unit 14-Design-and-Planning.pptx
- 1. Design and Planning FACILITY PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT
- 2. Design Consideration 1. Attractive appearance 2. Efficient plan 3. Location 4. Suitable material 5. Workmanship 6. Sound financing 7. Competent Management
- 3. Description:- 1.Over all appearance- very imp. Consideration, should be attractive, reflect the architecture of that area (durbar square), have character of the services being provided in that hotel. 2.Functional and appeal to the eye. All the services should meet various principles of layout and design. 3.Geographical location of the Hotel guides the design. e.g. Hotel nearby airport or railway station, the reception will be designed in such a way that it could handle large number of guests at one time because there is a possibility of guest checking in large groups and around the clock. Similarly, Hotel at hill stations, beaches, in heart of the cities and metros will be designed differently. 4.Designed to be able to use material locally available, cost effective and efficient. 5.Available workmanship and designer should take advantage of local expertise. efficient but also economical. 6.Finance- very imp factor. availability of ready funds and management of finance is a crucial factor and it should be considered very carefully in Hotel Design. 7.(necessary ability, skill or knowledge) The design of a Hotel will depend upon the quality of management available to operate the establishment. If we have the quality management and manpower only then Hotel should be designed for sophisticated equipment and high tech gadgets. These are some of the consideration, which affect the design of hotel
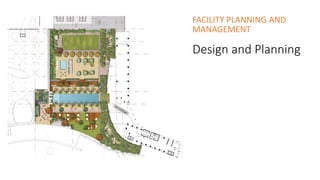
- 5. Landscaping The development of outdoor space to provide various amenities – privacy, comfort, beauty and ease of maintenance.
- 6. Living Elements: Flora or fauna, gardening, the art and craft of growing plants with a goal of creating a beautiful environment within the landscape Natural Elements: landforms, terrain shape and elevation, bodies of water Human Elements: structures, buildings, fences, other material created/installed by human Abstract Elements: weather and lighting conditions Element used in Landscaping
- 7. To describe the vegetation(plant) material like aquatic plants, semi- aquatic plants, field layer plants (grasses and herbaceous plant), shrubs and trees. Soft Landscaping
- 8. To describe the construction material like brick, gravel, rock or stone, concrete, timber, bitumen, glass, metal etc. Also describes outdoor furniture and other landscape product Hard Landscaping
- 9. • Location, types of driveways and entrance • The first or principal view guests see • Drainage condition • Existing trees • Underground and overhead utility lines • Recreational facilities • Direction of sun and wind • Watering facilities Consideration
- 10. • Create and aesthetically pleasing environment. • Reduce noise. • Help structures blend with terrain. • Screen unsightly sights. • Provide privacy. • Reduce pollution and conserve natural resources. • Control people and vehicles. • Reduce damage and injury. • Create places for recreation. • Increase property value • Create pride in homes, community, etc Purpose of Landscaping
- 11. • Environmental aspect • Social aspect • Aesthetic aspect • Economical aspect Environment- (environmental restoration as in environmental remediation) Greenery, fresh air, water restoration, humidity/moisture. Social – provide different kind of space for different activities (swimming pool- recreation, pathways- jogging, yoga and meditation spaces, outdoor dining/bar- parties, gathering, eating spaces, playing space for kids Aesthetic –pleasant view,comfort/relaxing/calming/enjoyable environment Economy – increase the revenue, guest, Objective
- 12. Activities
- 13. Activities
- 14. Parking
- 15. Parking • Safe and secure parking facility for the vehicles is a fundamental right of all visitors. • Most of the hotels are unable to provide sufficient parking space for their guests. • Planning of parking totally depends on the availability of the space, size, configuration and contours of a site.
- 16. Types of Parking According to service: • Self-parking Driver parks and retrieves his/her own car • Attended Parking (Valet Parking) Car is left at the entrance by the driver and an attendant then parks the car. When driver returns attendant retrieves the car and transfers it to the driver at the exit. • Automated parking A mechanical system designed to minimize the area required for parking cars. An automated parking system will transport vehicle to and from parking spaces.
