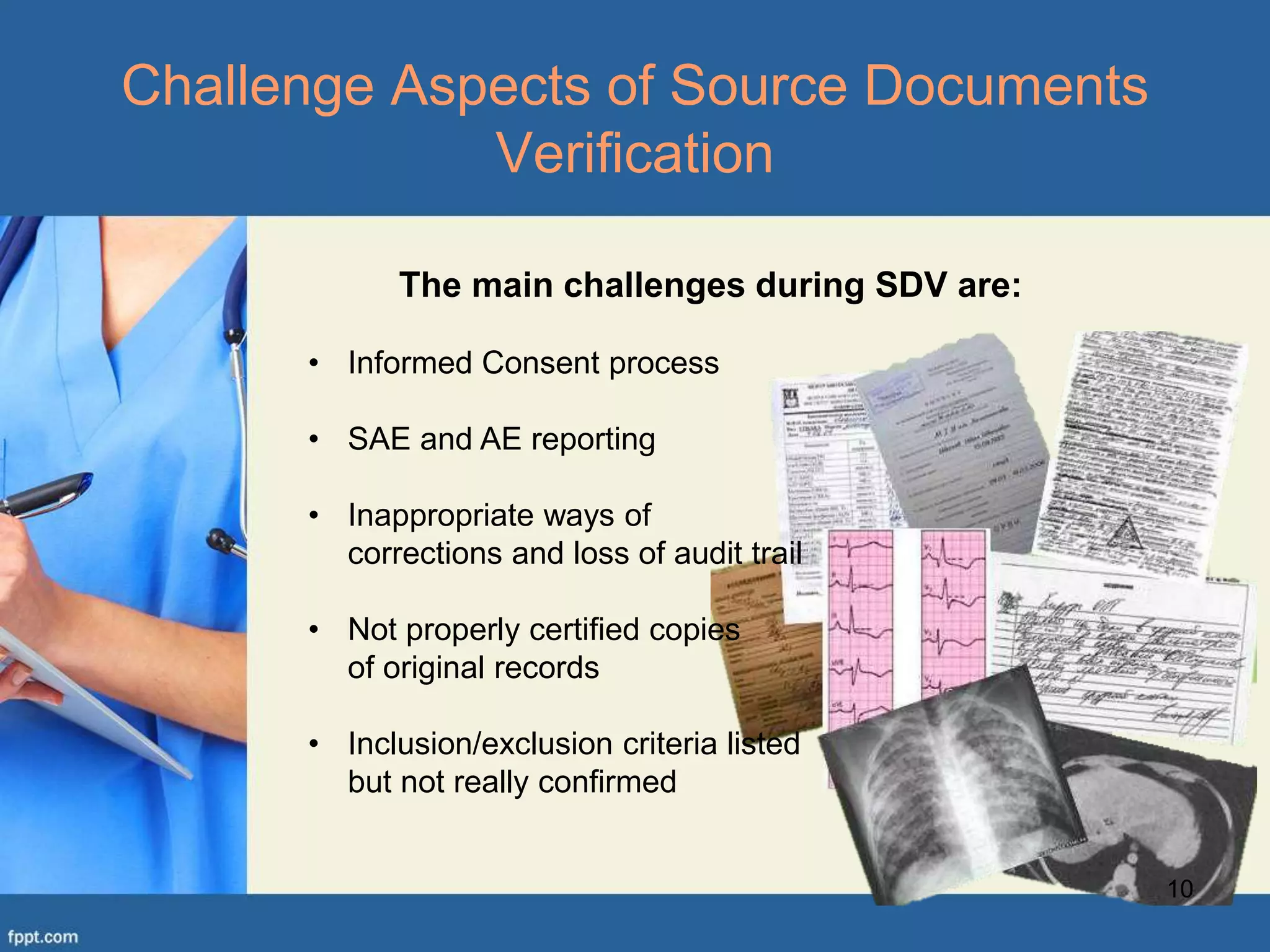
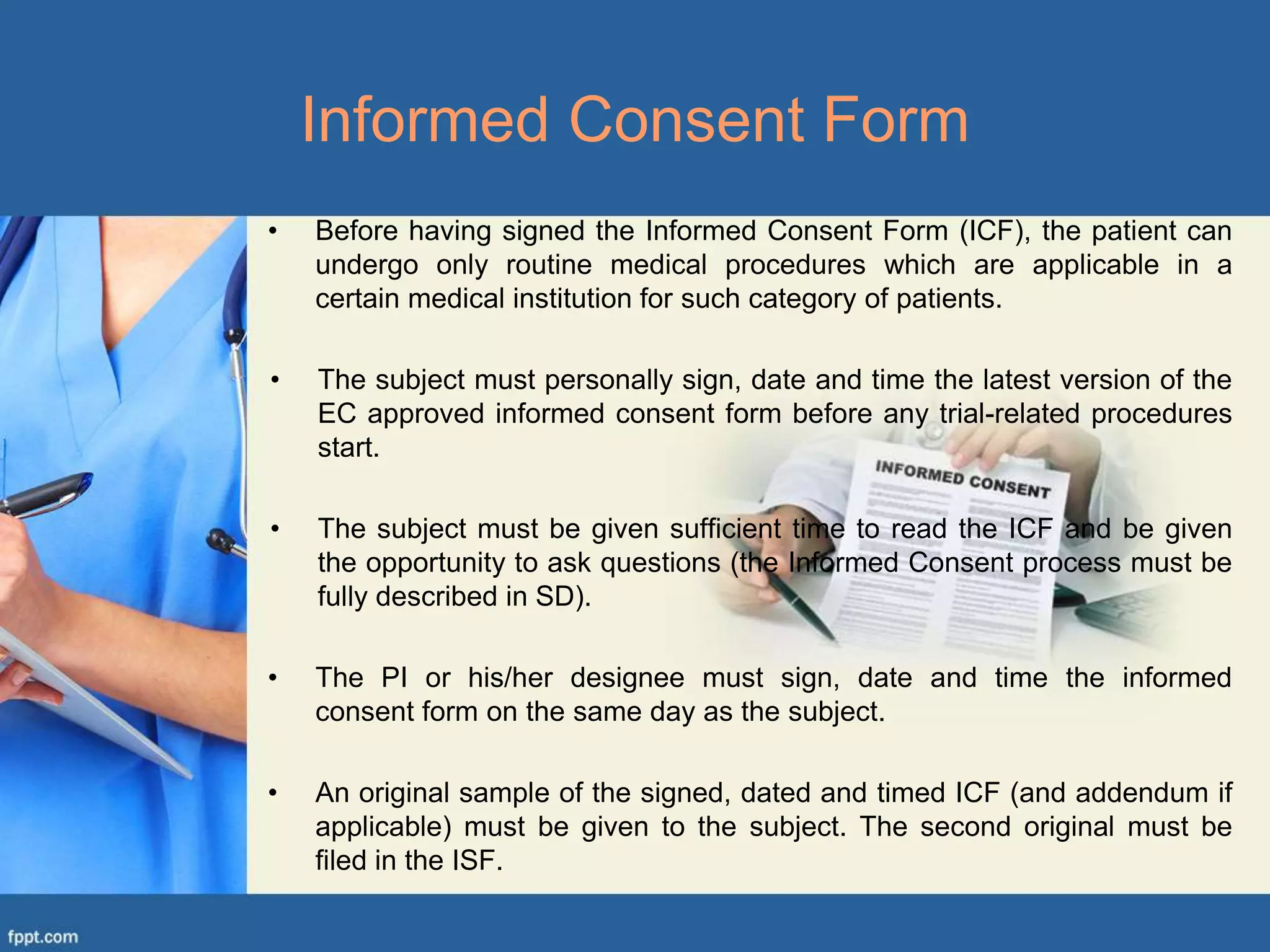
This document defines a source document as an original document where clinical trial data is first recorded, such as medical records, laboratory notes, or subjects' diaries. Source documents can be either electronic or paper. Electronic source documents must meet requirements regarding computer system validation, electronic records, electronic signatures, and technical support. Paper source documents are typically handwritten forms or records with the investigator's original signature. The document discusses challenges of source document verification like informed consent processes and adverse event reporting. It provides examples of informed consent procedures for patients who cannot read, are disabled, or lack decision-making capacity.