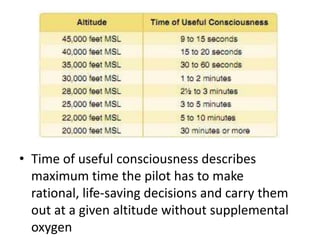
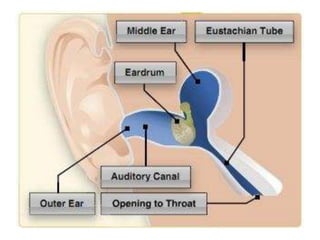
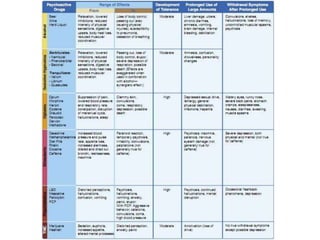
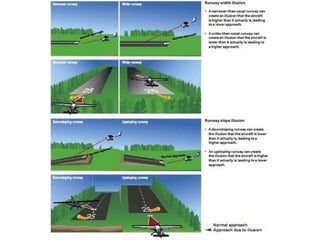
A valid medical certificate is required to exercise pilot privileges and is obtained through an exam with an Aviation Medical Examiner. There are three classes of medical certificates - third, second, and first class - with increasing standards and privileges. Physiological and psychological factors like hypoxia, hyperventilation, spatial disorientation, fatigue, and stress can affect pilot performance. Vision plays a key role in flight but can be impacted by illusions like autokinesis and false horizons in certain conditions.