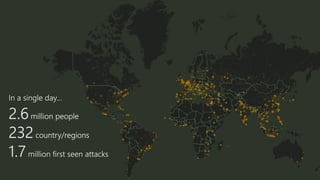
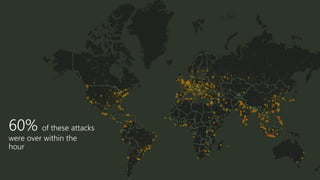
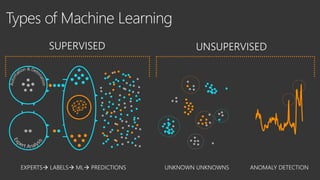
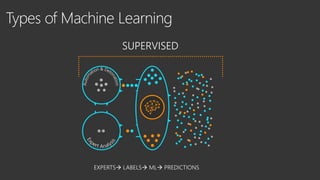
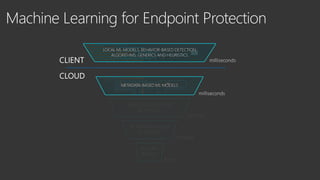
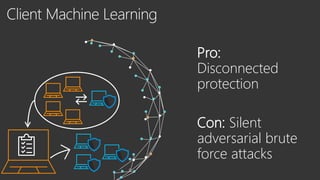
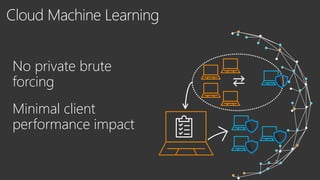
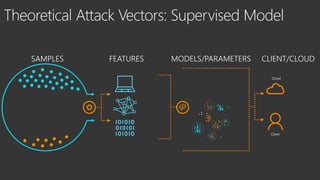
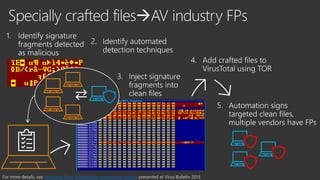
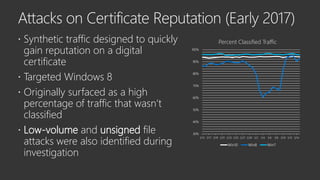
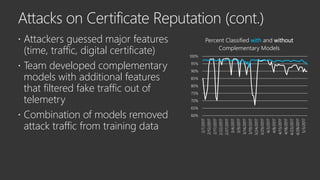
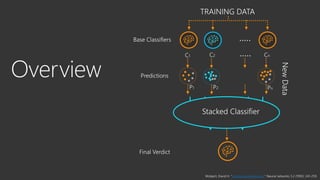
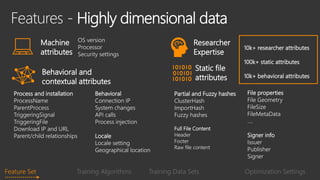
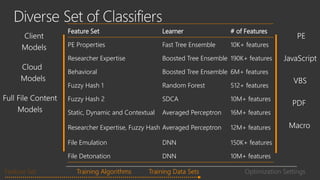
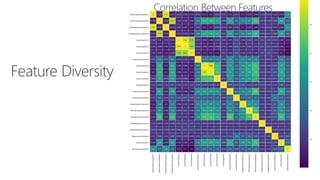
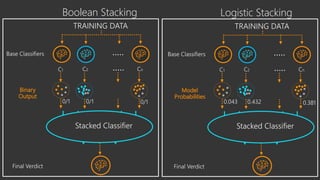
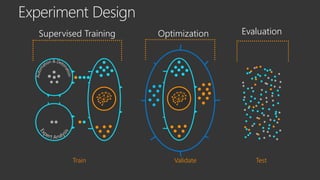
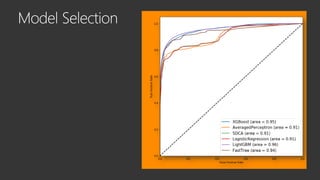
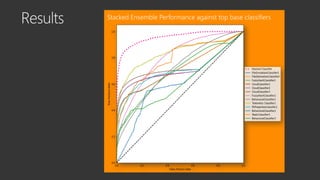
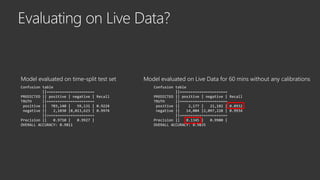
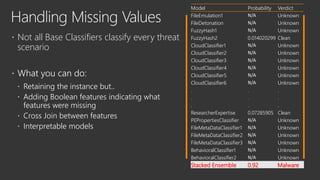
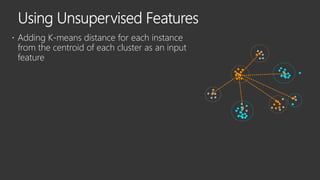
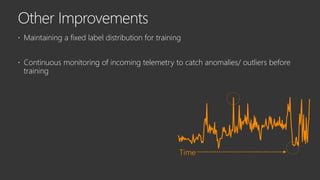
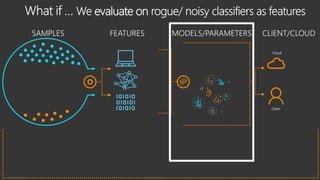
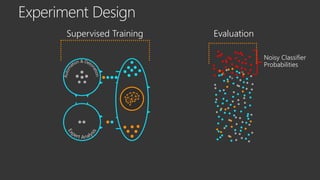
