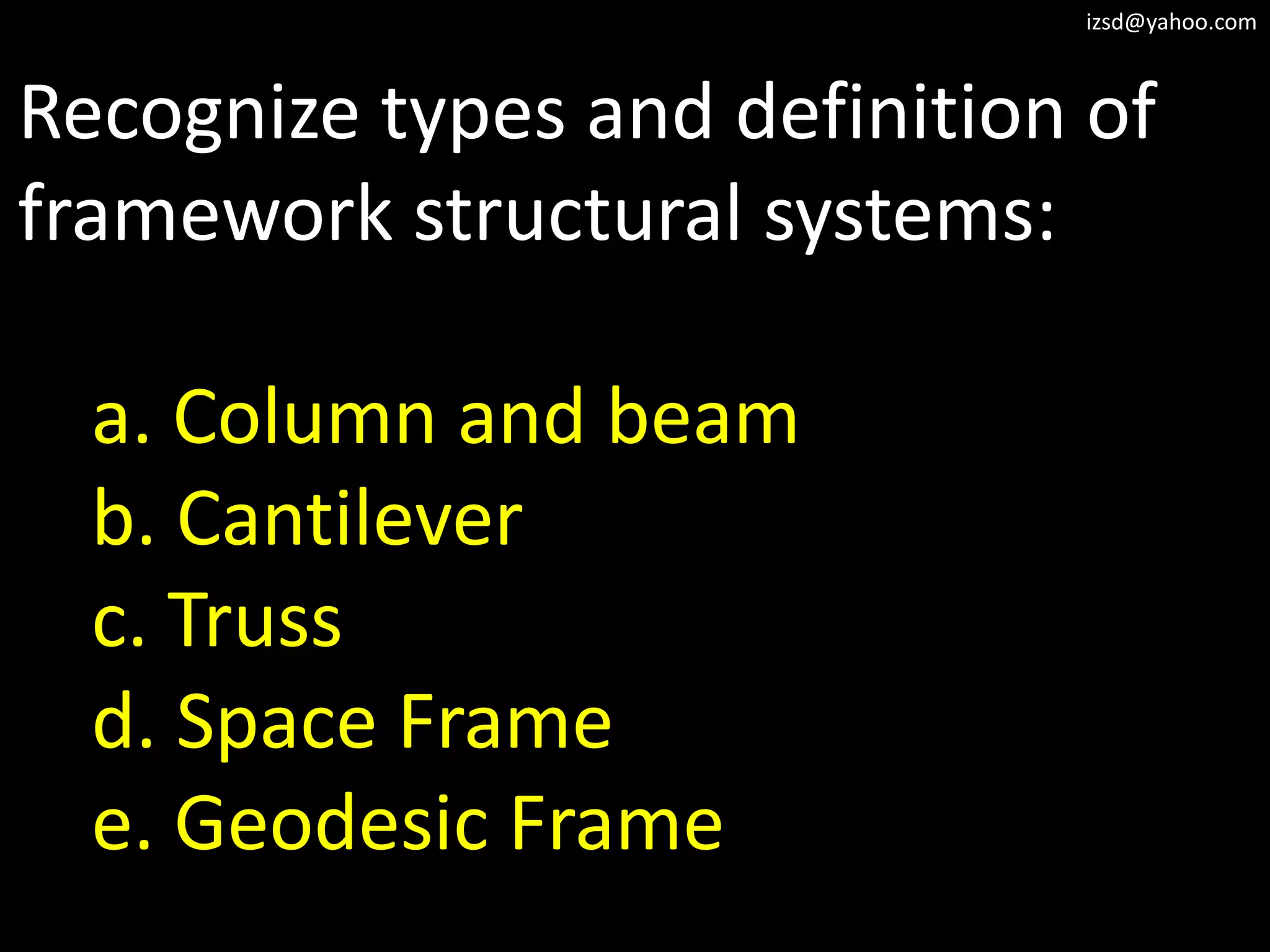
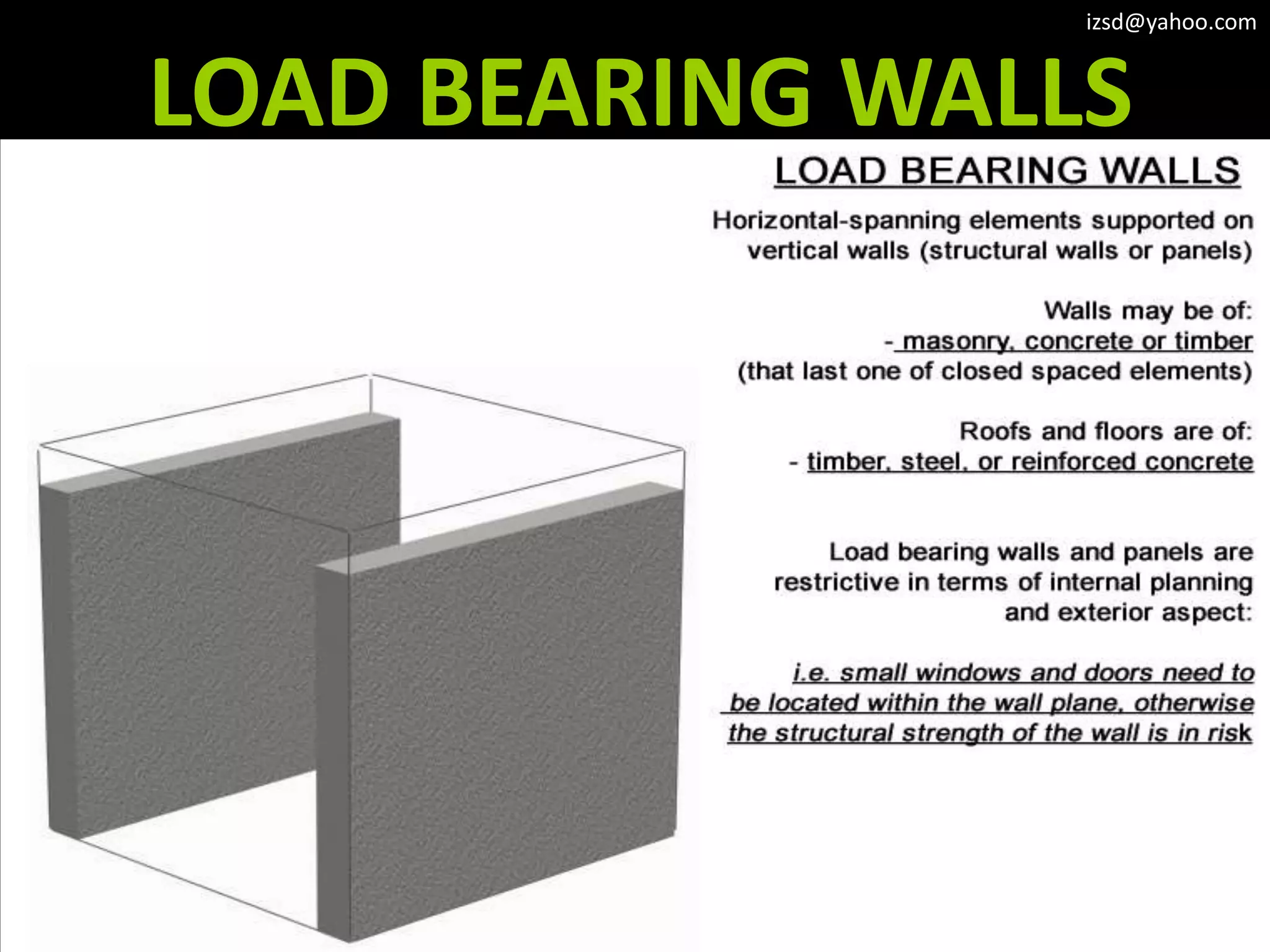
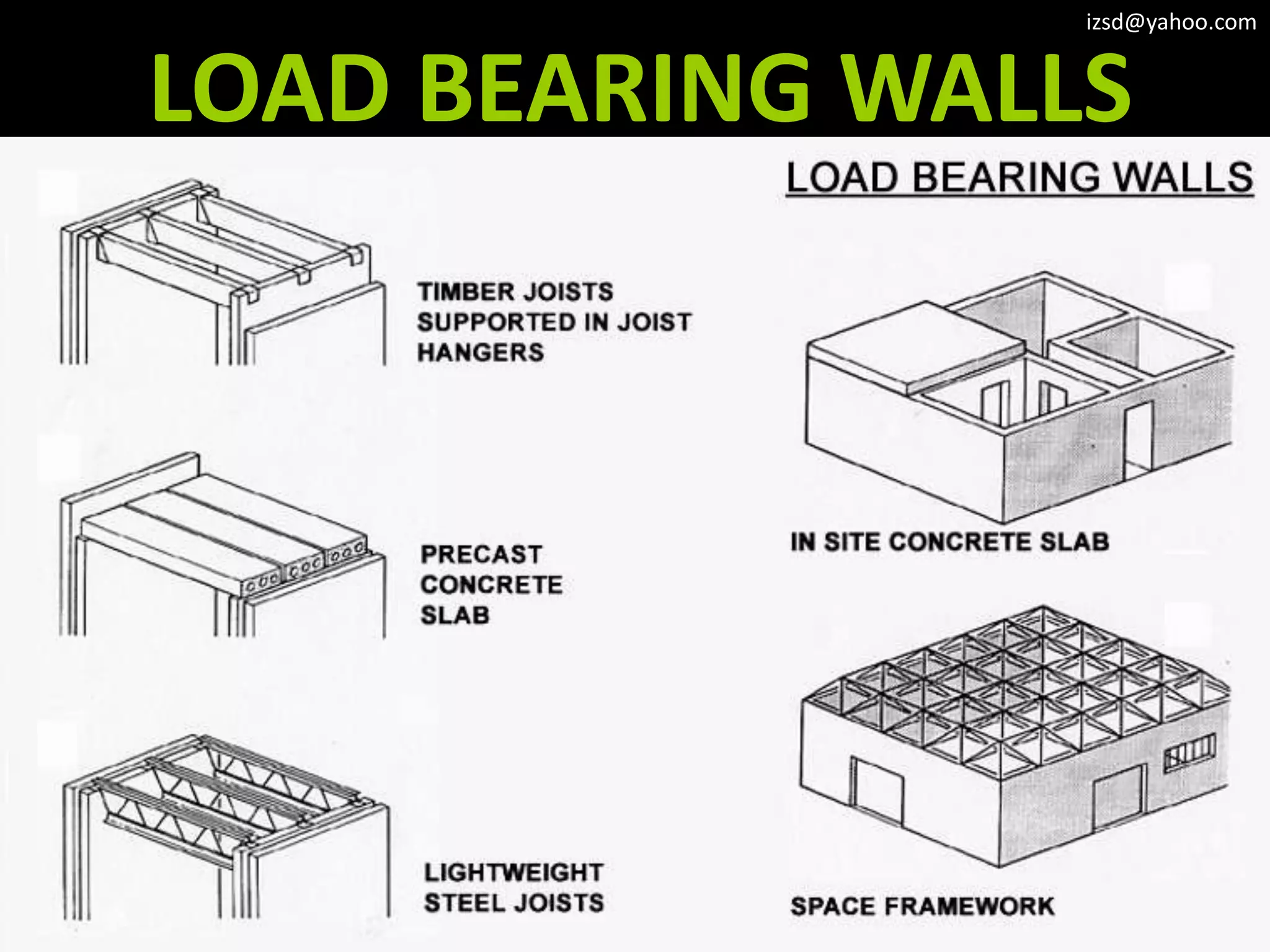
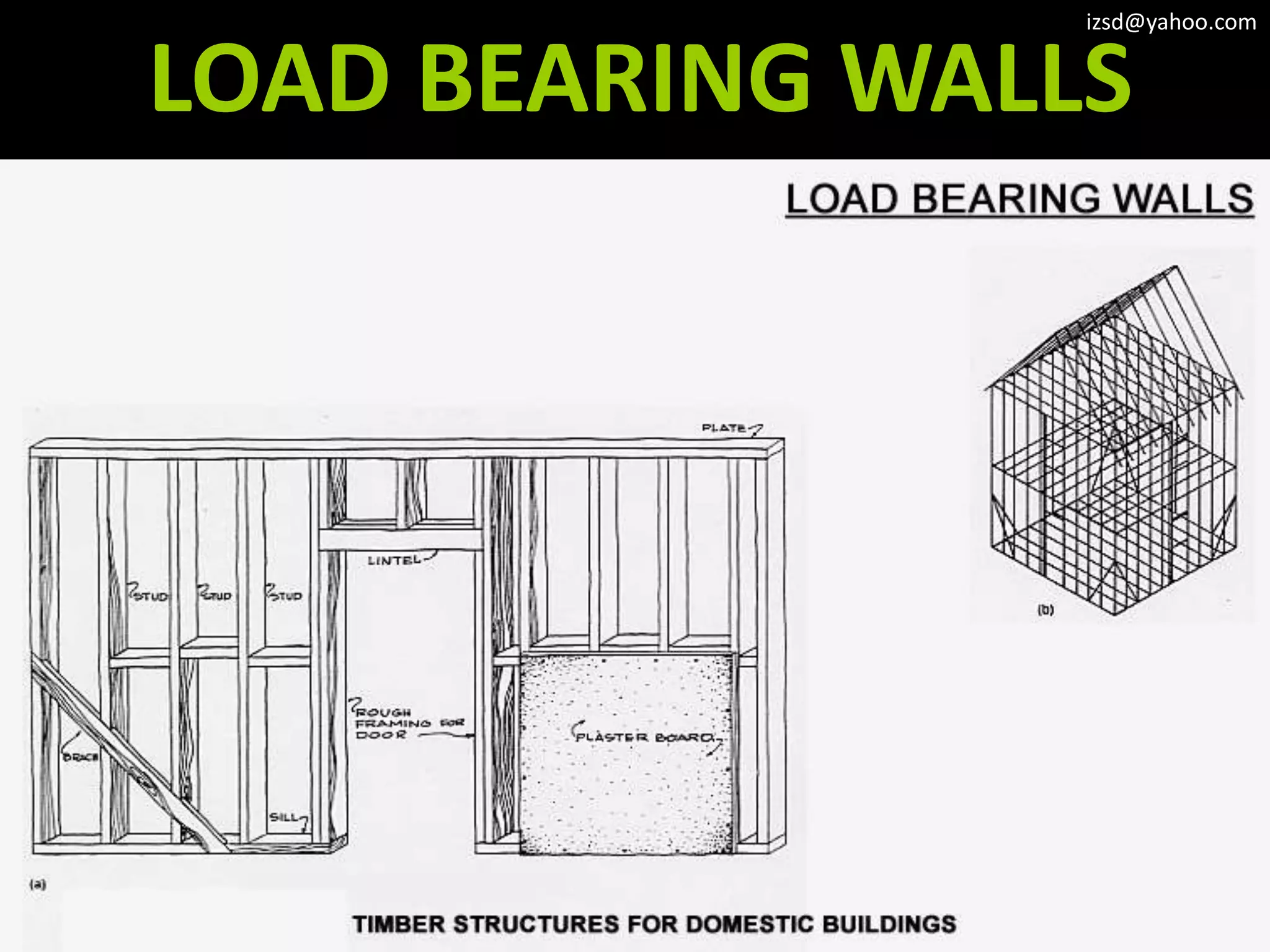
