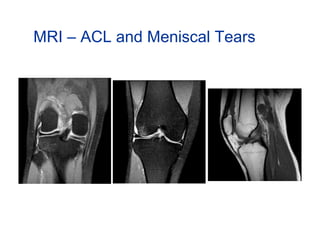
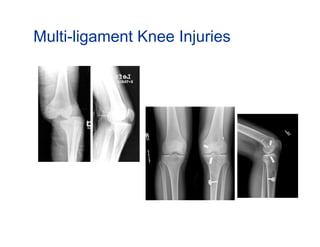
The document summarizes information from an orthopedic seminar on various knee injuries and conditions. It discusses meniscal tears, ACL tears, multi-ligament injuries, tibial plateau fractures, patellofemoral pain, knee arthritis, and knee replacement surgery. Treatment options are provided for each condition including arthroscopic surgery, bracing, physical therapy, injections, and different surgical procedures.