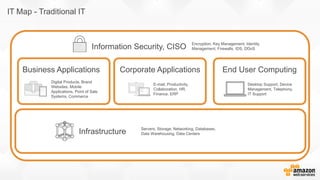
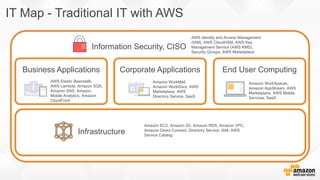
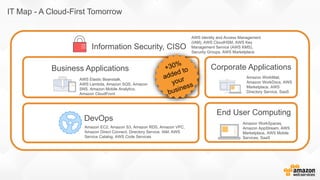
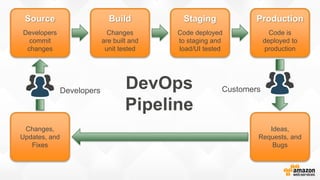
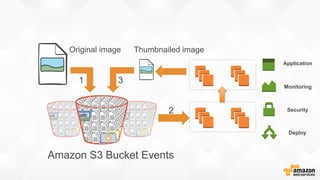
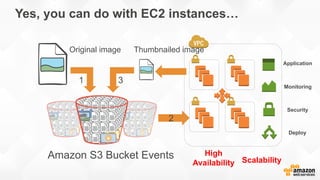
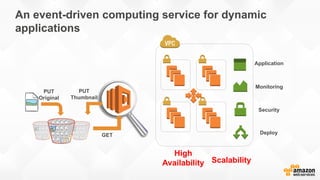
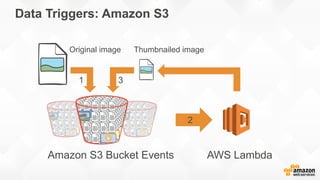
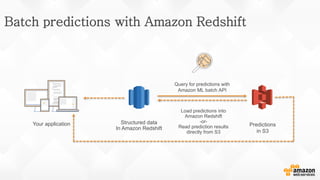
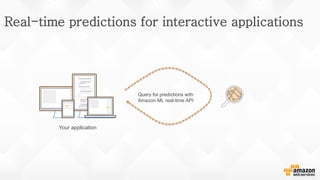
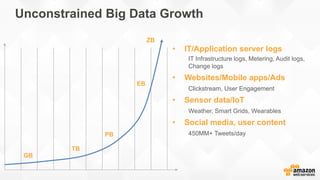
The document discusses a paradigm shift towards cloud-first solutions, emphasizing the adoption of AWS services for improved resource allocation and customer focus. It outlines the integration of various AWS tools such as EC2, Lambda, and Aurora to enhance scalability, availability, and application management. The content highlights the challenges of traditional IT setups and how containerization, microservices, and machine learning can optimize businesses' operational efficiency.


































![Simulate failures using SQL
• To cause the failure of a component at the database node:
ALTER SYSTEM CRASH [{INSTANCE | DISPATCHER | NODE}]
• To simulate the failure of disks:
ALTER SYSTEM SIMULATE percent_failure DISK failure_type IN
[DISK index | NODE index] FOR INTERVAL interval
• To simulate the failure of networking:
ALTER SYSTEM SIMULATE percent_failure NETWORK failure_type
[TO {ALL | read_replica | availability_zone}] FOR INTERVAL interval](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-150427052001-conversion-gate01/85/AWS-Summit-Seoul-2015-AWS-Aurora-Lambda-EFS-Machine-Learning-ECS-58-320.jpg)