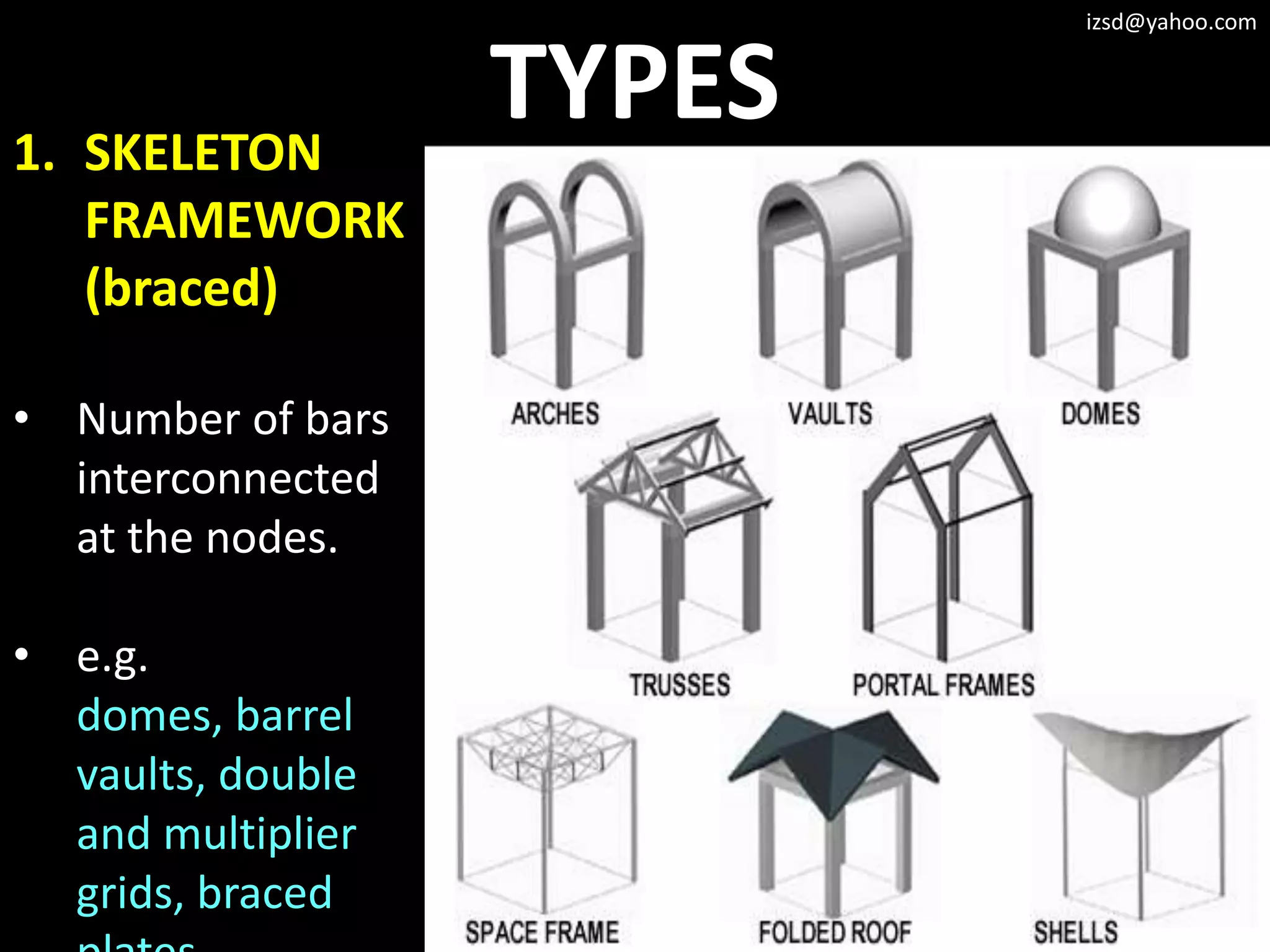
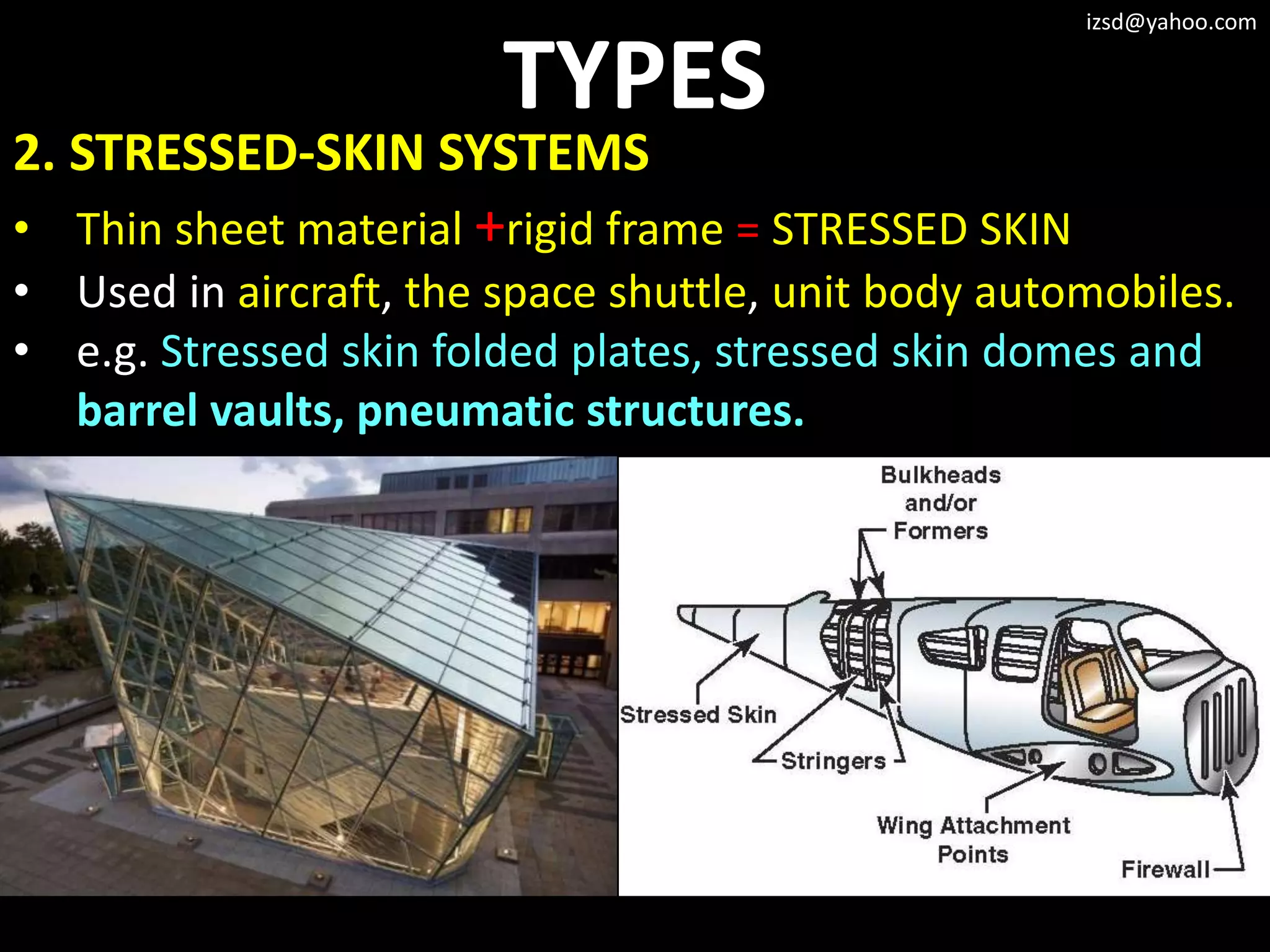
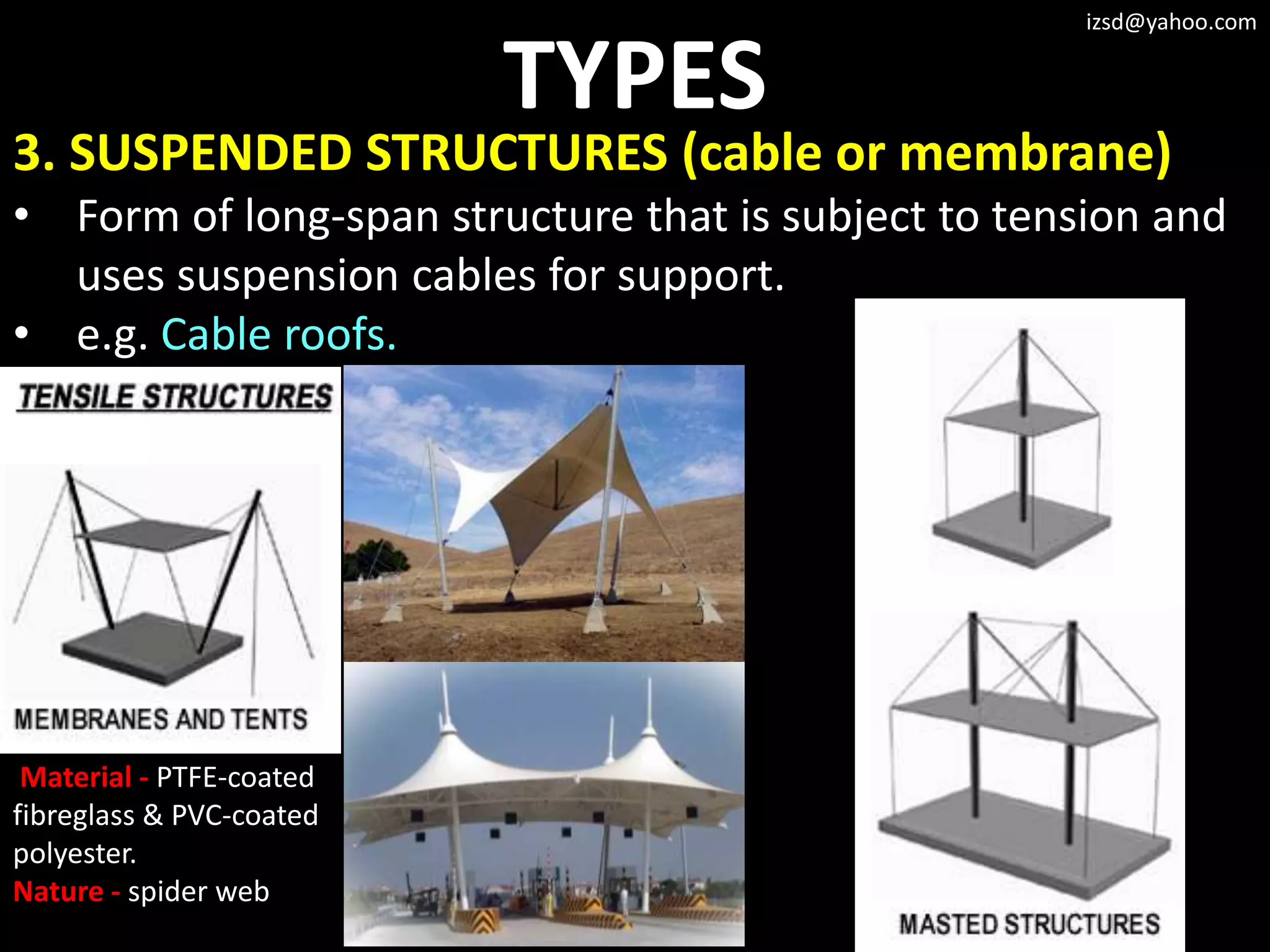
