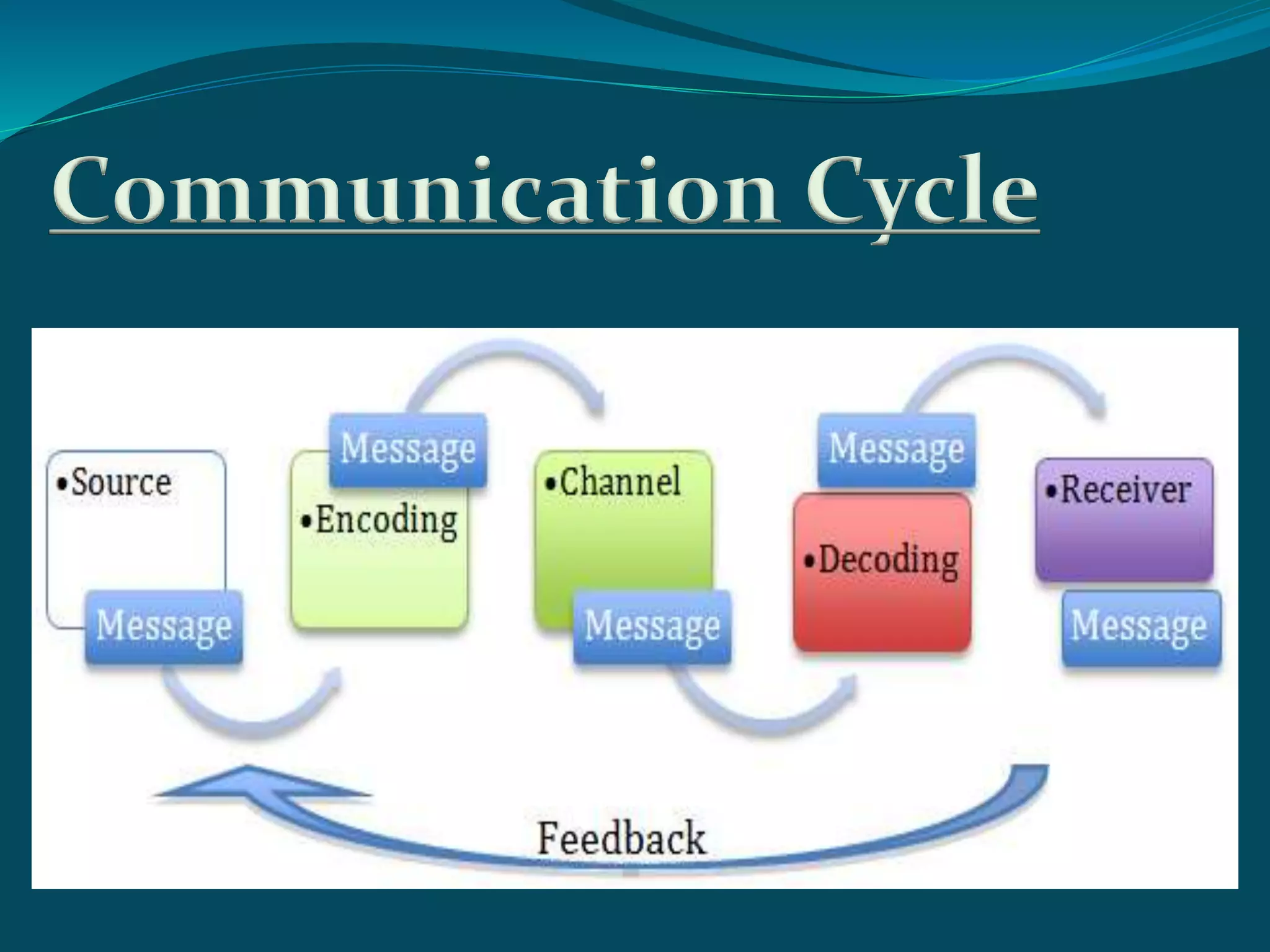
The document provides a comprehensive overview of communication, defining it as the sharing of information between a sender and a receiver. It discusses the communication cycle, effective communication essentials, and the impact of noise on communication, categorizing it into channel noise and semantic noise. Additionally, it explores different types of communication, including general, technical, intrapersonal, interpersonal, extra-personal, and mass communication.