- 17. Types of Parking 1. On street parking - vehicles are parked on the sides of the street itself - usually controlled by government agencies 2. Off street Parking - vehicles are parked off the street itself - usually controlled by commercial agencies itself
- 19. - Surface parking - Multistoried parking - Roof parking - Mechanical parking - Underground parking Off street parking
- 20. Surface parking
- 22. Roof parking
- 25. Parking Space requirement according to Hotel standard Thumb rule 1000Sqft is sufficient for parking three cars in suburban area and 900sqft in urban area. Hotel Category Government of Nepal IS 5 and 4 star Hotels 25% of no. of guest room One space for every 4 guest rooms 3 star Hotels 20 vehicle One space for every 8 guest rooms 2 star Hotels 10 vehicle One space for every 10 guest rooms 1 star Hotels 5 vehicle
- 26. General planning and design Parking • Aesthetically pleasing and functional parking areas that fulfill the needs and requirements of the users should be the primary goal • To most people, the ideal parking space is a few steps from their home or office door • The designer must look at a number of concerns to logically, efficiently, and economically site parking areas
- 27. General planning and design Parking Some common parking area planning and design guidelines are: • Use 36 square meters per vehicle (includes entry, circulation, and parking spaces) as a typical planning and cost estimating factor • Locate separate visitor and reserved parking at the front entry of the facility • Eliminate dead-end parking areas • Locate entrances and exits away from busy intersections • Locate aisles and rows of parking parallel to the long dimension of the site with parking on each side of an aisle • Use rectangular parking areas to minimize land area requirement.
- 28. General planning and design Parking Geometry • Parking areas take on many configurations. • Parking spaces may be parallel, perpendicular, or angled (30, 45, or 60 degree) to the driving lane, or aisle. • The area required by each parking configuration will vary. • As a general rule of thumb, the closer to perpendicular, the more vehicles can be parked per meter. Perpendicular, or 90 degree parking, accommodates 82 vehicles per 100 meters versus just less than 40 vehicles for 30 degree.
- 29. General planning and design Parking Some of the advantages and disadvantages of the various parking configuration 1. Parallel • For the designer, the parallel parking configuration can be used where suitable off-street parking cannot be accommodated or is not practical. • For the driver, parallel parking requires experience, confidence, and patience. • Parking spaces should be a minimum of 7.5 meters long and at least 2.75 meters wide. On- street parallel parking spaces should be 3.35 meters wide.
- 30. General planning and design Parking • Advantages Works well in extremely narrow, linear spaces Requires minimum pavement area • Disadvantage Less than ideal visibility of adjacent traffic Inefficient use of on-street space
- 31. General planning and design Parking Perpendicular • effective in long term parking areas • the most efficient and economical since it accommodates the most vehicles per linear meter. Advantages • Works well with either one- or two-way aisles • Handles the most vehicles per square meter of pavement • Handles most vehicles per linear meter Disadvantages • Requires widest area • Difficult maneuvering for some drivers • Two-way traffic can create some visibility problems
- 32. General planning and design Parking Angled - 60 Degree • ideal for a fast turnover rate or predominantly short term use. Advantages • Easy maneuvering in and out of parking spaces. • Good visibility. • Most common short term parking configuration. Disadvantages • Requires more pavement per vehicle than perpendicular configuration. • Handles less vehicles per linear meter.
- 33. General planning and design Parking User walking distance • Long term users-employees, will generally accept longer walking distances from parking area • Short term users -customers or visitors expect shorter walking distances. Not more than 75 m Grading and drainage. • Parking areas must be properly sloped and drained to take care of runoff. Apply the following minimums: Ideal slope for all parking area pavements is 2% Longitudinal pavement slope should be between 1%-5% Pavement cross slope should be between 1%-10% Storm water should be collected on the perimeter of parking areas with a minimum of 2% slope along gutter
- 34. If you are planner, what points would you consider while designing 1) Landscaping 2) Parking in hotel. Give your opinion. Question to solve 1. Garage Entrance: Locate the entrance so that it is readily accessible to the guest drop-off area 2. Hotel Access: Provide a secure and convenient interior route usually and elevator, from the garage to the hotel lobby. 3. Safety and security: Design the garage to be visually open, with wide aisles; provide security cameras to scan area. 4. Guest Comfort: Increasing Lighting levels, raising ceiling height, painting surfaces light colors, providing art, murals or music 5. Signage: Provide clear signage, both for drivers (to enter and exit) and pedestrians (to lobby or street)
- 35. Different parking spaces (in Hotel) - Visitors/ guest , staff, VIP Parking space according to the time - Long term, short term - Some restricted parking areas includes handicap spaces, carpool spaces(taxi, hotel taxi/ vehicle), loading zones, service vehicle zones, timed areas Typical plan of parking area
- 36. Flow Diagram of a hotel Try once?