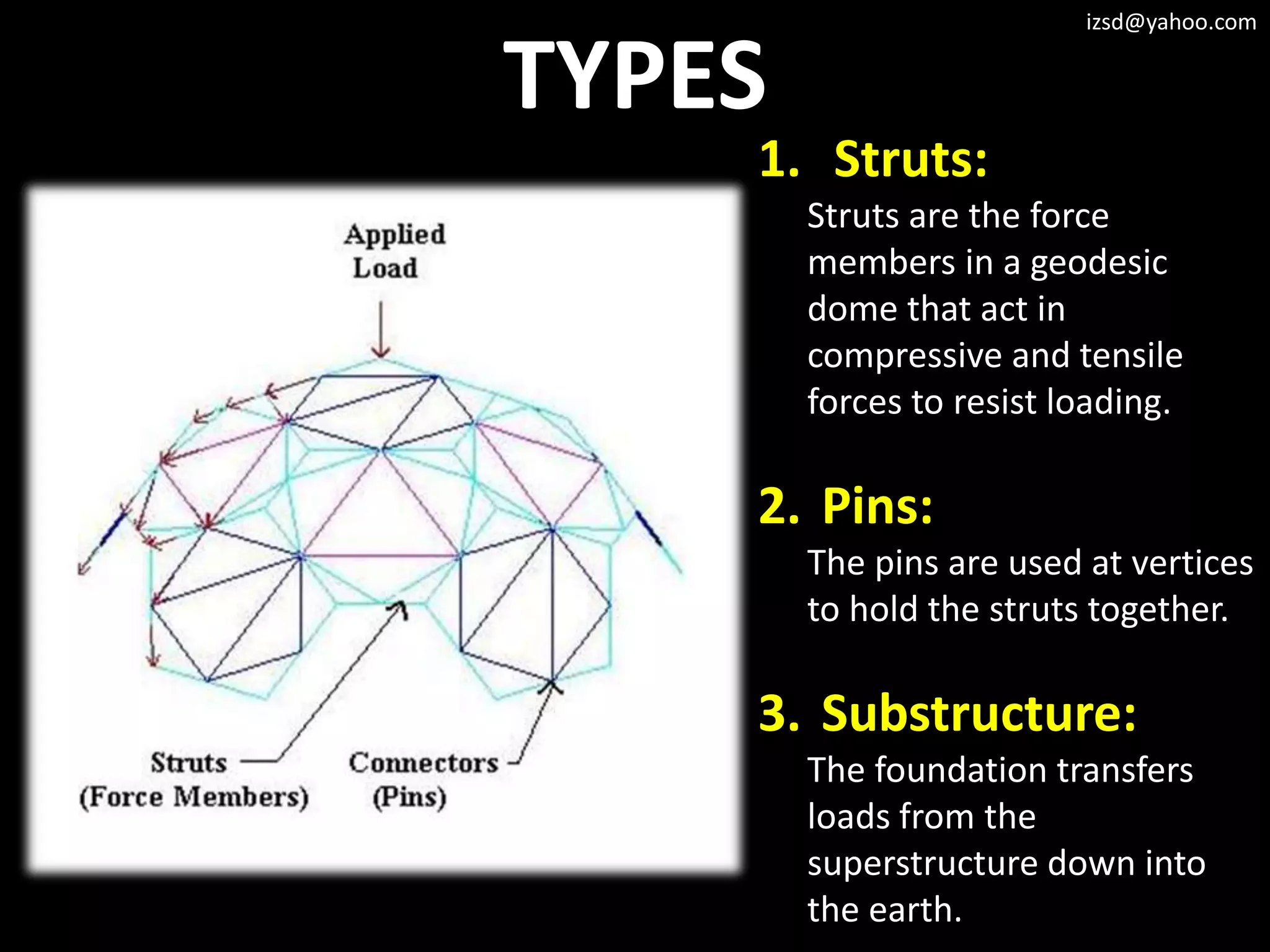
The document discusses various structural framework systems including:
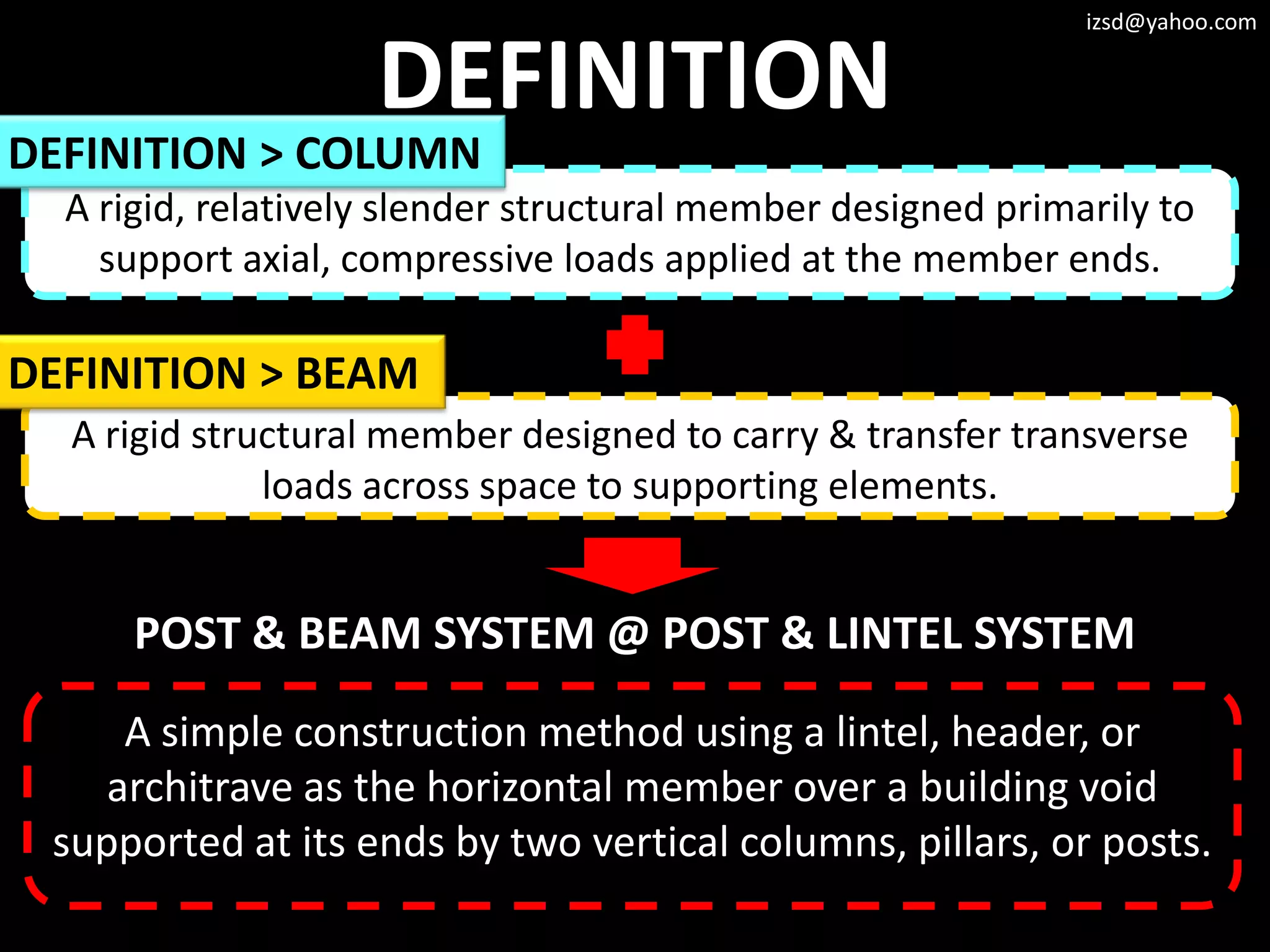
