Periodontal pocket
- 2. CONTENTS • Definition • Classification • Clinical features • Pathogenesis • Histopathology • Periodontal disease activity • Site specificity • Pulp changes associated with periodontal pockets • Relationship of attachment loss and bone loss to pocket depth • Area between base of pocket and alveolar bone relationship of pocket to bone • Periodontal abscess • Periodontal cyst • Conclusion • Reference
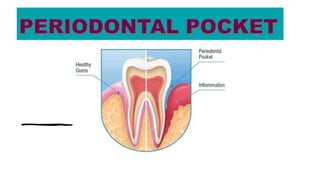
- 3. INTRODUCTION • Gingival sulcus is the space between the neck of the tooth and the circumferential gingival tissue. • Sulcus , when it deepens { as in periodontal disease } due to the apical migration of junctional epithelium, accompanied by attachment loss, it is referred to as periodontal pocket. • Probing depth of clinically normal gingival sulcus = 2-3mm
- 4. DEFINITION • The Periodontal pocket is defined as a pathologically deepened gingival sulcus . - CARRANZA 1OTH edition • It is one of the most important clinical features of periodontal disease.
- 6. CLASSIFICATION Deepening of the gingival sulcus may occur by Coronal movement of the gingival margin (gingival enlargement) Apical displacement of the gingival attachment A combination of the two processes
- 7. Acc. To MORPHOLOGY Acc. To NATURE OF SOFT TISSUE WALL Acc. To NUMBER OF SURFACES involved Acc. To DISEASE ACTIVITY CLASSIFICATION
- 8. Acc. To NATURE OF SOFT TISSUE WALL Edematous pocket Fibrotic pocket Acc. To DISEASE ACTIVITY Active pocket Inactive pocket Acc. To MORPHOLOGY Gingival Pocket Periodontal pocket Acc. To NUMBER OF SURFACES involved Simple Compound Complex
- 9. 1.ACCORDING TO MORPHOLOGY A. Gingival pocket (pseudo pocket)- This type of pocket is formed by gingival enlargement without destruction of the underlying periodontal tissues. The sulcus is deepened because of the increased bulk of the gingiva. B. Periodontal pocket - This type of pocket occurs with destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues. Progressive pocket deepening leads to the destruction of the supporting periodontal tissues and loosening and exfoliation of the teeth. Periodontal pocket Suprabony pocket Intrabony pocket
- 10. Gingival Suprabony Intrabony pocket pocket pocket
- 11. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SUPRABONY & INTRABONY POCKETS • SUPRABONY POCKET Supracrestal or supra alveolar. Base of the pocket is coronal to the level of alveolar bone. Lateral wall consist of the soft tissue alone. • INTRABONY POCKET Infrabony, subcrestal, intraalveolar. Base of the pocket is apical to crest of alveolar bone. Lateral wall consist of the soft tissue and bone.
- 12. Suprabony pocket ØHorizontal pattern of bone destruction. ØTranspetal fibers are arranged horizontally. ØPDL fibers [facial & lingual] follow normal horizontal-oblique course Intrabony pocket ØVertical (angular) pattern of bone loss. ØTranseptal fibers are arranged obliquely. PDL fibers follow angular patern of adjacent bone
- 13. ACCORDING TO THE NUMBER OF SURFACES INVOLVED SIMPLE POCKET- It involves only one tooth surface. COMPOUND POCKET- It involves two or more tooth surface. COMPLEX POCKET- Where the base of the pocket is not in direct communication with the gingival margin. It is also known as a spiral pocket. Simple Compound Complex SIMPLE POCKET- It involves only one tooth surface. COMPOUND POCKET- It involves two or more tooth surface. COMPLEX POCKET- Where the base of the pocket is not in direct communication with the gingival margin. It is also known as a spiral pocket.
- 14. CLINICAL FEATURES SIGNS-- • Enlarged, bluish – red thickened marginal gingiva with a 'rolled' edge. • A bluish red vertical zone from the gingival margin to alveolar mucosa. • Gingival bleeding and suppuration. • Tooth mobility. • Loss of stippling. • Diastema formation. Gingival bleeding Gingival suppuration
- 15. SYMPTOMS • Localized pain or "pain deep in the bone". • Usually painless but may give rise to localized /radiating pain or sensation of pressure after eating which gradually reduces. • A foul taste in localized areas. • Sensitivity to hot and cold. • Toothache in the absence of caries is also sometimes present. • A tendency to stuck material inter proximally. • Urge to dig a pointed instrument in the gums. • Feeling of loose teeth.
- 16. CORRELATION OF CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES OF THE PERIODONTAL POCKET CLINICAL FEATURES HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES 1. Gingival wall of pocket presents- i. Bluish red discoloration ii. Flaccidity iii. A smooth, shiny surface iv. Pitting on pressure i. Circulatory stagnation. ii. Destruction of gingival fibers & surrounding tissues. iii. Atrophy of epithelium. iv. Edema and degeneration. 2. Gingival wall may be pink and firm 2. Fibrotic changes 3. Bleeding is elicited by gently probing soft tissue wall of pocket 3. Increased vascularity, thinning and degeneration of epithelium, & proximity of engorged vessels to inner surface. 4. On probing, inner aspect of pocket is generally painful 5. Pus may be expressed by applying digital pressure. 4. Pain on tactile stimulation is caused by ulceration of inner aspect of pocket wall. 5. Pus occurs in pockets with suppurative inflammation of inner wall.