- 38. Some key definitions Plinth Area • Build up covered area of a building area measured at floor level of any storey. • Calculated by external dimensions of the building at the floor level excluding plinth offsets if any, and courtyard, open area, balcony and cantilever projections Floor Area • the total area of the floor in between walls and consist of the floor and all rooms, verandah, passage, corridors, staircases, entrance hall, kitchen, store, bath and WC. Floor area = Plinth area – area occupied by walls Floor Area Ratio (FAR): • Ratio of total covered area (plinth area) and area of the plot. FAR=total covered area of all floors/Plot area
- 39. Some key definitions Carpet Area • useful area, the total floor area minus circulation area, verandah, corridors, passages, staircase, lift, entrance halls, etc. and other non-useable area. Carpet area should be floor are excluding: • Sanitary accommodation, verandah, corridor, and passages • Kitchen, pantries, entrance halls, porches stores • Canteens, ac ducts and plant room Circulation area: • Area of verandahs, passages, corridor, balconies, entrance hall, porches and staircases used for movement of people in building. Can be divided into two parts: • Horizontal area is are of verandah, passages, corridor, balconies, porch, etc. • Vertical area is area occupied by staircases, lifts and entrance hall adjacent to them, which are required for vertical movement.
- 40. Flooring • a permanent covering of a floor, or any finish material applied over a floor structure to provide a walking surface. • Materials almost always classified as flooring include carpet, laminate, tile and vinyl • The floor under the flooring is called the subfloor, which provides the support for the flooring. • The choice of flooring materials is affected by factors cost, endurance, noise insulation, comfort, cleaning effort.
- 41. Carpeting • soft floor covering made of bound carpet fibers or stapled fibers. • used extensively in hotels and institutional establishment • The type of carpet selected will depend upon the suitability and traffic in the area. • used in bedrooms, lounges, TV rooms, restaurants, office and corridors. • A good quality carpet should be able to withstand spillages, cigarette ash and grit. • They must also be resilient to heavy furniture • typically used indoors and can be used in both high and low traffic areas. • Typically lasts for 15-18 years before it need to be replaced. The quality of a carpet is usually measured in face weight (weight/area) The higher the face weight the more luxurious a carpet will feel Carpets come in a variety of natural or synthetic materials including wool, hemp, jute, bamboo, nylon, olefin, acrylic, wool and polyester.
- 42. Wood flooring • Many different species of wood are fabricated into wood flooring in two primary forms: plank and parquet • Hardwoods are typically much more durable than softwoods Engineered hardwood • a thin solid wood layer on top with a composite core • a less expensive option than buying hardwood but cannot be sanded and refinished • installed with a click-lock method Bamboo flooring • floor manufactured from the bamboo plant and is a type of hardwood flooring, though technically not a wood • known to be durable and environmentally friendly • available in many different patterns, colors, and textures.
- 43. Wood flooring Cork flooring • flooring material manufactured from the by-product of the cork oak tree • considered to be eco-friendly since the cork oak tree bark is stripped every nine to ten years and doesn't damage the tree. • comes in both tiles and planks, and can have glue or glues-less installation.
- 44. Laminate • a floor covering that appears similar to hardwood but is made with a plywood or medium density fiberboard ("MDF") core with a plastic laminate top layer • HDF laminate consists of high density fiberboard topped by one or more layers of decorative paper and a transparent protective layer • Laminate may be more durable than hardwood, but cannot be refinished like hardwood • Laminate flooring is available in many different patterns which can resemble different woods or even ceramic tile. • It usually locks or taps together. • Underlayment is required for laminate flooring to provide moisture and noise control.
- 45. Hard flooring • a family of flooring materials that includes concrete or cement, ceramic tile, glass tiles, and natural stone products. • Ceramic tile - clay products which are formed into thin tiles and fired. Varieties of ceramic tiles include quarry tile, porcelain, and terracotta. • Stone flooring is uses a similar installation method to ceramic tile. • Slate and marble- stone flooring that requires polishing and sealing. • Terrazzo (Stone aggregates)- can also be used instead of raw cut stone • Porcelain stoneware can be used instead of natural stone. It’s a ceramic material like a tile • Concrete or cement finished floor - used for its ability to be treated for different feel and its durability, such as polished concrete. Epoxy resurfacing of concrete flooring is used to update or upgrade concrete floor surfaces in commercial and residential applications.
- 46. Resilient flooring • made of materials that have some elasticity, giving the flooring a degree of flexibility called resilience • Resilient flooring includes many different manufactured products including linoleum, sheet vinyl, vinyl composition tile (VCT), cork (sheet or tile), and rubber. • Performance surfaces used for dance or athletics are usually made of wood or resilient flooring. • PVC and polypropylene are becoming more popular in specialty applications such as trailer flooring and garage flooring.
- 47. Seamless chemical flooring • Many different seamless flooring materials are available such as - latex, polyester, urethane or epoxy compounds which are applied in liquid form to provide a completely seamless floor covering. • These are usually found in wet areas such as laboratories or food processing plants.