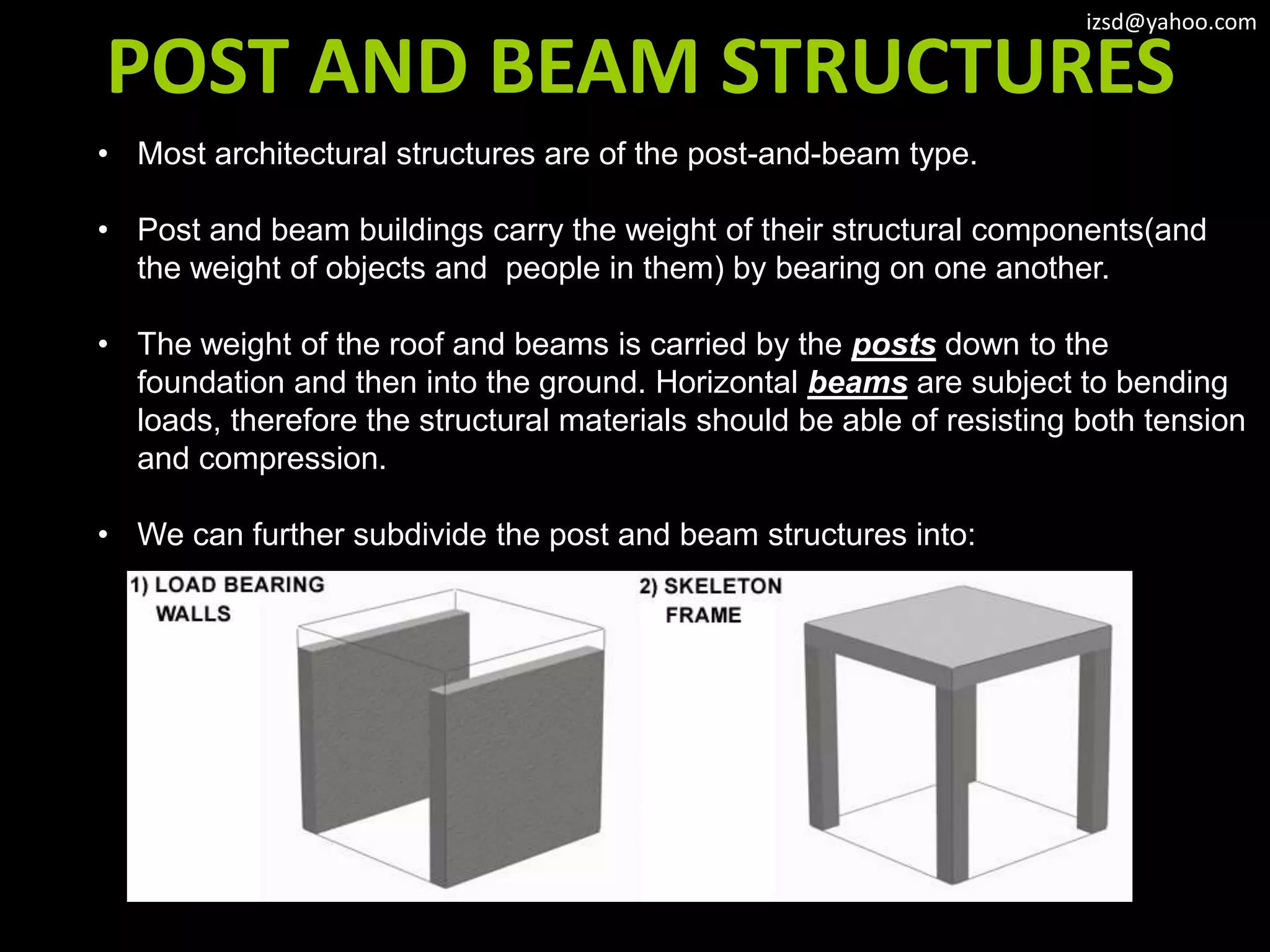
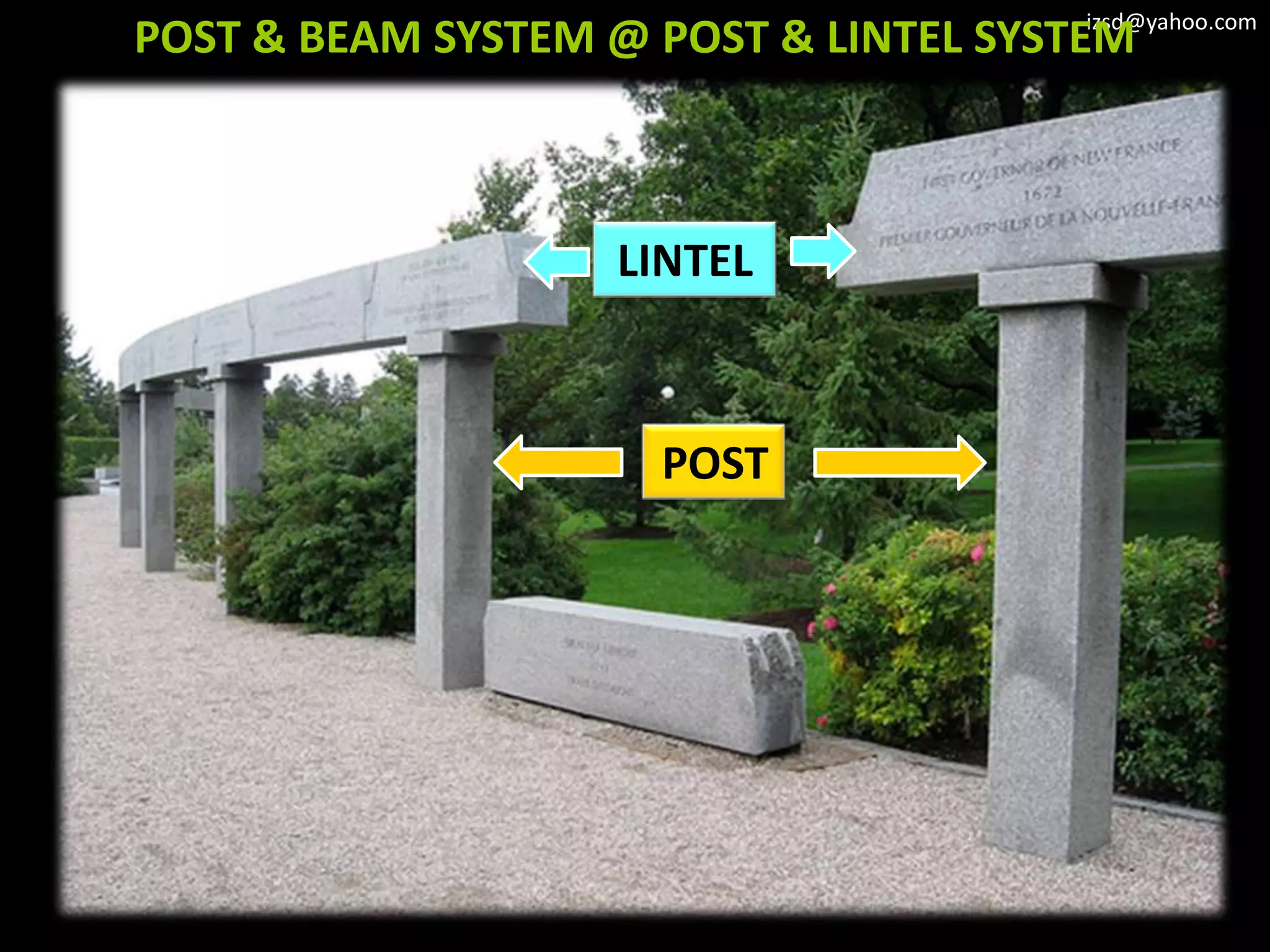
1) Column and beam frameworks which use vertical columns supporting horizontal beams.