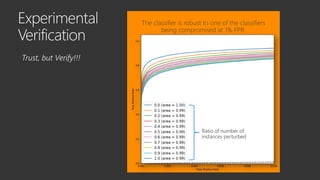
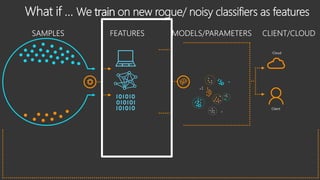
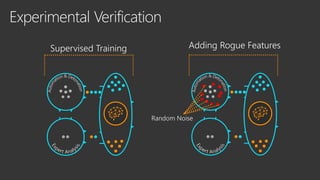
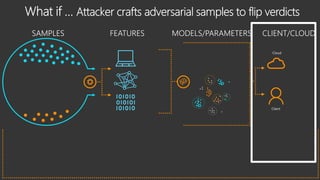
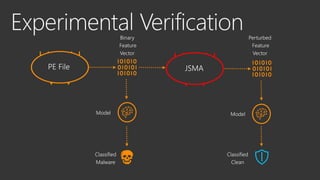
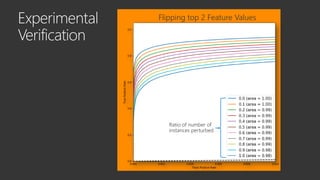
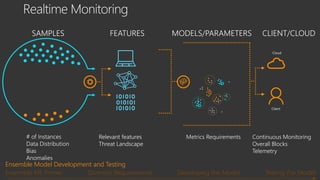
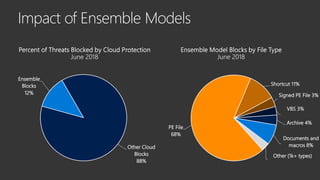
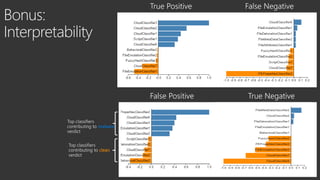
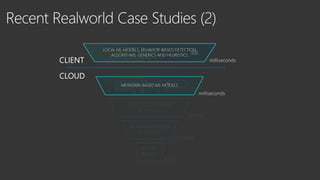
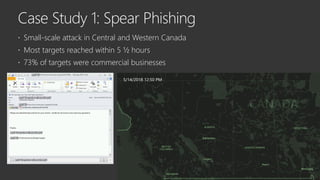
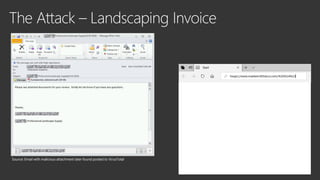
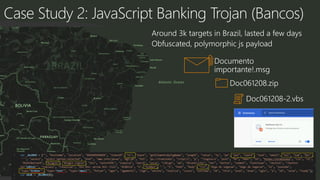
The document provides an overview of Windows Defender's endpoint protection capabilities, highlighting features such as blocking low-reputation downloads and detecting malicious activity through machine learning models. It emphasizes the development of ensemble models to counter adversarial attacks, focusing on their efficiency in classifying threats and improving predictive power. Additionally, it addresses challenges in model training and the importance of maintaining robust defenses against various attack vectors.