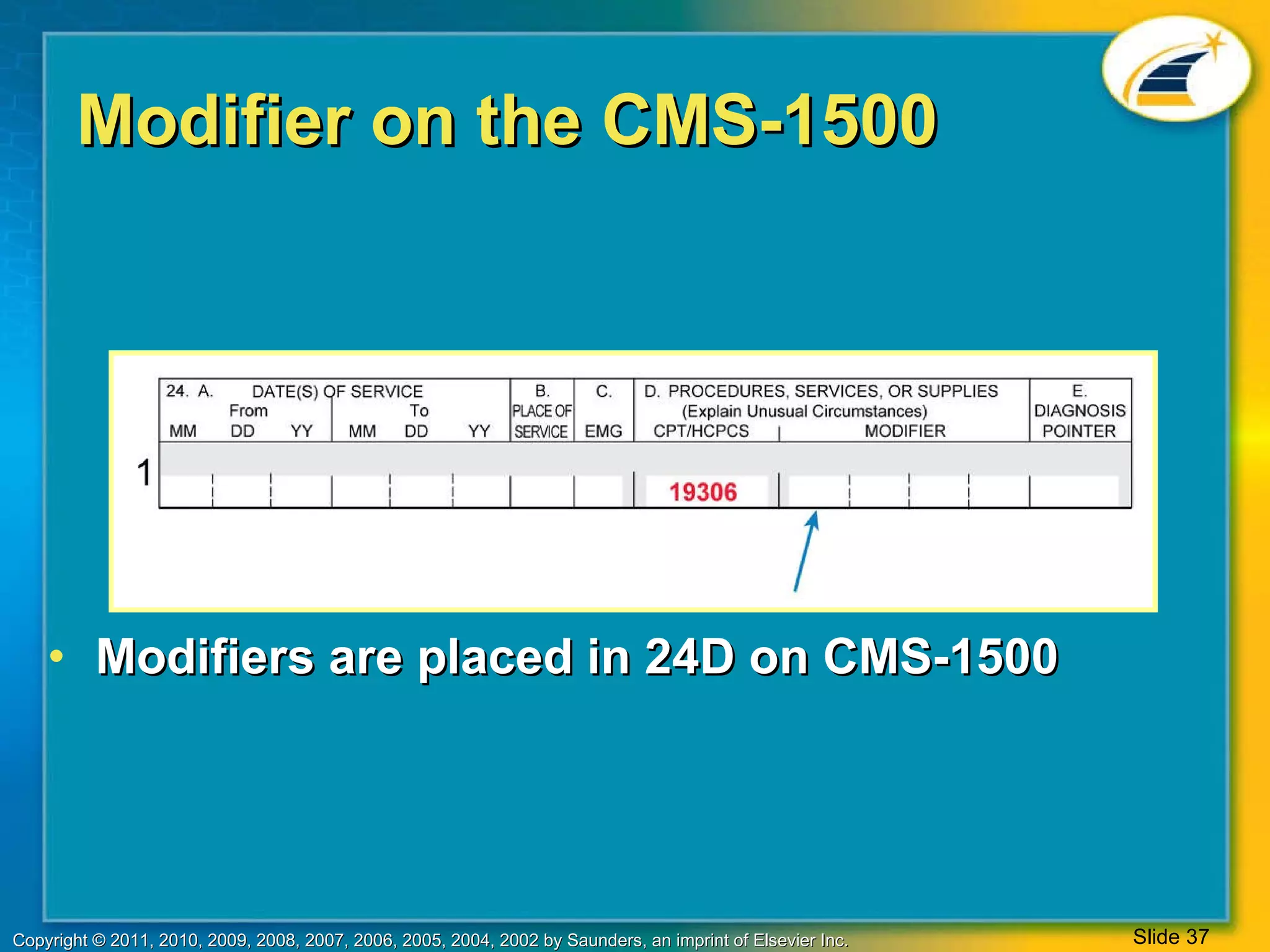
The document provides an overview of medical coding systems used in the United States, including the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). It describes the different levels of service codes, types of CPT codes, format and organization of the CPT manual, and use of modifiers. It also summarizes HCPCS and its use of national codes to cover a wide variety of medical services, providers, and supplies.