Embed presentation
Download to read offline



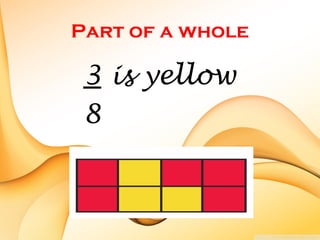
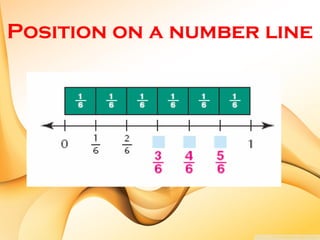

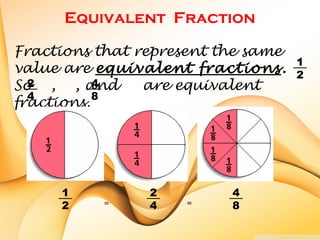
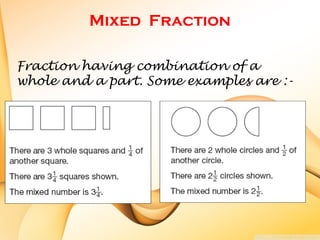


The document defines key terms related to fractions, including that a fraction represents equal parts of a whole with a numerator and denominator. It explains that the numerator is the top number naming the shaded or unshaded part, while the denominator names the total pieces of the whole. Examples of proper fractions, equivalent fractions, mixed fractions, and how fractions are represented on a number line are also provided.









