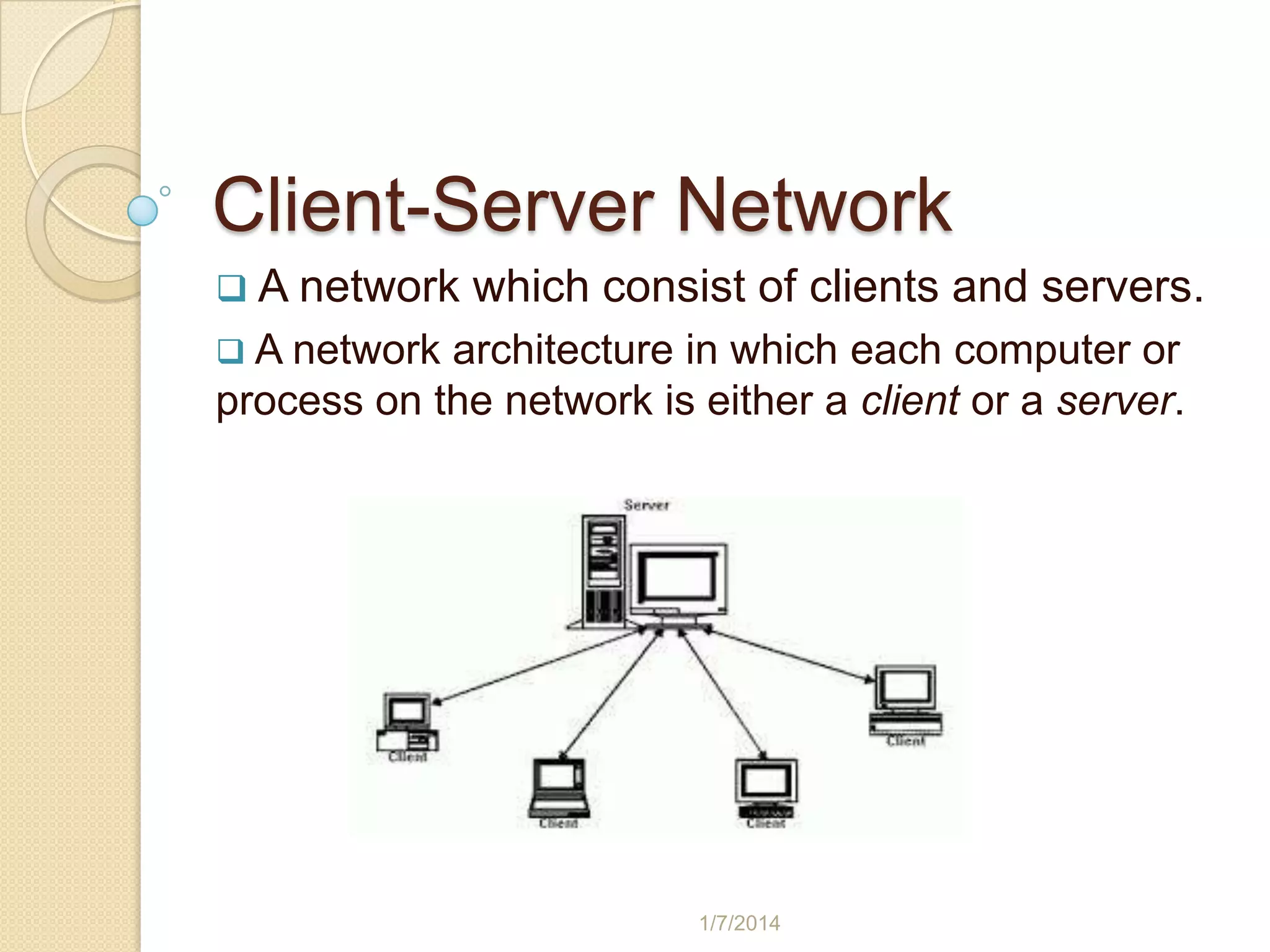
The document discusses client-server networks. In a client-server network, computers are either clients or servers. Servers provide services and control access to hardware/software resources, storing programs, data, and handling user authentication and access to stored files. Clients request resources from servers and can get, send, delete or modify files on a server. Different types of servers include application servers, message servers, proxy servers, database servers, web servers, and others like FTP, mail, virtual, telnet and news servers. Client-server networks have advantages like reducing traffic and providing faster responses, security and accessibility, but disadvantages include costs, single point of failure if server fails, and need for professionals for maintenance. An example of