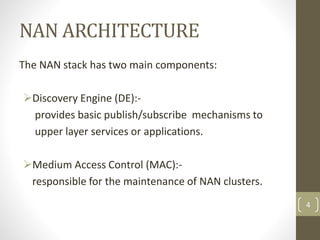
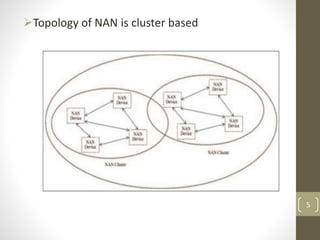
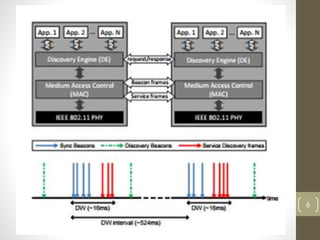
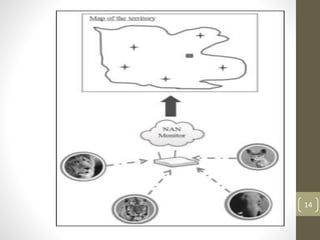
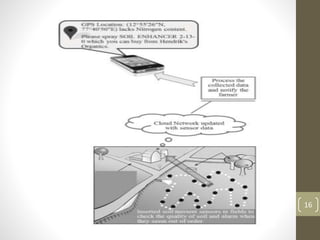
WiFi Aware, also known as Neighbor Awareness Networking (NAN), allows devices to discover each other and share information in real-time without needing to establish a connection. It uses short broadcasts so devices can learn about nearby devices without draining batteries. NAN is optimized for crowded environments and avoids dependency on GPS or cellular by continuously scanning the local area. NAN clusters devices and uses beacons to synchronize them while discovery beacons share cluster information and service frames advertise available services. Applications include tracking animals in forests using sensors on animals and coordinators in vehicles, monitoring soil conditions on farms using field sensors and a coordinator, and monitoring patient health in hospitals using wristbands that update medical staff.