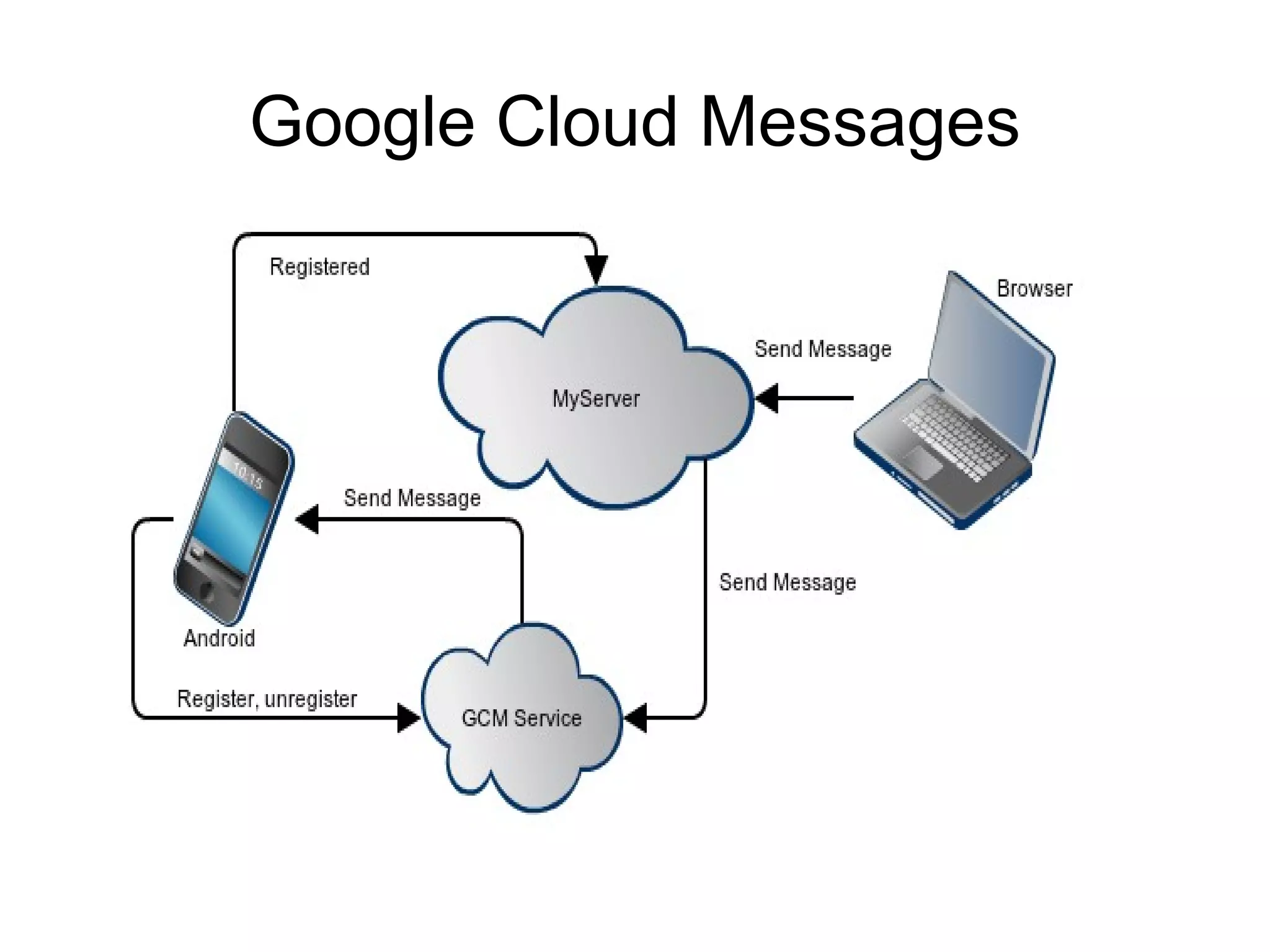
The document discusses a new model for local area messaging that combines passive Wi-Fi monitoring with cloud messaging to deliver customized notifications to nearby mobile subscribers. It highlights the advantages of anonymous monitoring and the method of detecting users based on their Wi-Fi probe requests without requiring active participation. The proposed approach aims to enhance proximity-based marketing and information delivery in smart cities, emphasizing real-time detection while protecting user privacy.