- 48. Furnishing Hard furnishing • Furniture should be planned well to follow hotel design in order to feel united. • The most important thing is that hotel furniture must anticipate and accommodate hotel guest needs. • A hotel facility includes bedroom, swimming pool, bar, fitness center and others. In every existing facilities at the hotel is closely associated with furnishing especially hotel furniture. • First-class hotel furniture should have the best characteristics for furniture that can be used for a long time.
- 49. Furnishing Points to be considered in choosing furniture • Function: Hotel furniture must optimally function to make hotel guests feel comfortable and sincere in the hotel. • Style: Hotel furniture style usually adjusted with hotel design. Style hotel furniture includes contemporary, classic, casual, tropical, Asian, American and others. • Comfort: comfort is important in order to make guests feel comfortable. All the furniture should also be comfortable and aesthetically pleasing. Cleanliness of the furniture should also be checked regularly • Quality: quality material, properly produced, great in finishing makes quality furniture which will last for many years and less maintenance that will not affect hotel monthly budget much.
- 50. Furnishing Hotel Room Furniture Headboard TV Furniture: one of the hotel room furniture that cannot be left out in the room. Luggage Rack: to put a suitcase or luggage for easy to grasp. Nightstand: serve as a barrier between two mattresses and also used to put small items such as phone or car keys nearby so that it is easy to pick it up. Dressing table and chair Love seat and coffee table: addition furniture where Love seat or two seater sofa are placed against the window with coffee table in front of it. Wardrobe Mini Bar Furniture: must placed furniture (not to mention for low rated hotel). Guests can store food, beverages or even medications that must be stored in cold temperature.
- 51. Furnishing Soft Furnishings • include fibres that are used for curtains, loose covers, cushions, bedspreads and quilts. • contribute greatly to the appearance of the room by bringing to its colour, pattern and texture. • Some articles in addition provide warmth and comfort. • Each article is subjected to variable amount of wear and tear.
- 53. - is the space which influence guest the most as they are likely to spend the greatest amount of their time - Instead of studying to add features, more often analyze the elements to eliminate - test every individual piece that add value to the guestroom and to the guest experience - Major planning goal – maximize the amount of saleable guestroom space and minimize the circulation and supporting areas. Guest room (Important)
- 54. - must be designated no. of guestroom - Guestroom and service elevator should be conveniently located - Stairways must be meet the building code - Adequate(enough) linen storage should be provided - Small electrical and telephone equipment closets are usually necessary Guestroom Floor Planning
- 55. 1. Double loaded slab - Most common configuration/ most efficient where rooms are laid out on the both sides of a central corridor - About 70% of the gross floor area devoted to guestroom - Has minimum corridor space per guestroom - Back to back bathrooms and many options for elevator and stairway placement - low-rise hotels with one to three stories typically use a design with guestrooms on both sides of a corridor Guestroom Floor Configuration
- 56. 2. Tower Plan - Rooms are grouped around the central vertical core - The most compact with guest room facing outside - About 65% of the gross floor area devoted to guestroom 3. Atrium Plan - rooms with a single loaded corridor encircling a multistory lobby space - The least efficient, with single loaded corridor overlooking the lobby - About 60% of the gross floor area devoted to guestroom Guestroom Floor Configuration
- 57. 1. Bed- Determine the exact room mix for the hotel, provide adequate spacing including bedside table and adequate lighting, consider TV viewing angle 2. Work area – Provide a desk or worktable, consider chair height and comfort and provide a phone and adequate lighting 3. Lounge area- Provide a soft seating group, consider comfort, lighting, tables, TV viewing angle, and adequate space for folding sofa, assess need for mini bar 4. Clothes storage/dressing area- Determine requirement for drawer space, the size of the closet and luggage storage need, provide full length mirror 5. Bathroom – select bathroom fixtures and accessories consider light, counter space, ventilation, and finishes 6. Décor- Evaluate furniture, fixture and equipment(FF&E)- carpet, wall covering, sheer and black out drapes, bedspreads 7. Other- screen views into guestroom from corridor, provide a separate dressing area, assess the need for balcony, adjoining room Basic Design criteria
- 58. - is one of the greatest challenges in hotel design - 65 and 85 percent of the total floor area - Maximize the amount of saleable guestroom space - minimize the horizontal circulation, and necessary support area. - chief goal for hotel planners is to find an efficient floor plan for guest rooms Planning of the guest room
- 59. - Guest-room planning comprises several important architectural objectives - The architect should select a particular plan configuration and orient the building to 1. enhance the appearance and visibility of the structure, 2. reduce energy costs 3. accommodate possible future expansion ( In case of high lodging demand or owner wants to add room there should be the provision by extending the guest-room wings, adding additional floors, or building a new structure.) Planning of the guest room
- 61. - The most prominent (important) of the hotel’s space - One of the key planning objective is to cluster the public facilities like- restaurant, lounges, function rooms, front desk, guest elevator and so forth around the lobby (to ensure that hotel guest can find the various facilities with minimum difficulties) - when a guest linger (spent long time) in it, it serves as an informal gathering space - Also functions as a control point, which the staff visually oversees access through the building Lobby