- 17. PATHOGENESIS Inflammatory changes in the C.T. OF gingival sulcus Collagenases and MMPs Activate fibroblasts for phagocytizing collagen Gingival collagen fiber destruction Proliferation of apical cells of J.E. along the root
- 18. PMNs volume reach 60% or more Detachment of the coronal portion of J.E. from the root Pocket formation
- 19. • Two mechanisms of collagen loss Collagenases & other enzymes secreted by various cells such as fibroblasts, PMNs leukocytes & macrophages, becomes extracellular & destroy collagen; these enzymes that degrade collagen and other macromolecules into small peptides are called MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES Fibroblast phagocytize collagen fibers by extending cytoplasmic process to the ligament- cementum interface & degrade the inserted collagen fibrils & the fibrils of the cementum matrix.
- 20. • The transformation of a gingival sulcus into periodontal pocket creates an area where plaque removal becomes impossible , & the following mechanism, is followed Plaque accmulation Gingival inflammation Pocket formation Area difficult to clean
- 25. HISTOPATHOLOGY 1. SOFT TISSUE WALL I. Connective tissue Edematous and densely infiltrated with plasma cells (approx. 80%), lymphocytes and a scattering of PMNs. Blood vessels - increased in number, dilated and engorged. Exhibits varying degrees of degeneration. Shows proliferation of endothelial cells with newly formed capillaries, fibroblast and collagen fibers. ii. Junctional epithelium: At the base of the pocket is usually much shorter Coronoapical length is reduced to only 50-100 μm.
- 26. iii. Lateral wall: Most severe degenerative changes. Epithelial buds or interlacing cords of epithelial cells project from the lateral wall into the adjacent inflamed C.T. & apically than the J.E. Densely infiltrated by leukocytes & edema from the inflamed C.T. Cells : vacuolar degeneration and form vesicles. Ulceration and suppuration.
- 28. 2. BACTERIAL INVASION Studies have shown that bacterial invasion occurs in the apical & lateral areas of the pocket wall. Intercellular spaces of the epithelium - Filaments, rods and coccoid organism with predominant gram-negative cells • Porphyromonas gingivalis • Prevotella intermedia , • Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
- 29. 3. MICROTOPGRAPHY OF GINGIVAL WALL 1. AREAS OF RELATIVE QUIESCENCE- showing flatten surface with minor depression and mounds and occasional shedding of cells. 2. AREAS OF BACTERIAL ACCUMULATION-presenting as epithelial surface depressions, with abundant debris and bacteria clumps penetrating into the enlarged intercellular spaces. These bacteria are usually cocci, rods, and filament with few spirochetes.
- 30. 3. AREAS OF EMERGENCE OF LEUKOCYTES- where leukocytes appear in the pocket wall through holes located in the intercellular spaces. 4. AREAS OF LEUKOCYTE- BACTERIA INTERACTION- where numerous leukocytes are present & covered with bacteria in an apparent process of phagocytosis. Bacterial plaque associated with epithelium is seen either as an organised matrix covered by a fibrin-like material in contact with the surface of cells or as bacteria penetrating into the intercellular spaces
- 31. 5. AREAS OF INTENSE EPITHELIAL DESQUAMATION- which consist of semi – attached and folded epithelial squames , sometimes partially covered with bacteria. 6. AREAS OF ULCERATION- with exposed connective tissue. 7. AREAS OF HEMORRHAGE- with numerous erythrocytes. Areas of haemorrhage Areas of ulceration
- 32. 4. PERIODONTAL POCKET AS HEALING LESIONS • Periodontal pockets are chronic inflammatory lesions which undergo repair. • The condition of the soft tissue wall of the periodontal pocket result from the interplay of the destructive and constructive tissue changes. • Their balance determine clinical features of the pocket wall. Constructive tissue changes Formation of C.T. cells, collagen fibers, appear more firm & pink Destructive tissue changes Fluid & cellular inflammatory exudate, pocket wall is bluish red ,soft, spongy & friable with smooth, shiny surface FIBROTIC POCKET EDEMATOUS POCKET
- 33. 5. POCKET CONTENTS Debris – microorganism and products ( enzymes, endotoxins, and other metabolic products) Gingival fluid Food remnants Salivary mucin Desquamated epithelial cells Leukocytes Plaque-covered calculus
- 34. 6. SIGNIFICANCE OF PUS FORMATION Secondary sign. Nature of the inflammatory changes. Not an indication of depth of pocket/ severity of destruction.
