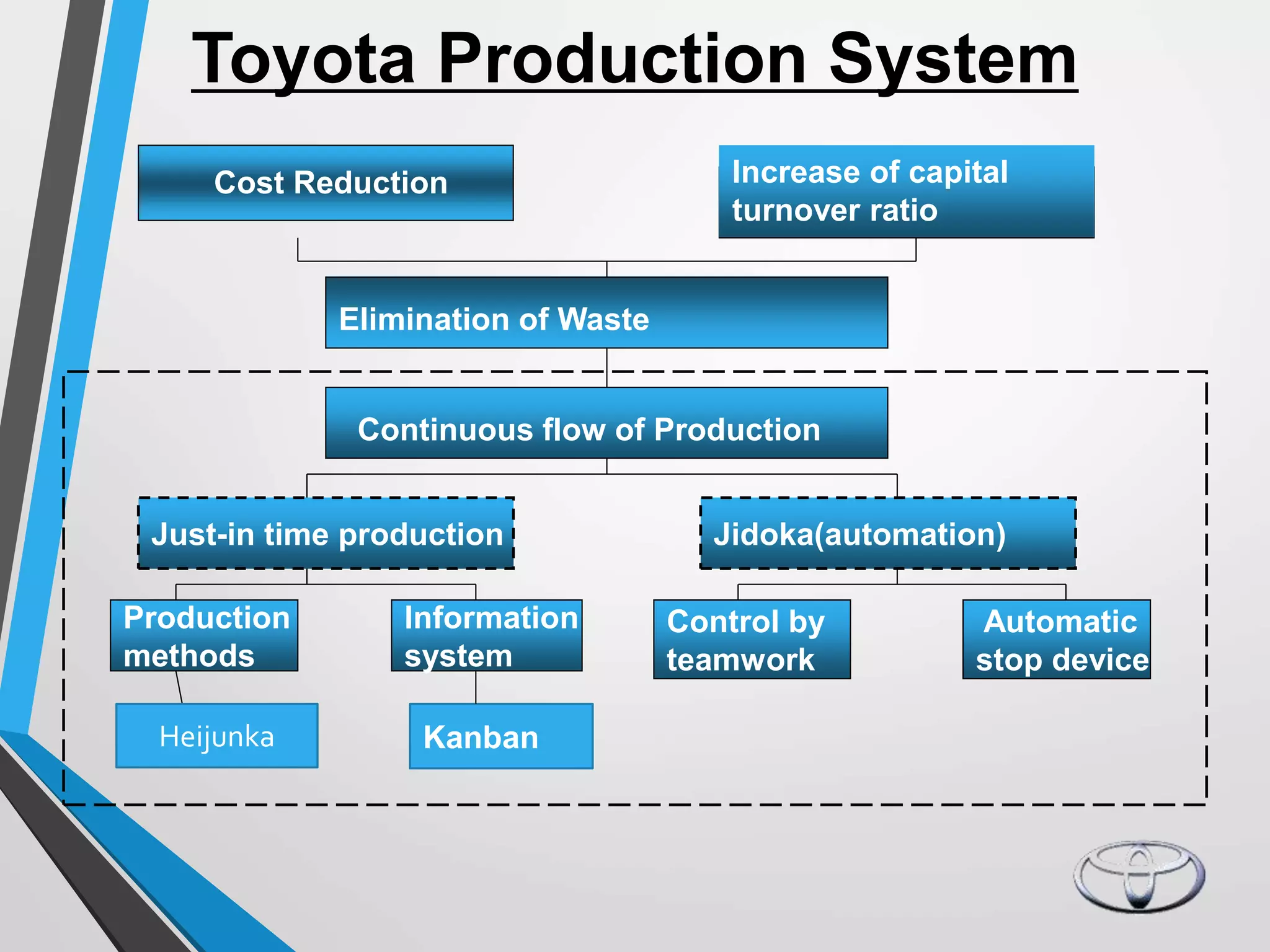
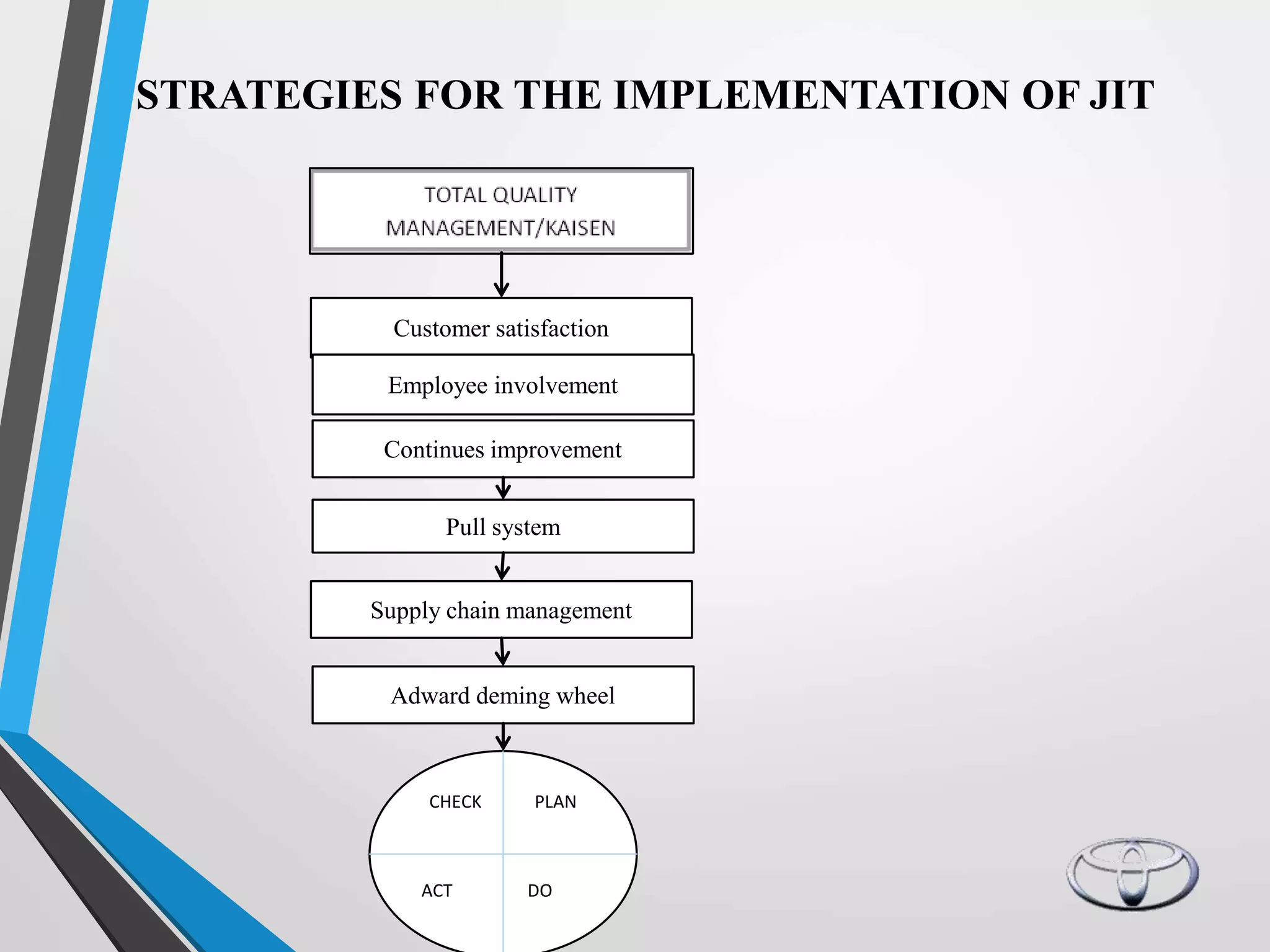
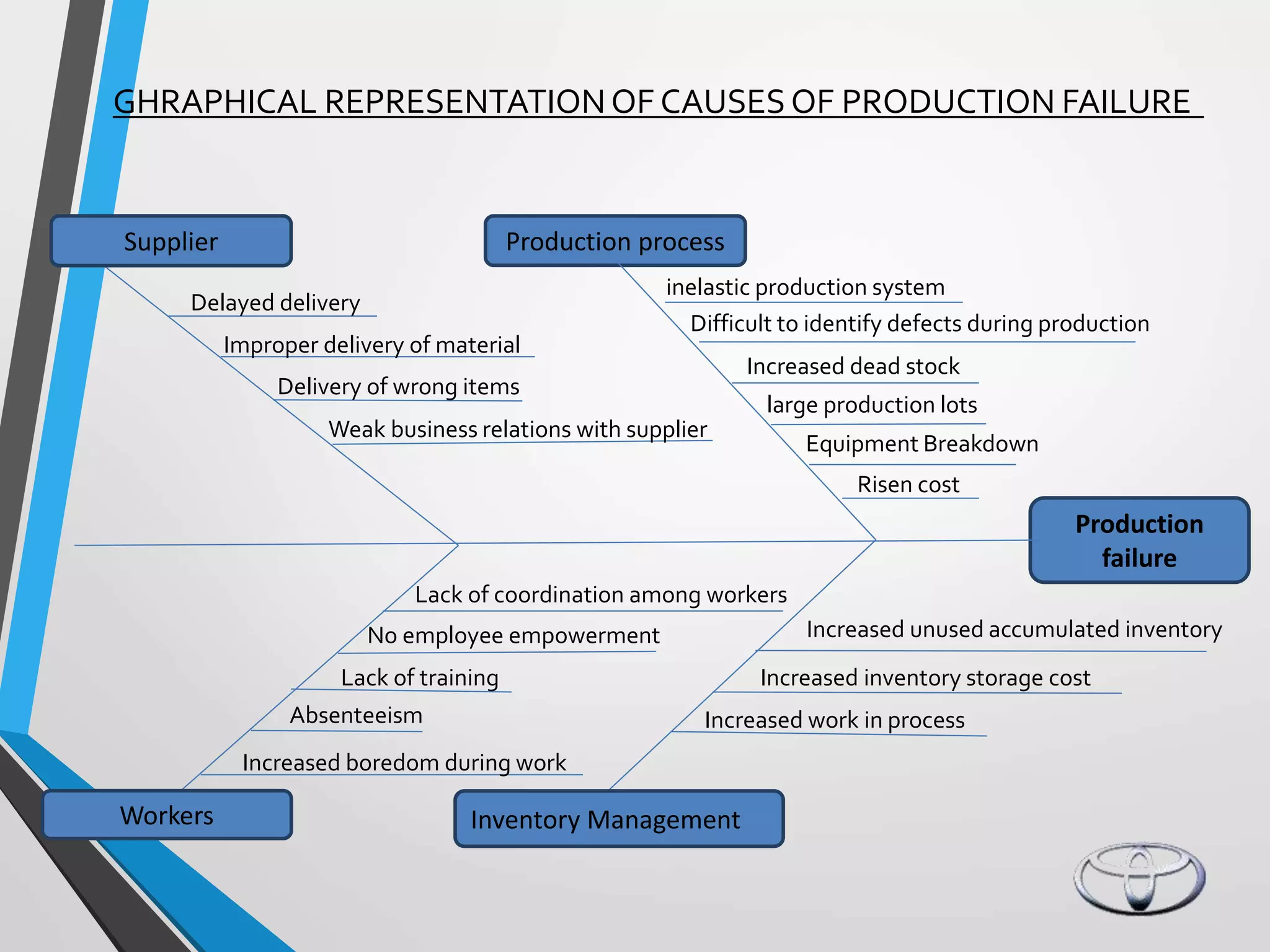
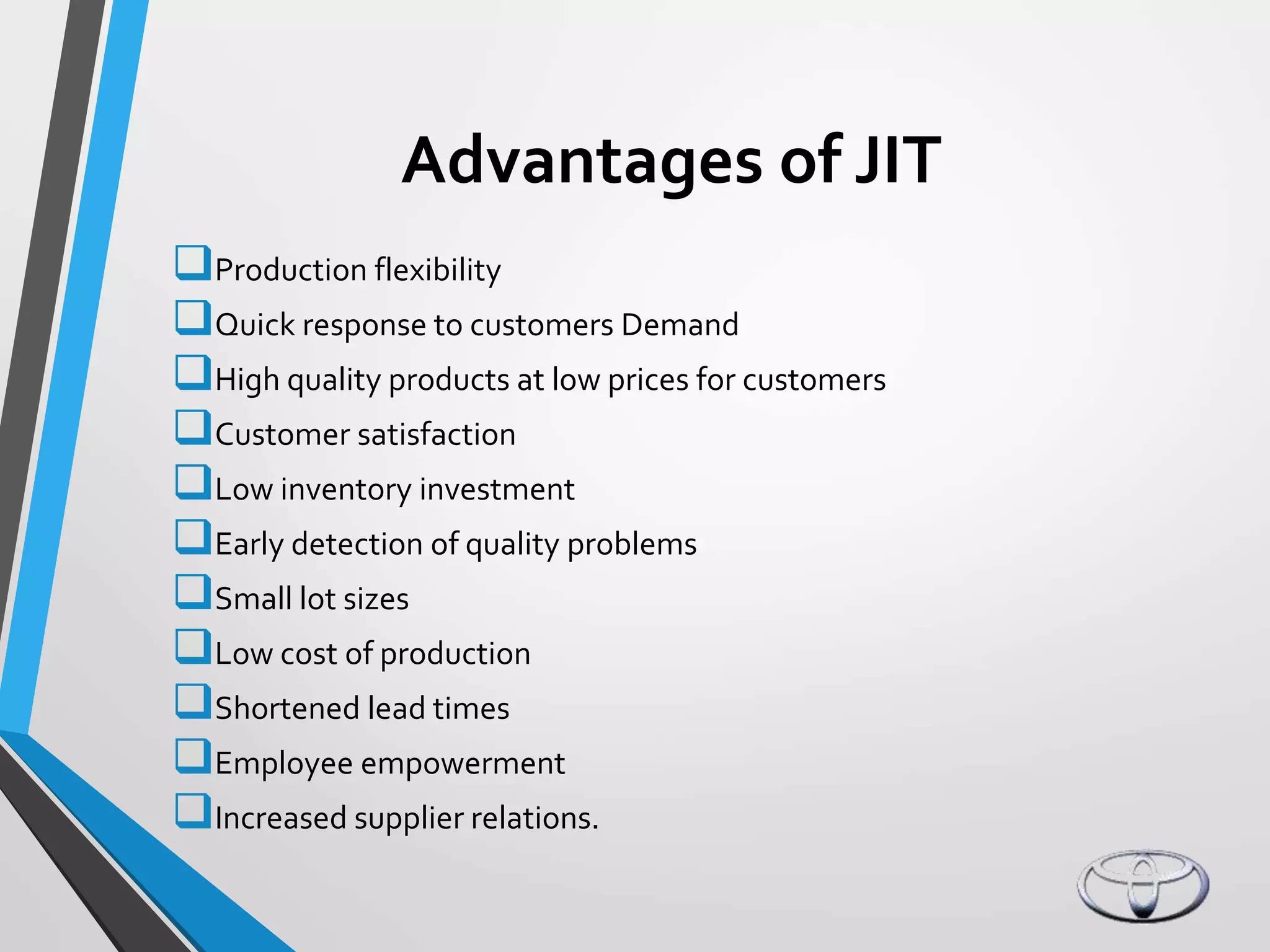
Toyota implemented the Just-In-Time (JIT) production system to eliminate waste and reduce costs. JIT focuses on producing only what is needed when it is needed through continuous improvement efforts. Toyota pioneered JIT, which relies on small lot sizes, pull production, and close supplier relationships to minimize inventory and expose problems. Key aspects of Toyota's legendary production system include kanban cards to regulate production, heijunka level scheduling, and employee participation. JIT helped Toyota become the world's largest automaker through low costs, high quality, and customer satisfaction.