- 62. 1. Entrances: consider additional exterior entrances for the main lobby, banquet facilities, restaurants, health club, or other high traffic areas 2. Front Desk Location: Locate the desk so that it is immediately visible to the entering hotel guest and so that desk personnel can visually oversee access to the passenger elevators. 3. Office access: Provide entrances to the front office, safe deposit area, executive offices, and sales and catering offices. 4. Guest elevators: locate elevators close to the front desk and the main entrance and provide sufficient elevator lobby space for handling luggage. Lobby design and planning criteria
- 63. 5. Seating area: provide a seating area near the desk and entrance including some private seating groups, locate additional seating contiguous with the lobby bar. 6. Circulation: establish clear paths to the front desk, elevators, restaurants and bars, meeting and banquet area; where possible, separate hotel guest traffic from convention- oriented visitors. 7. Retails areas: provide lease space convenient to the guest circulation areas or with exterior frontage. 8. Bellman/Luggage: Position bellman station near the front desk, elevators, and front entrance; locate luggage storage nearby. 9. Support Functions: locate such accessory functions as toilets, coats, house phones, public phones, meeting director, and assistant manager’s desk conveniently in relation to other areas. Lobby design and planning criteria
- 64. Lobby Planning Checklist Front desk area Stations for registration, cashier, information Assistant manager’s desk Bellman station, luggage cart storage Luggage storage House and pay phones Seating area Seating capacity and type Food or beverage service Water feature or other focus
- 65. Lobby Planning Checklist Circulation Access to public elevators Access to restaurants and lounges Access to function rooms Access to recreation facilities Access to retail shops and other public area Access to parking garage Retail area Sundries shop (newsstand, toiletries, souvenirs) Travel services (city tours, airlines, rental cars) Clothing (men, women, specially shops) Gifts (jeweler, florist, toy, books) Other service (bank, copy center)
- 66. Size of desk: Provide individual work stations each 6ft (1.8m) long for registration and cashier; assume two stations for 150 rooms, one more for each additional 100 rooms. Queuing space: Provide sufficient space in front of the desk for guests to line up; for convention hotels provide at least 20ft (6.1m) clear of circulation. Assistant manager’s desk: if required, provide a desk, seating and storage near the front desk for concierge or assistant manager; consider making the desk a major decorative feature within the lobby. Bellman station: provide a bellman station near the front desk and main entrance. Lobby design and planning
- 67. Luggage storage: provide a lockable storage area adjoining the bellman station with shelving for checked luggage; provide direct access to the curb. Telephones: include house phones close to the front desk and public phone convenient to the lobby, approximately 1 per 100 rooms. Furniture and fixtures: establish ambience of lobby area by providing special millwork detailing and finishes, front desk, bellman station, assistant manager’s desk and furnishings(lounge seating, decorative fighting, artwork) to establish the image of the hotel.; Lobby design and planning
- 68. Kitchen and Restaurant design and Planning
- 69. Points to be considered while designing a kitchen • Should be adjacent to the service area. • Corner location makes it convenient for receiving supplies and removal of garbage. • Should be situated over the ground to avoid flooding, drainage blockage/backflow. Should not be in basement areas where humidity, heat of kitchen render it prone to dampness, insect and pest infestation. Kitchen
- 70. 1. Drainage: • Efficiency of the drainage system determines the hygiene and sanitation of kitchen environment to a large extent. • Fat and grease get collected in drains restrict flow of water – all kitchens should be fitted with grease traps on all drainage inlets to prevent backflow or blockage. • Taking care on this during layout planning can prevent unnecessary recurring expenses during operation. • Drain pipe should be 10 to 15 cm. in diameter. Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 71. Electricity and Gas Connections: • Electric and gas points to be provided in a kitchen must be in confrontation with the plan of the equipment and also for the future plan • Depending on the size of the catering units, the requirement of power and light points may vary • For large kitchens it is safer and economical to have a pipeline gas supply with meter, avoiding changing of gas cylinders in between. Gadgets are available which indicates the quantity of fuel in each cylinders, helps the changing pattern • It is wise to make provision for more than one type of fuel in the kitchen to cope with failure and shortages. Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 72. Water Supply: • Provision for both hot and cold running water is necessary – this has to be made at the structural stage. (Smaller kitchens may have water heater above sink unit may be enough) Floors : • Should be smooth, but not slippery, hard wearing, free from joints, not easily damaged by spillage, easy to clean, preferably in dark plain color with appearance and durability factor Walls: • Hard plaster with emulsion, gloss paint, plastic finish, tiles whatever may be the material, the walls should be smooth, easy to clean, and impervious to moisture. Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 73. Ceilings: • Ceiling finish should be heat resistant. • A plaster finish is most suitable, though it requires frequent redoing. • While choosing finishing for walls and ceilings one must remember that dark colors reduce the level of illumination and affect visibility in kitchens. Work Surface • All work surfaces should be hard-wearing, smooth, and impervious. • Stainless steel is by far the best among work surfaces in the kitchens, though the initial cost is higher. • Marble though expensive is ideal as a work surface for food preparation work, because of its hardwearing and hygienic qualities, and beauty. Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 74. Lighting: • It should be designed to give the best possible illumination. • Apart from overall lightings, fittings need to fix directly above work tables and food preparation areas. • Recommended illumination for performing a task is 500 fluxes. • The lights should be mounted at height not less than 2.4 meters from the floor and the fittings not more than 2.2 meters apart. • Note:- (Luminous flux is a measure of the power of visible light produced by a light source or light fitting). Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 75. Ventilation: • In kitchen it is very important to prevent the process of condensation which leads to formation of moulds and bacteria resulting in contamination of food. • Proper ventilation is not only important for a fresh and comfortable environment, but vital to the preparation and provisions of safe and healthy food. • Modes of ventilation: There are two types of mode, e.g., Windows and Ventilator hoods. Ventilation plays an important role in kitchen especially where fumes are generated. Feature to be considered while designing a Kitchen
- 76. Exterior
- 77. Exterior elements of the building • Roof • Exterior walls(including door and windows) • structural frame (beam+ pillar) • foundation - Various part of the building must work together, if any one part is neglected, it can have adverse effect on the others - Function of the building are to provide the usable space and shelter people, equipment, fixtures and furnishing from the weather. Exterior design
- 78. - Critically important part of the building - Primary purpose- to keep water from penetrating below the roof material - Often ignored until it leaks (if water gain access to the building through the roof system. Great damage can result, first to the roof and later to the structural element) • Interior finishes are also quickly destroyed by roof leaks (eg- new paint job is ruined by few minutes leakage) • Life expectancy of roof depends upon the quality of the construction material, the skills of the builders, and the effectiveness of the preventive maintenance Roof
- 79. - Composed of a deck and a covering - Deck is the structural material the covering is placed upon, usually made of wood, metal and concrete - Roof system is the combination all the component of the roof that act together to create a weather and climate barrier for the building - Common types of roof material- asphalt, fiberglass, shingles and roll roofing, split wood shakes, sawn wood shingles, clay and concrete tile, steel and aluminum and various types of built-up and single ply material - In addition, many roofing system include insulation as part of the roof system which also plays a key role in controlling energy usage of the building Roof (Basic structure)
- 80. • Two basic function : 1. To enclose the usable parts of the building 2. To provide support for higher floor and roof system • Built to provide protection against the weather and to support the building • Constructed of various material like – timber, concrete and steel • Wall can be classified as bearing (supporting) and non-bearing (depending on whether they support other building elements or only themselves) • Preventive Maintenance – Includes Painting, cleaning and inspection Exterior Walls
- 81. • Openings are made through a building’s exterior walls for windows and door • Need sealants around their edges to keep moisture out and weather-stripped to prevent heat loss or gain Windows and doors
- 82. • Door may be wooden or metallic, solid or hollow and some doors are mostly glass such as revolving doors • Revolving doors - they don’t get the wear regular doors receive from constantly being opened and closed as they reduce the amount of outside air that gets into the building. • Fire safely codes may stipulate that a regular door be installed next to a revolving door as an emergency exits Windows and doors
- 83. • Skeleton that provides support for the entire building • Failure in the structural frame leads problem to the entire building • Typical construction material used in structural frame includes – steel, concrete and ordinary or heavy timber. Structural Frame
- 84. • Traditionally constructed of stone or concrete and rest on a solid, underground footing base • If firm foundation material is not available at a reasonable depth, it may be necessary to go deeper by using piles • Designed to carry the various loads of the building: dead load (weight of building), live load (weight of people, furniture, equipment) and load and stresses imposed by nature(wind, rain, snow, earthquake) • Foundation walls also serves as basement wall. In this case it take on the added load caused by lateral pressure from the soil • Foundation walls serving basement wall be waterproofed Foundation
Editor's Notes
- The design of a hotel is one of the major considerations in planning of an efficient hotel Design is the process of planning the form and structure of a functional object. Designers are interested in human psychology, communication, interactive processes, visual perception, logic, cultural tendencies, historical movements and aesthetics Decoration is the process of furnishing or adorning an object with ornamental embellishments. Decorators are interested in dressing things up for aesthetic purposes, with no concern for functionality, clarity of communication, logic or interactive processes. Most decorators are hobbyists, people who have an interest or talent for choosing colors, patterns, furnishings and materials.