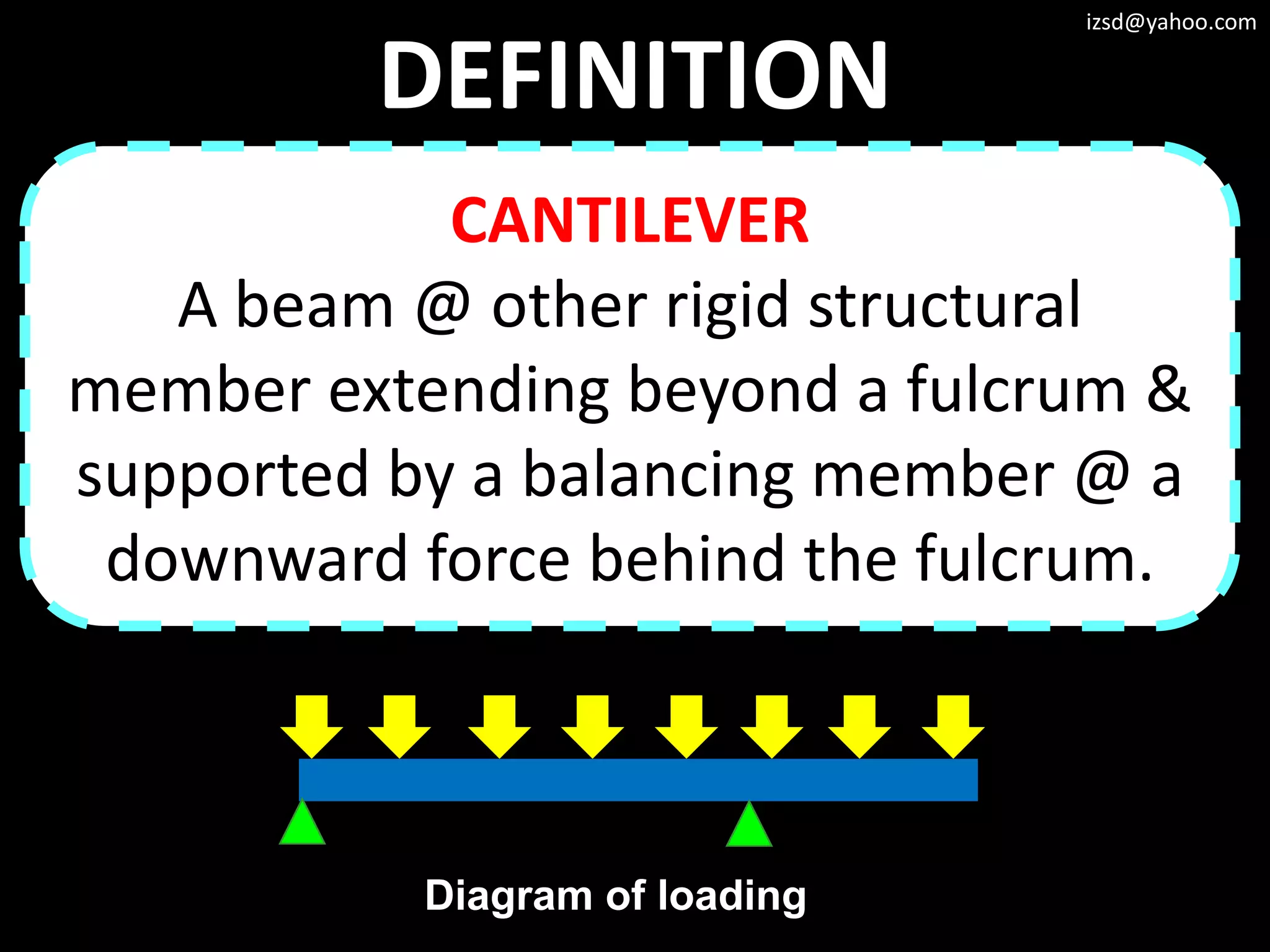
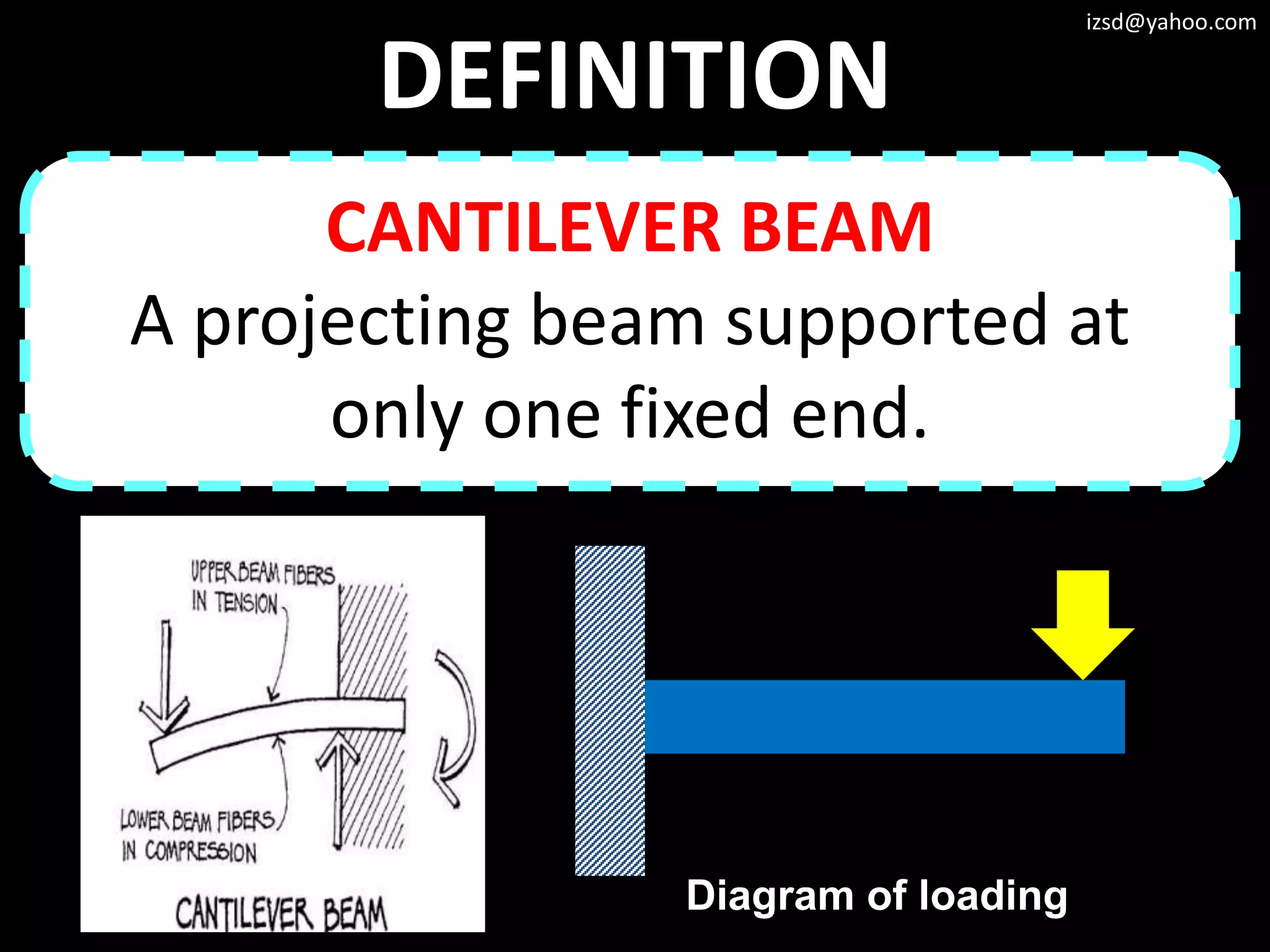
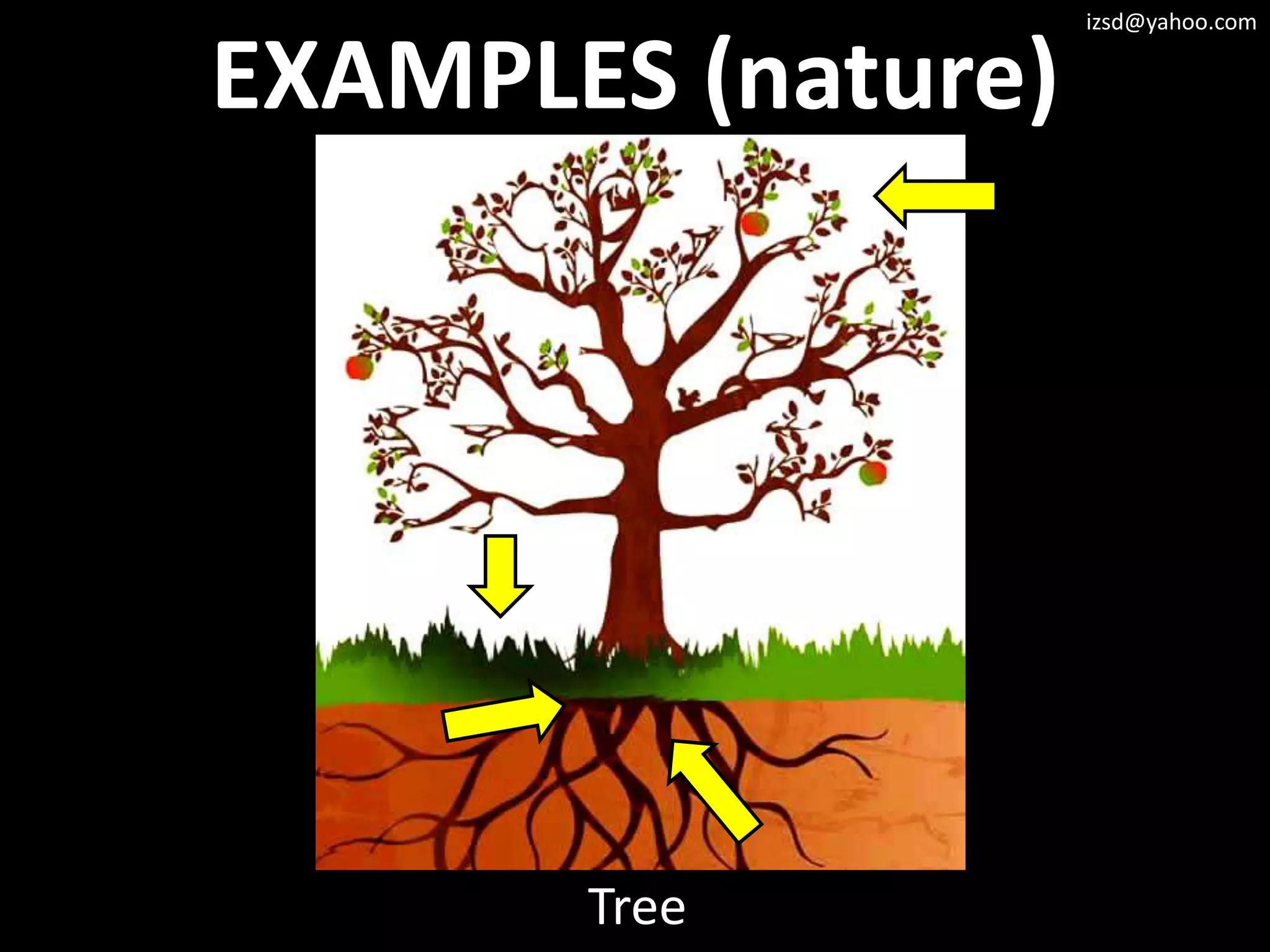
2) Cantilever structures which use beams supported