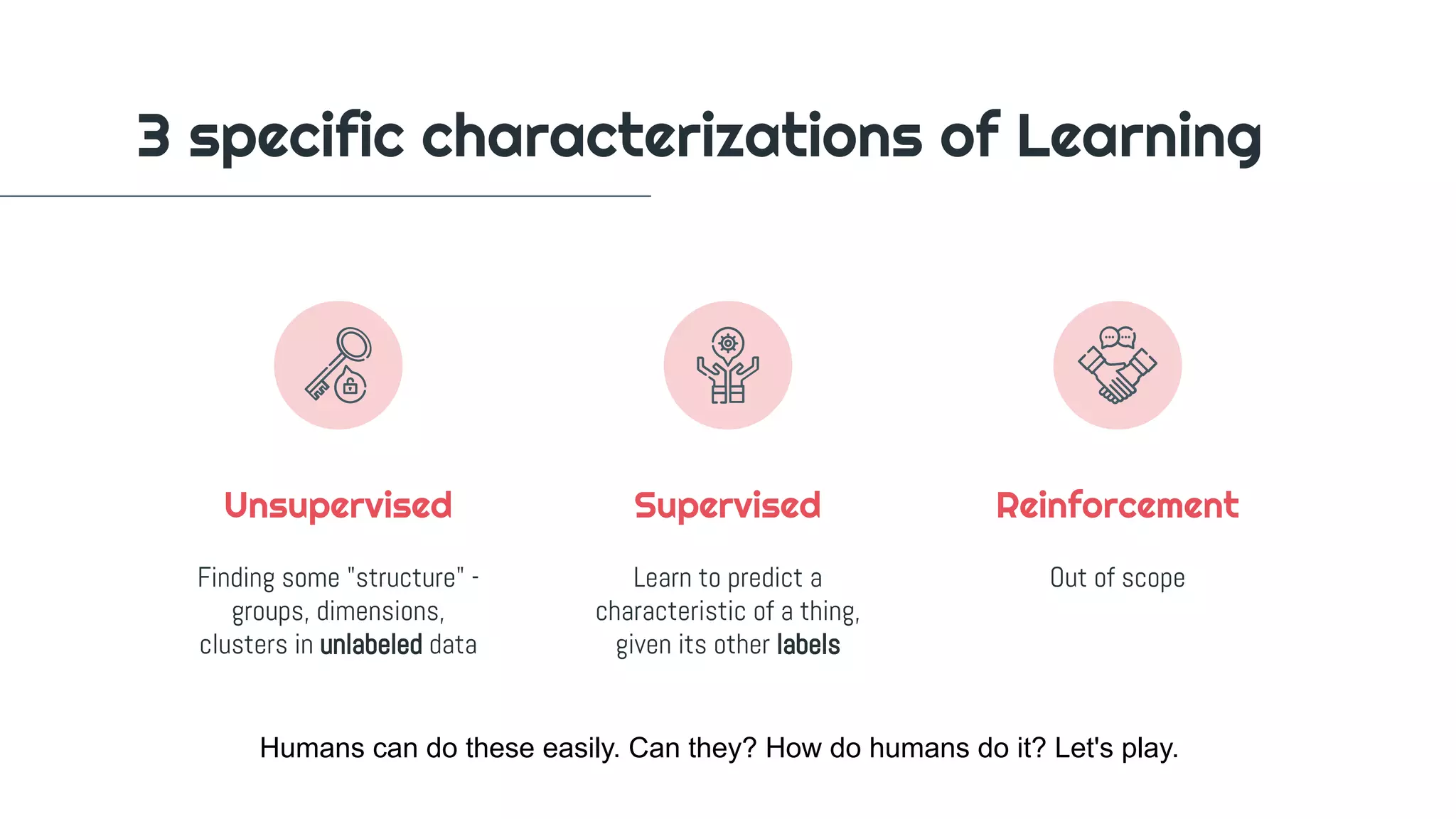
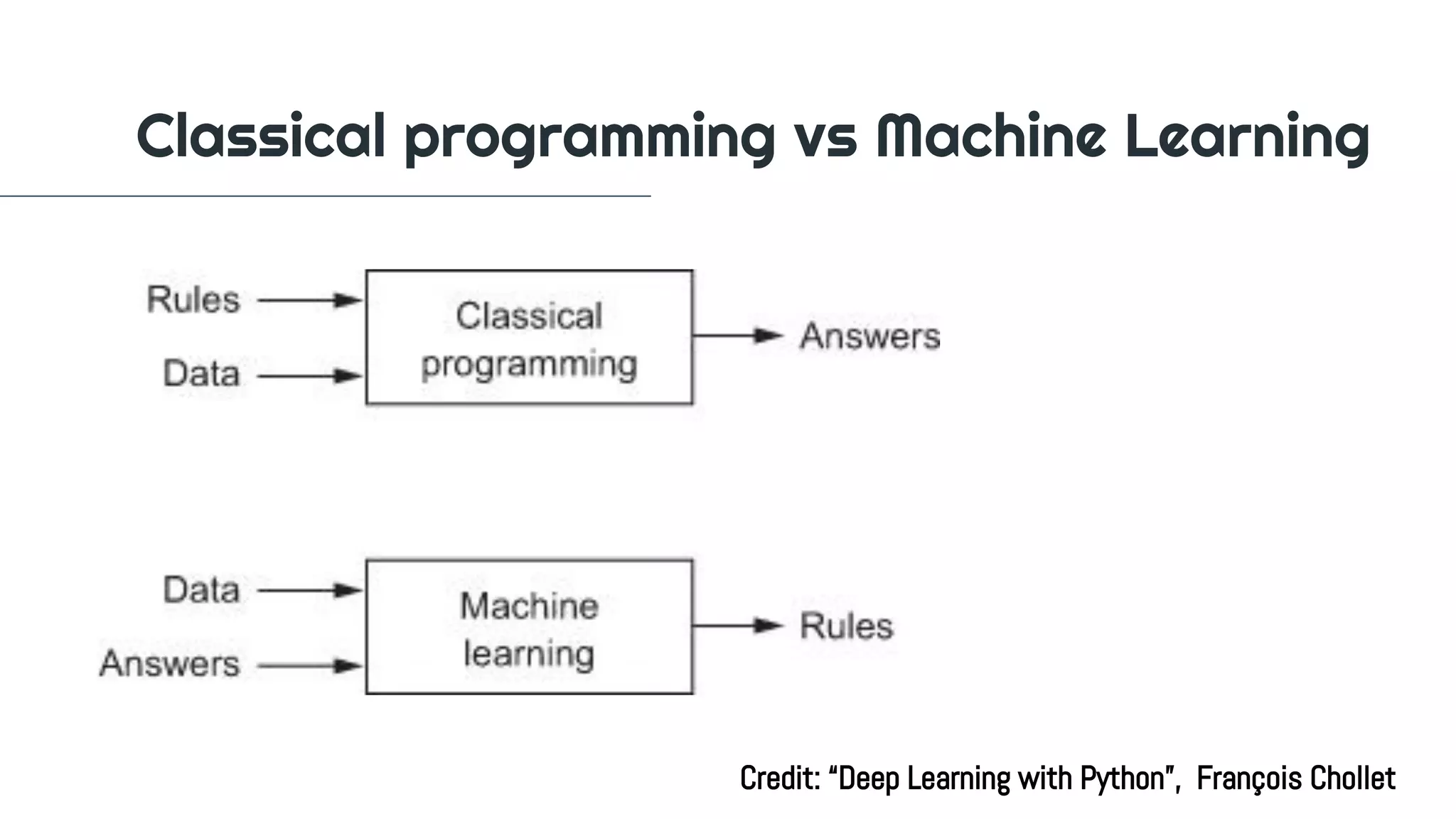
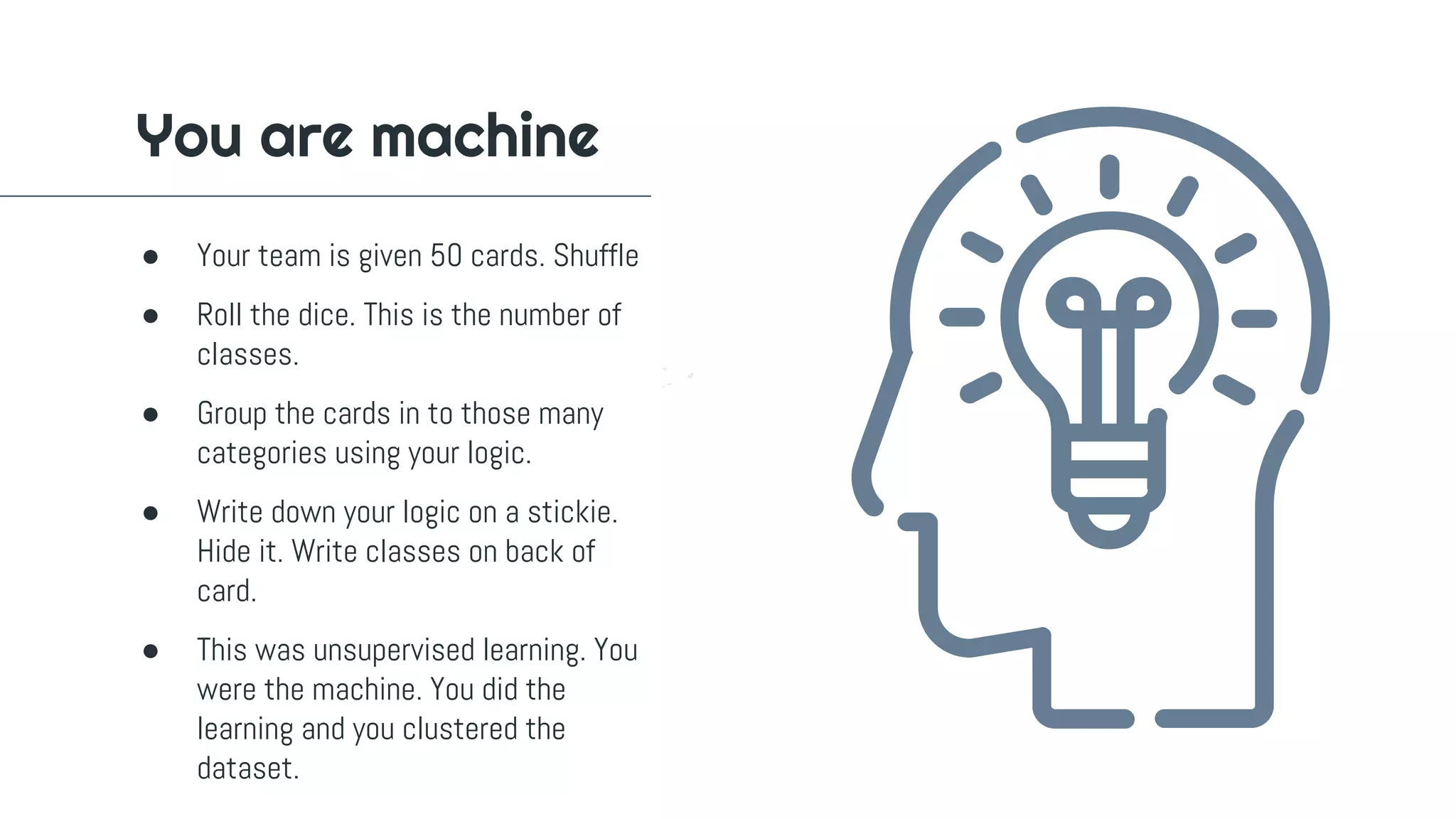
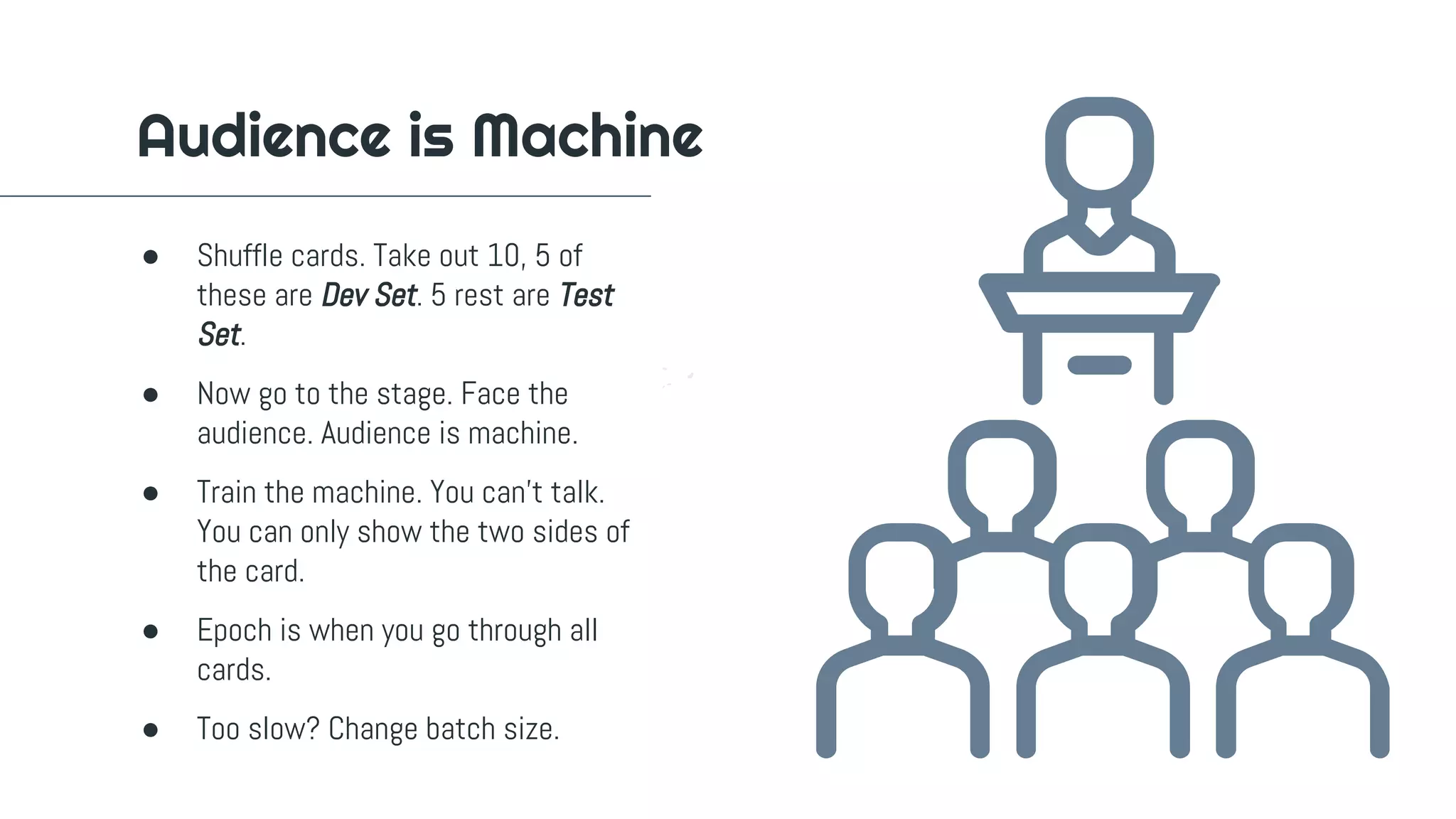
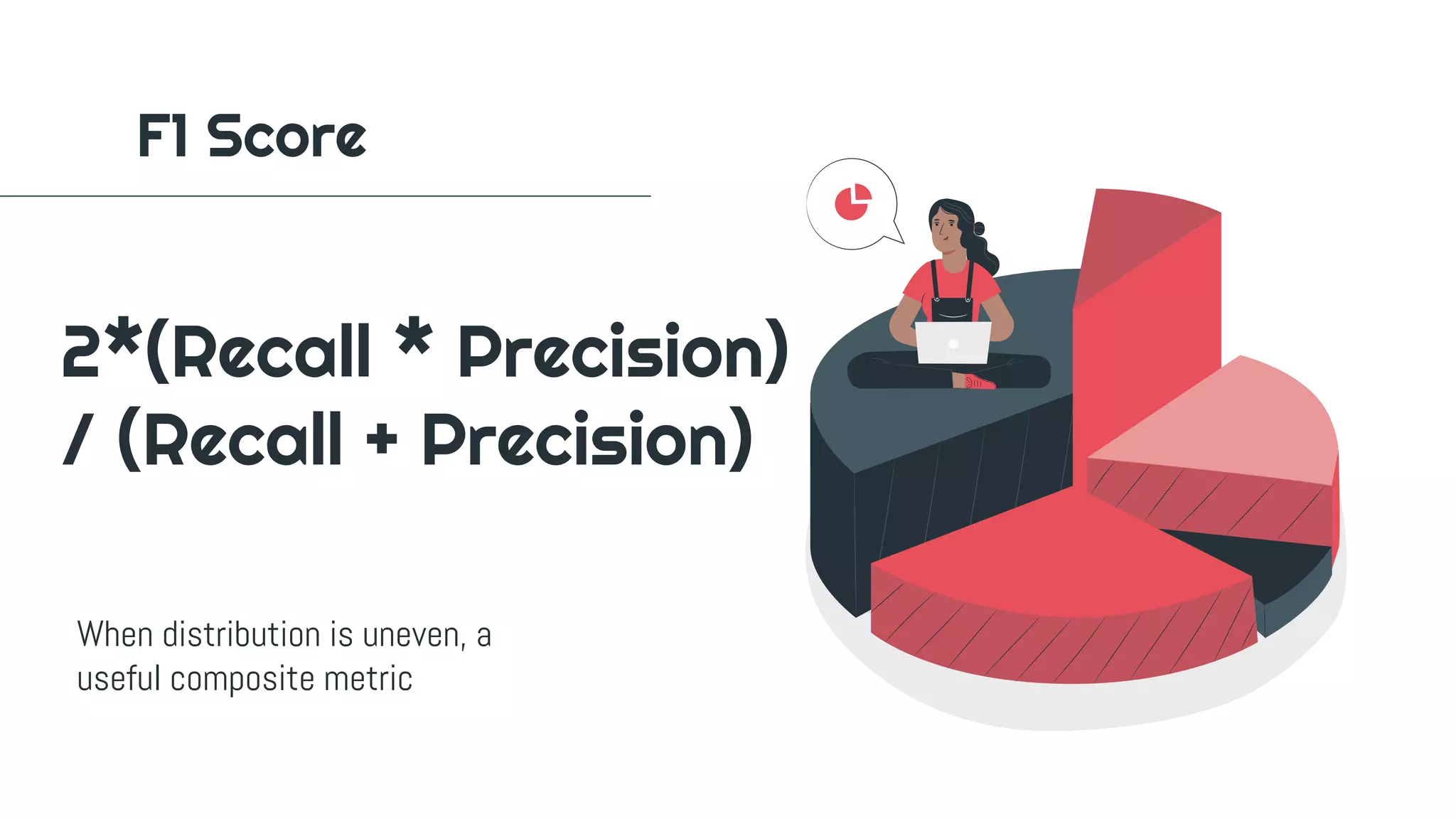
The document outlines a workshop on machine learning, covering definitions and relationships of key concepts like AI, ML, and deep learning. It details the machine learning workflow, goals for practical application, and various learning methodologies including supervised and unsupervised learning. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of evaluating model performance and provides instructions for setting up a Python environment for data science experiments.



![—John McCarthy, coined term ‘AI’[1]
“It is the science and engineering of
making intelligent machines, especially
intelligent computer programs. It is
related to the similar task of using
computers to understand human
intelligence, but AI does not have to
confine itself to methods that are
biologically observable.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningworkshoptsec2020-201126133807/75/Machine-Learning-Workshop-TSEC-2020-9-2048.jpg)
![—Merriam Webster Dictionary [2]
“The capability of a
machine to imitate
intelligent human
behavior.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningworkshoptsec2020-201126133807/75/Machine-Learning-Workshop-TSEC-2020-10-2048.jpg)