- 35. 7. ROOT SURFACE WALL • Cause pain •Recurrence of infection •Complicate periodontal treatment. CHANGES IN ROOT STRUCTURAL CHEMICAL CYTOTOXIC
- 36. A. STRUCTURAL CHANGES PATHOGENIC GRANULES AREAS OF INCREASED MINERALIZATION AREAS OF DEMINERALIZATION
- 37. I. PATHOGENIC GRANULES • Represents areas of collagen degeneration or areas where collagen fibrils have not been fully mineralized initially. II. AREAS OF INCREASED MINERALIZATION • highly mineralized superficial layer increase the tooth resistance to decay • associated with increased perfection of the crystal structure. III. AREAS OF DEMINERALISATION- • Commonly related to root caries , dominant organism is A. viscosus
- 38. B. CHEMICAL CHANGES • The mineral content of the exposed cementum is increased. Exposed cementum may absorb calcium, phosphorous & fluoride from its environment. Development of highly calcified layer that is resistant to decay. • The ability to absorb substance may be harmful, because absorb material may be toxic.
- 39. C. CYTOTOXIC CHANGES • Endotoxins found in the cementum of periodontally involved teeth. • Endotoxins limits the proliferation and attachment of fibroblasts to the diseased root surfaces.
- 40. Surface morphology of tooth wall with periodontal pocket
- 41. PERIODONTAL DISEASE ACTIVITY • Periodontal pockets go through periods of exacerbation and quiescence resulting from episodic bursts of activity followed by periods of remission. PERIODS OF REMISSION OR QUIESCENCE/INACTIVITY PERIODS OF EXACERBATION/ACTIVITY • Gram positive bacteria proliferates • Reduced inflammatory response • Little or no born and connective tissue attachment loss. • Build up of unattached log with its gram negative, motile, and anaerobic bacteria • Bone and connective tissue attachment loss • pocket deepens.
- 42. SITE SPECIFICITY Periodontal destruction does not occur in all parts of the mouth at the same time but rather on a few teeth at a time or even only some aspects of some teeth at any given time.
- 43. Pulp changes associated with periodontal pocket Spread of infection from periodontal pockets causes pathological changes in the pulp leading to painfull symptoms Involvement of the pulp occurs through either the apical foramen or the lateral canals in the root.
- 44. RELATIONSHIP OF ATTACHMENT LOSS & BONE LOSS TO POCKET DEPTH Pocket formation causes loss of attachment of the gingiva and denudation of the root surface. The severity of the attachment loss is generally, but not always, correlated with the depth of the pocket. This is because the degree of attachment lost depends on the location of the base of the pocket on the root surface, whereas the pocket depth is the distance between the base of the pocket and the Crest of the gingival margin.
- 46. AREA BETWEEN BASE OF POCKET AND ALVEOLAR BONE Normally, the distance between the apical end of the junctional epithelium and the Alveolar bone is relatively constant. The distance between the apical extend of the calculus and the alveolar Crest in human periodontal pockets is most constant, having a mean length of 1.97 mm. Wade, assessed the relation between pocket base, epithelial attachment and alveolar process and found that the distance from attached plaque is never less than 0.5 mm and never more than 2.7 mm.
- 47. Periodontal abscess A localised purulent inflammation in the periodontal tissues. Also known as - lateral or parietal abscess. Abcesses localised in the gingiva, due to injury to the outer surface of the gingiva, and not involving the supporting structures are called Gingival Abscesses.
- 48. MICROSCOPICALLY • localised accumulation of viable and non viable PMNs within the periodontal pocket wall. • PMNs liberate enzymes digest tissue & cells pus (present in center of the Abscess) • overlying epithelium exhibits intracellular and extracellular edema • invasion of leukocytes. • Chronic abscess when its purulent content drains into a fistula into the outer gingival surface
- 49. -PERIODONTAL ABSCESS FORMATION MAY OCCUR IN THE FOLLOWING WAYS- Extension of infection from a periodontal pocket Lateral extension of inflammation from the inner surface of periodontal pocket In a pocket that describes a tortuous course around the root, a periodontal Incomplete removal of calculus during treatment of a periodontal pocket After trauma to the tooth or perforation of the lateral wall of the root in endodontic therapy.
- 50. PERIODONTAL CYST • Uncommon • Lesion that produces localised destruction of the periodontal tissues along a lateral root surface • Most often in the mandibular canine-premolar area.
- 51. • The following possible etiologies have been suggested: 1. Odontogenic cyst 2. Lateral dentigerous cyst 3. Primordial cyst of supernumerary tooth germ. 4. Stimulation of epithelial rests of the periodontal ligament by infection from a periodontal Abscess or the pulp through an accessory root canal.
- 52. Asymptomatic Present as a localised tender swelling. Radiographically, radiolucent area bordered by a radiopaque line. Radiographic appearance cannot be differentiated from that of a periodontal Abscess.
- 53. Microscopically, the cyst lining maybe; A loosely arranged, non-keratinized, thickened, proliferating epithelium; A thin, non keratinized epithelium; or An odontogenic keratocyst.
- 54. CONCLUSION Understanding the etiopathogenesis, histopathology and progression of periodontal pockets is essential to provide the patient with the successful treatment outcomes and monitoring the response to therapy.
- 55. REFERENCE • CARRANZA 10th AND 13th EDITION • SHALU BATHLA textbook of PERIODONTICS