- Landscape An expanse of scenery that can be seen in a single view . A section or expanse of rural scenery, usually extensive, that can be seen from a single point of view.
- landscaping also refers to any activity that modifies the visible features of an area of land, including nature, natural, human element. Example – basketball court, canteen in the college itself Landscape requires expertise in horticulture and artistic design
- Bitumen - a tarred road surface, a black viscous mixture of hydrocarbons obtained naturally or as a residue from petroleum distillation. It is used for road surfacing and roofing.
- Form the first (and often last) impression of the quality of the hotel establishment from the exterior of the building and the grounds in with it is set An attractive, clean and well maintained appearance is a reassuring indicator of commitment to high standards with Creatively designed, inspirational gardens can influence whether a guest returns and/or recommends the hotel to others Sets the visual tone for the entire property A large part of the first impression guest receive Allowing the ground to decline into mediocrity will severely diminish the property’s attractiveness which may result in lower revenues. Grounds should always be kept at it best to keep the property’s “curb appeal” high Mediocrity- quality or state of being average quality; not very good Revenues – income Curb appeal - attractiveness of the exterior of a residential or commercial property
- Objective – Achieve Environment- (environmental restoration as in environmental remediation) Greenery, fresh air, water restoration, humidity/moisture Social – provide different kind of space for different activities (swimming pool- recreation, pathways- jogging, yoga and meditation spaces, outdoor dining/bar- parties, gathering, eating spaces, playing space for kids Aesthetic – pleasant view, comfort/relaxing/calming/enjoyable environment Economy – increase the revenue, guest,
- Place where guests and visitors can relax, take exercise, dine and be entertained, as well as being a potential resource for produce and flowers Provides habitat for wildlife, shade and cool in hot climates, protection from wind and, in cities, a haven from traffic fumes and dust The ground need to accommodate convenient areas for guest parking, for deliveries – collection and the storage of equipment. These need to be incorporated thoughtfully into the landscape
- Bar, swimming pool, sunbath, Barbeque Garden, Camping area, spa and massage, parties, wedding, kid friendly zone, sports (like golf. Long tennis, badminton), (jogging, meditation, yoga, hiking, rafting ) gazebo is where you sit to appreciate your landscape,
- Area where a vehicle that one is driving brings to a halt and leave it temporarily, typically in a car park or by the side of the road
- Most common and cost effective parking facility and depends on available space and its configuration. Low cost land favor for on grade parking facility. requires a lot of maintenance in respect of property management. Break of surface is common problem which can be serious if not repaired immediately.
- A multi-story park is a building designed for car parking and where there are a number of floors or levels on which parking takes place The movement of vehicles between floors can be affected by: interior ramps - the most common type exterior ramps - which may take the form of a circular ramp vehicle lifts - the least common automated robot systems - combination of ramp and elevator
- designed to minimize the area required for parking cars. An automated parking system will transport vehicle to and from parking spaces. mechanical device that multiplies parking capacity inside a parking lot. Parking systems are generally powered by electric motors or hydraulic pumps that move vehicles into a storage position. Automatic multi-storey automated car park systems are less expensive per parking slot, since they tend to require less building volume and less ground area than a conventional facility with the same capacity. systems reduce pollution — cars are not running or circling around while drivers look for parking spaces.
- Underground parking refers to parking located below grade within an occupied building. Additional Structural Requirements: Below grade extension of the building structure to accommodate basement parking is required. This involves additional excavation, structural frame, floor slabs above, sloped vehicle access ramps, and basement perimeter walls and partitions separating parking from other building enclosed areas. Ventilation: The parking area is generally supplied with unconditioned air utilizing multiple speed fans Parking Management: Usually pre-manufactured booths with transaction windows and deal trays are installed at vehicular entrances/exits to manage entering and exiting vehicles.