at only one end such as balconies.
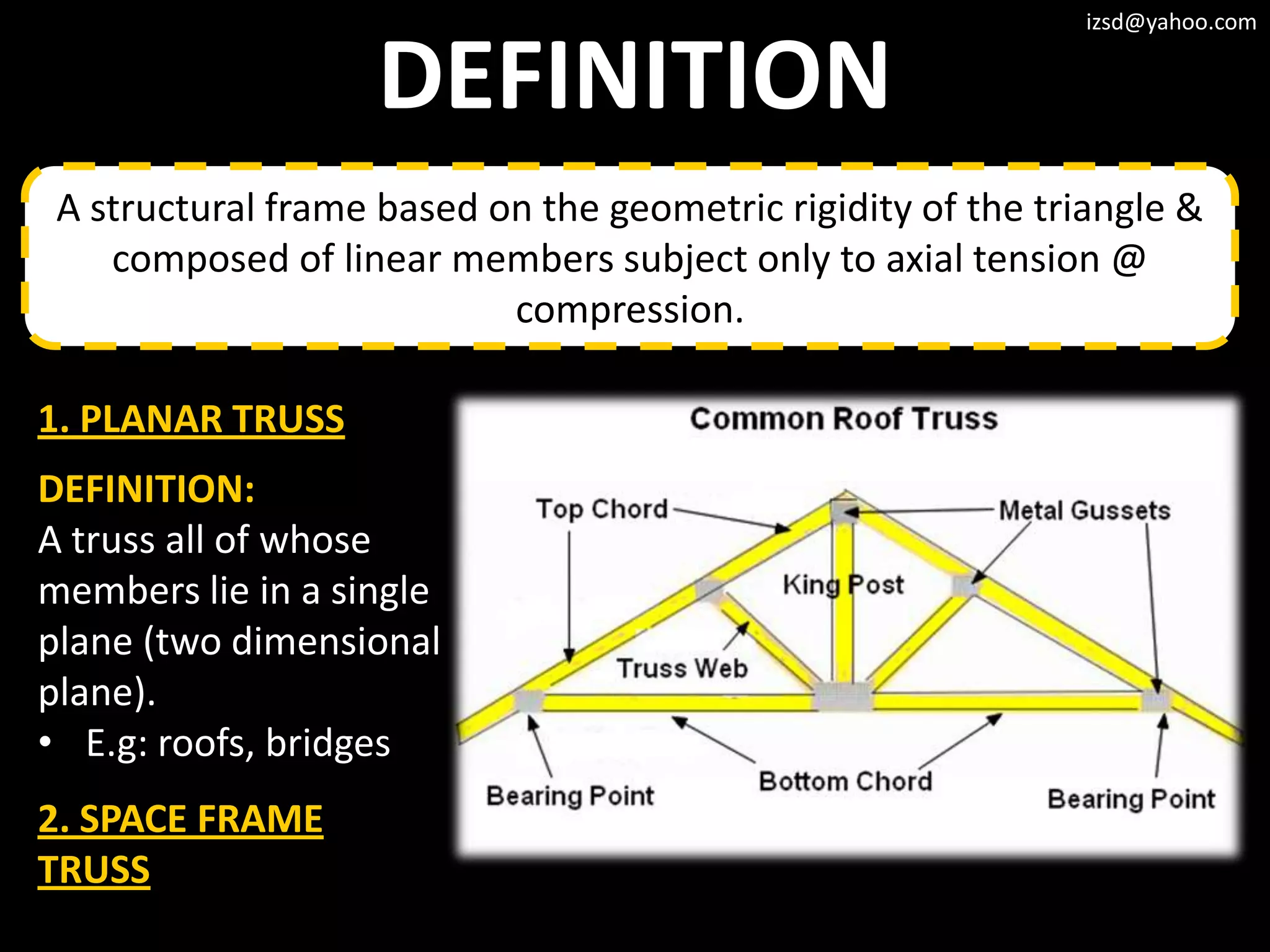
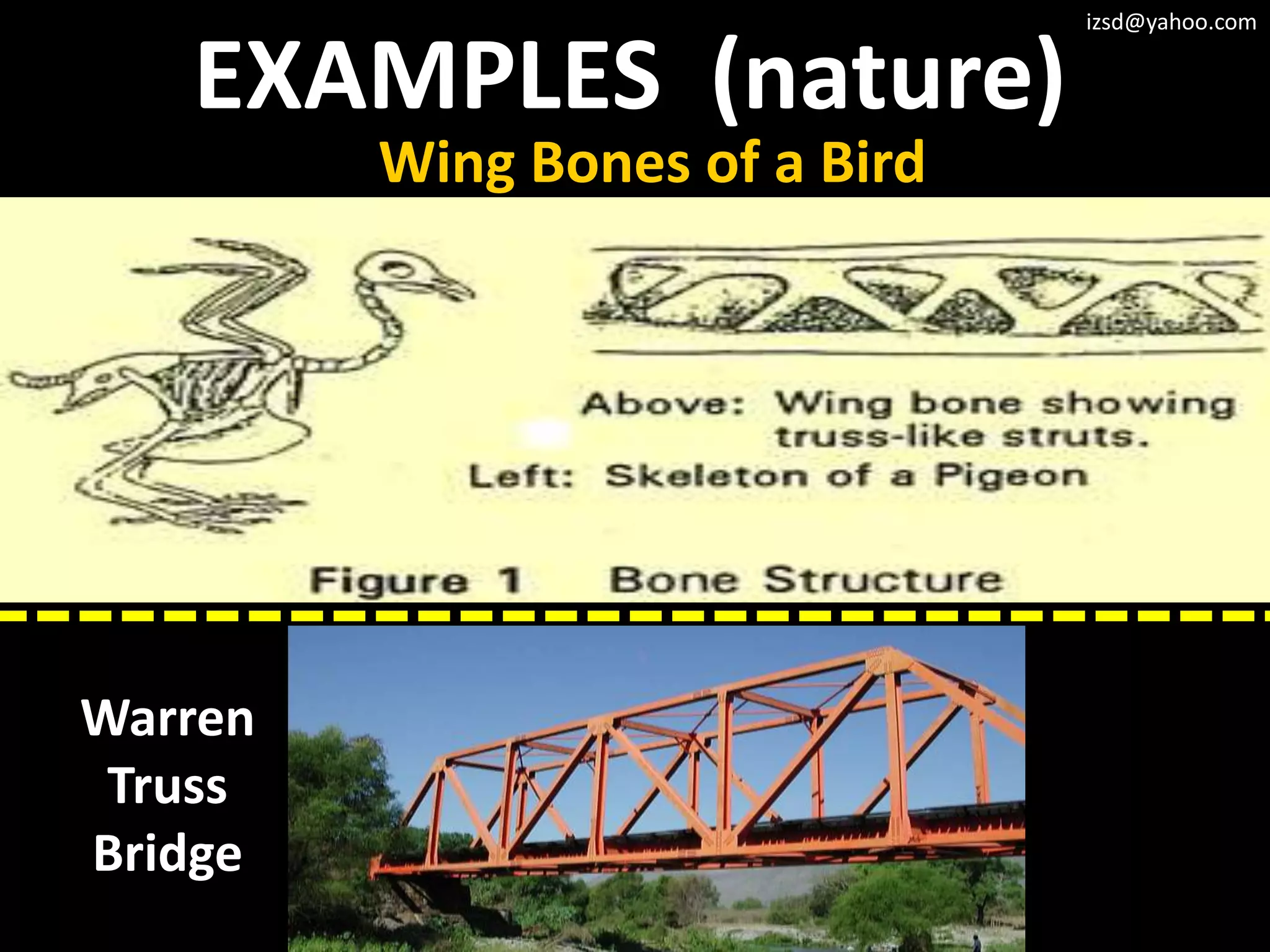
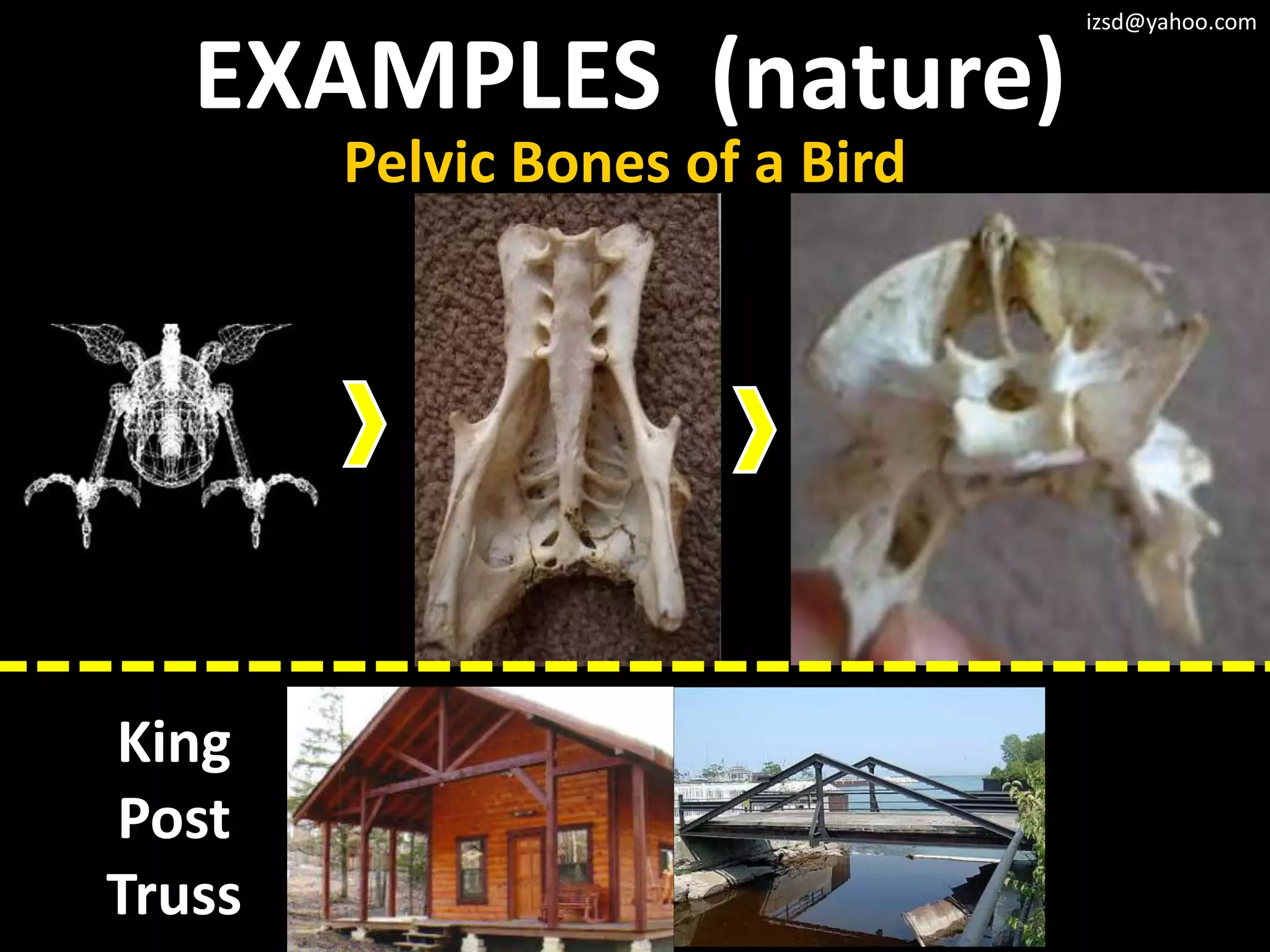
