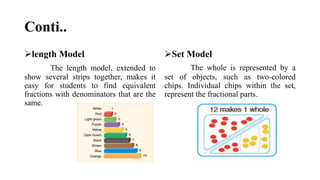
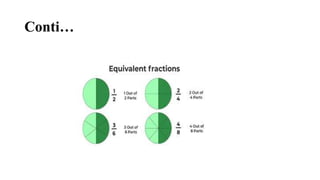
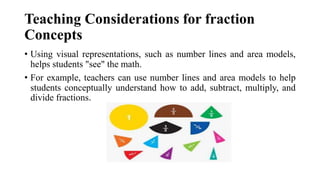
The document outlines the process of developing fraction concepts in elementary mathematics education, emphasizing the meaning, modeling, and operational understanding of fractions. It discusses various models, such as area, length, and set models, and highlights the importance of equivalent fractions and effective communication using fraction language. Furthermore, it stresses the role of educators in facilitating the understanding of fractions through visual aids and instructional strategies, aiming to prepare students for more advanced mathematics.