- Aesthetics The surface parking lot should not dominate the building site a combination of planning, architectural, and landscaping elements, the visual impact on the surrounding streets and developments can be minimized textures, patterns, and colors are encouraged in the design of surface parking in order to provide breaks in large monolithic areas of pavement distinguish between pedestrian and vehicular movement within the parking area. Parking area should be paved (most popular: concrete) Signage to indicate all major internal pedestrian access points as well as external major roads and buildings In surface parking lots, pavement markings should be reflective paint and traffic control signage is usually reflective metal
- maneuvering - move skilfully or carefully.
- Exterior Security Protection : CCTV cameras, limit vehicular access control Lighting : to provide security and access within the parking area at night and in basement
- Types of flooring:- 1. Mud flooring 2. Brick flooring 3. Marble Flooring 4. Granite flooring 5. Parketing 6. Terazzo flooring
- Endurance- the capacity of something to last or to withstand wear and tear.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Terrazzo- flooring material consisting of chips of marble or granite set in concrete and polished to give a smooth surface.
- Therefore, it is natural to try to improve the quality or functionality of guest room One of the difficulties ( example – a decorative valence added to the drapery treatment must be added in every room or a marble vanity counter appears in every bathroom, a more expensive nightstand or bedside lamp in every room). SO the cost multiplies Guestroom usually represent between 65- 85% of the total hotel area, any savings in the construction or furnishings of guest room is multiplied many times. (eg- a less expensive window treatment Designer has to carefully balance the functionality, aesthetic value and cost of each individual piece of furniture or decorative elements to test whether it adds value to the guestroom and to the guest experience
- The planning requirement for the guestroom floors are relatively But the way these are arranged can easily affect the total floor area by 10 percent. Therefore skill planning makes a substantial impact on the efficiency of the guestroom area. (Eg- the same 250 room hotel could vary by 10,000- 15,000 sq ft due to the entirely to the level of planning efficiency) The additional area translates into $1- $2 million in additional to the project cost depending upon the location and quality level of the hotel. Architects/designer must understand the importance of efficient and economical planning of the guestroom whereas hotel developer should insist to refine and modify the design until it meets the sufficiently high standards
- The money saved in the construction by careful and economical planning of the guest room floors may be enough to make a marginal project profitable or to pay for a larger guestroom or better quality furniture or additional public space as conference, recreational facilities
- Prominent – Important Cluster- gather, collect, group, come together, assemble; Linger- spend a long time over
- a concierge assists guests by performing various tasks such as making restaurant reservations, booking hotels, arranging for spa services, recommending night life hot spots, booking transportation
- a concierge assists guests by performing various tasks such as making restaurant reservations, booking hotels, arranging for spa services, recommending night life hot spots, booking transportation
- a concierge assists guests by performing various tasks such as making restaurant reservations, booking hotels, arranging for spa services, recommending night life hot spots, booking transportation
- a concierge assists guests by performing various tasks such as making restaurant reservations, booking hotels, arranging for spa services, recommending night life hot spots, booking transportation
- Hard plaster with an emulsion finish is most suitable as it is smooth and easy to clean. Ordinary emulsion paints are not washable, and removing marks or stains could the smudge the wall. Gloss paints are washable, but tend to show faults in old plaster work. Where the wall is near steam equipment, a plastic finish is better than tiles as it is non-absorbent and condensation from steam does not damage the surface. Any particular type of finish cannot be specified for a kitchen because the manager of the kitchen must decide what properties should be given priority
- Hard plaster with an emulsion finish is most suitable as it is smooth and easy to clean. Ordinary emulsion paints are not washable, and removing marks or stains could the smudge the wall. Gloss paints are washable, but tend to show faults in old plaster work. Where the wall is near steam equipment, a plastic finish is better than tiles as it is non-absorbent and condensation from steam does not damage the surface. Any particular type of finish cannot be specified for a kitchen because the manager of the kitchen must decide what properties should be given priority
- Preventive maintenance includes – regular inspection (before and after the most severe climatic season each year and after each major storm removal of all foreign objects (tree limbs, leaves, dirt and so on) repair of blisters (pockets of air or water between layers of roof system) exclusion of ponded water, maintenance of all flashing and maintenance of ballast. Inspection As a part of the inspection process, the condition of the roof should be documented This is especially true if the leak is found It is then impotant to locate the spot and write down the condition under which the leak occurred
- Sealants- material used for sealing something so as to make it airtight or watertight. A casement is a window that is attached to its frame by one or more hinges Glass in windows is referred to as glazing Tinted glass has been treated with a film or coating to reduce the transmission of light through it.
- .
- .
- .