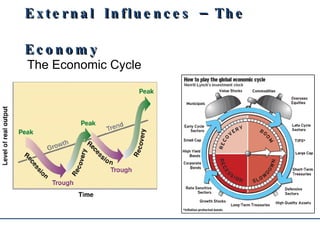
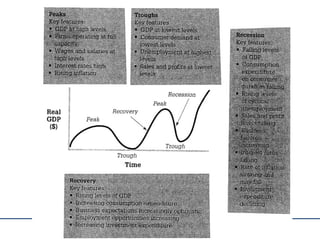
The document discusses various sources of change for businesses, including both external factors outside their control such as changing markets, economic conditions, and technology, as well as internal factors they can influence. It provides examples of external factors like globalization, e-commerce, and economic indicators, and how governments can impact businesses through policies. Internal changes come from accelerating technology, new systems and business cultures that companies introduce.