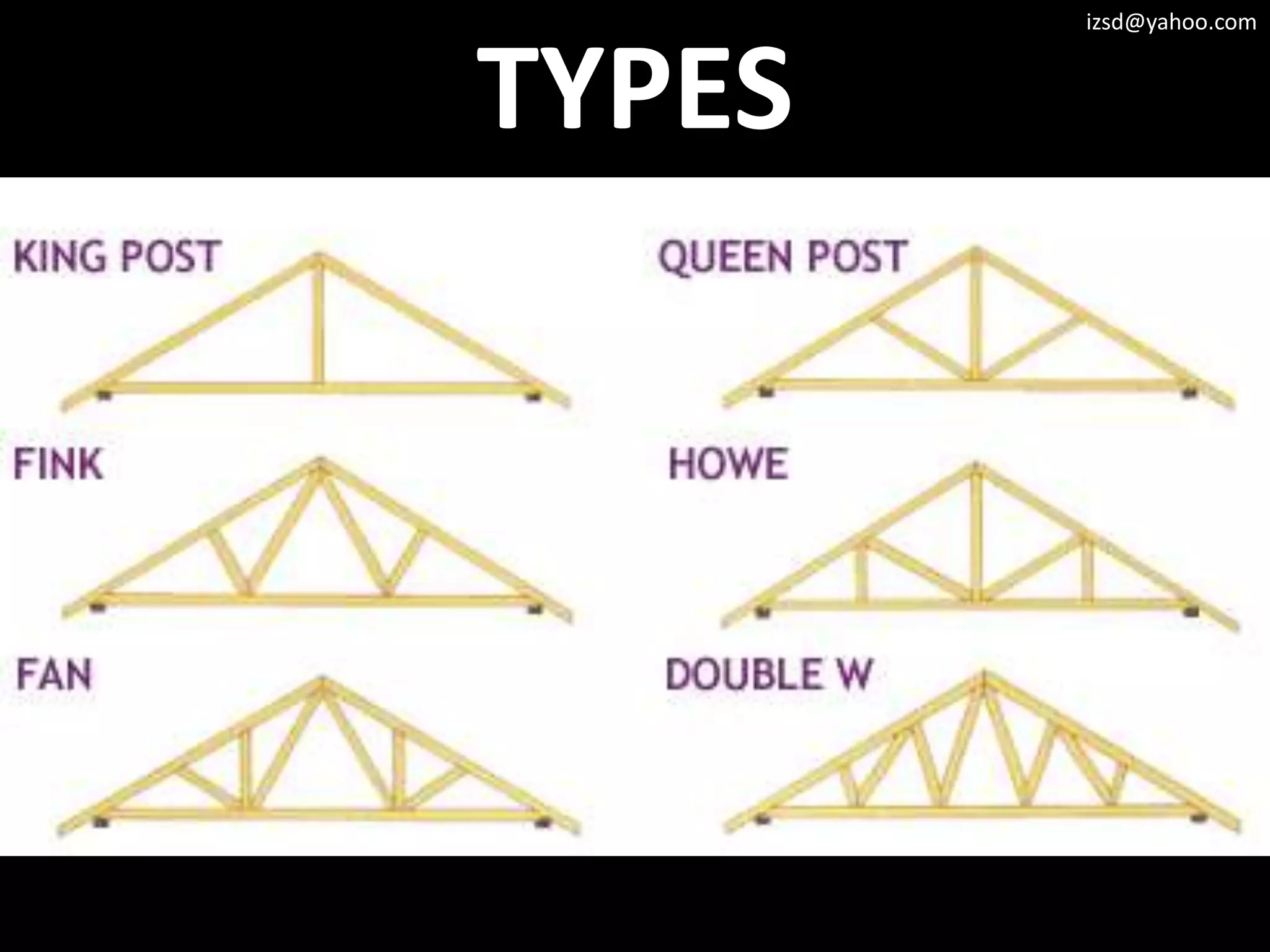
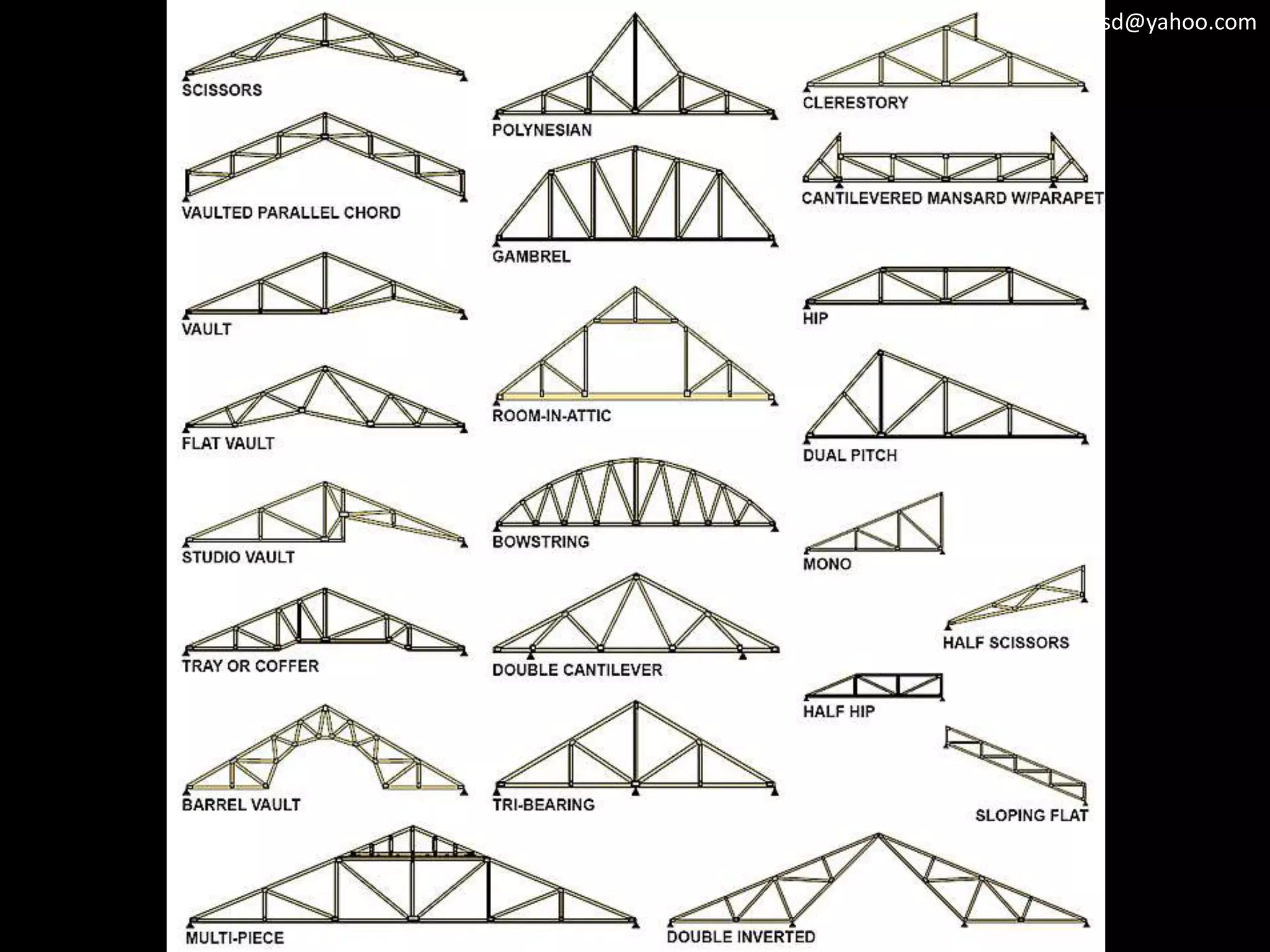
3) Truss frameworks which use a geometric arrangement of structural members in triangles to transfer loads.
