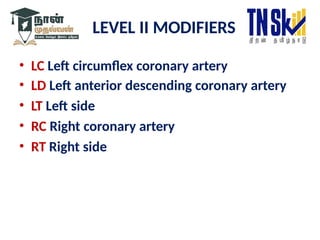
The document provides an overview of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), including its categories and coding structure, maintained by the American Medical Association. It details the different sections of CPT codes, including Evaluation & Management, Anesthesia, Surgery, and more, and explains how to select appropriate procedure codes and the use of modifiers for reimbursement. Additionally, it offers examples of codes and guidelines for coding practices within the CPT framework.