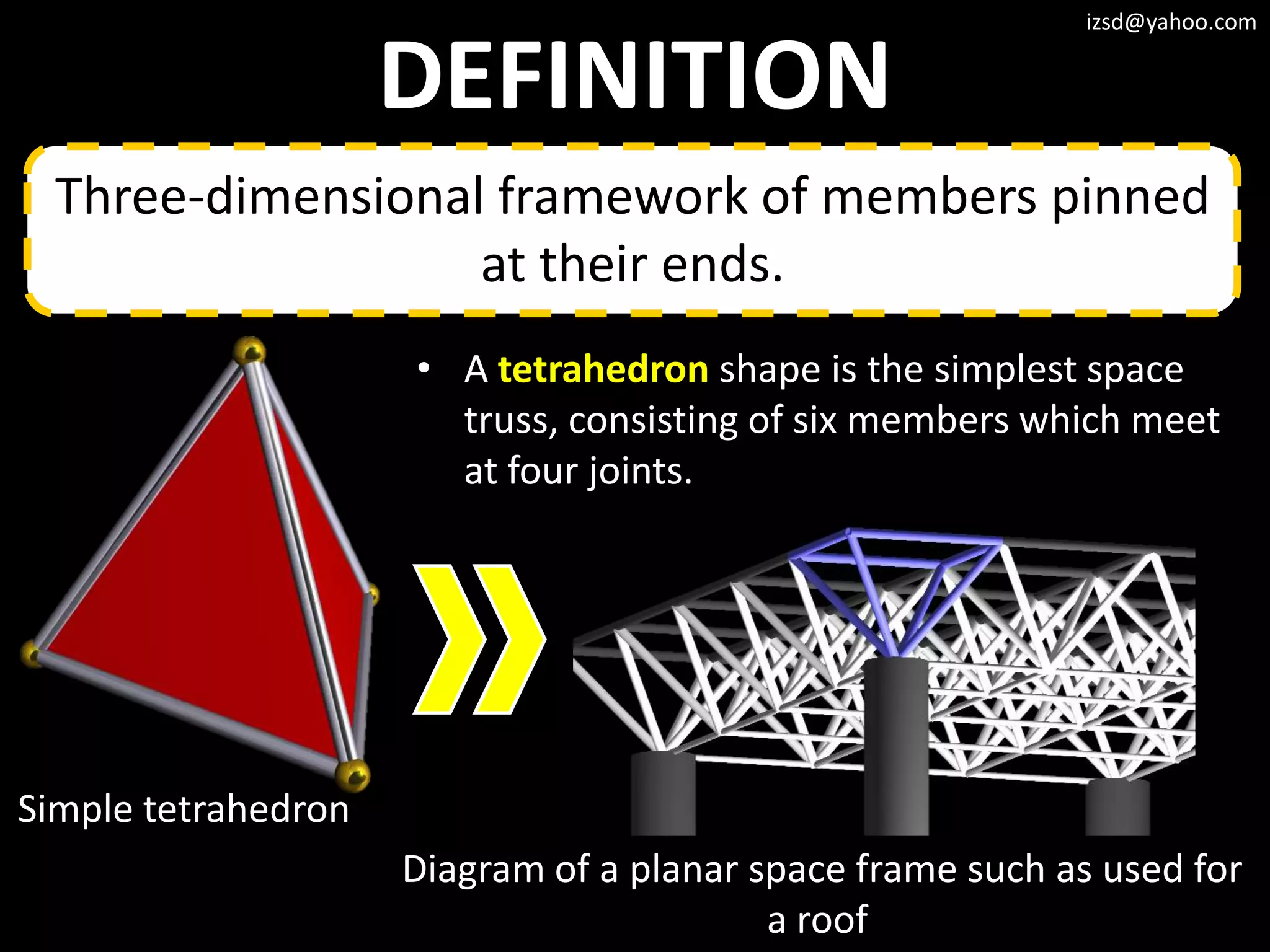
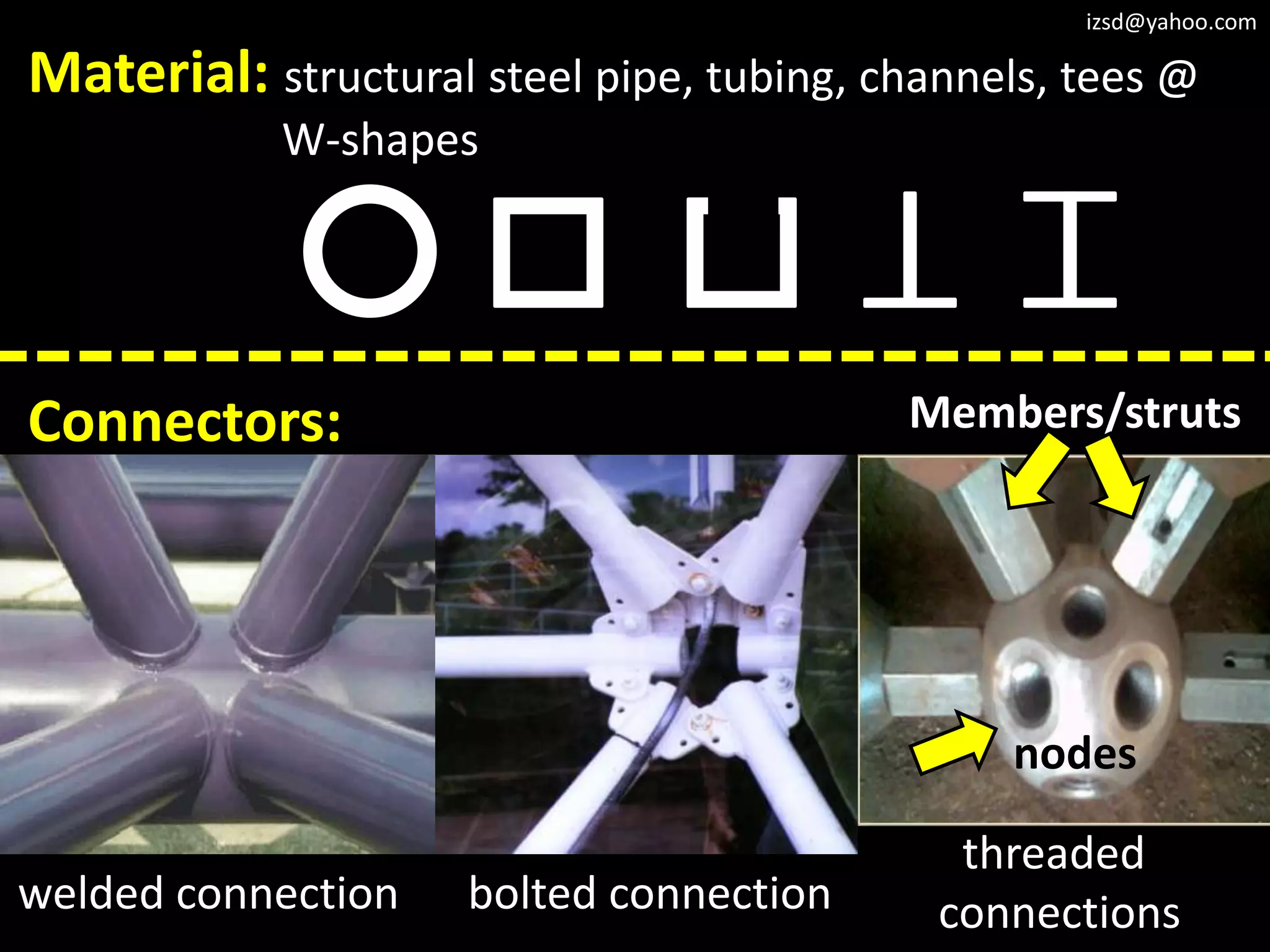
4) Space frame structures which use a three dimensional framework of members connected at their ends.
5) Geodesic dome frameworks which use a system of spherical triangles formed by members following great circles.