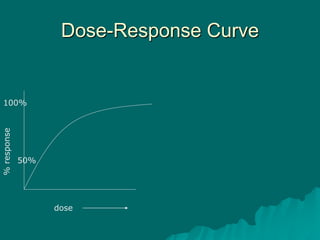
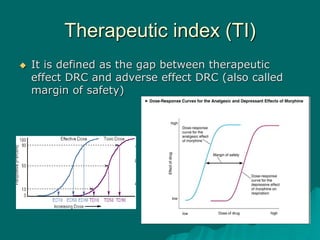
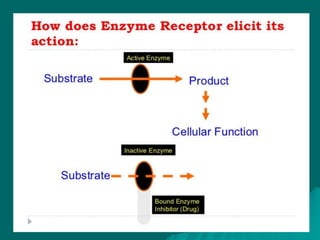
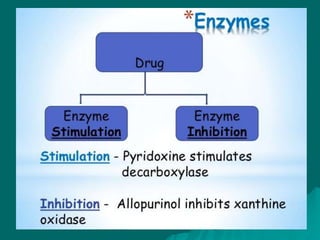
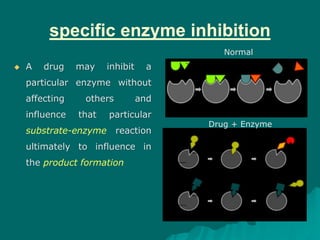
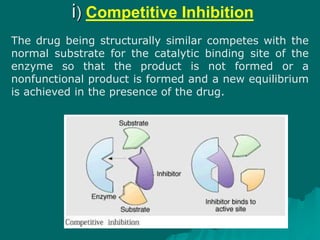
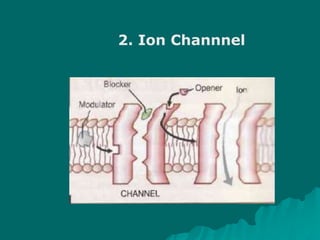
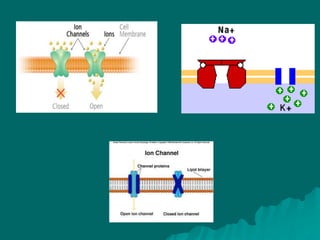
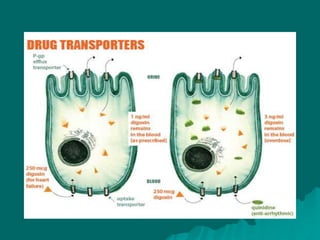
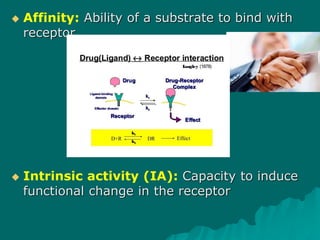
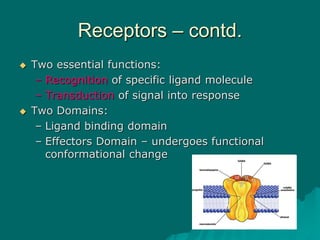
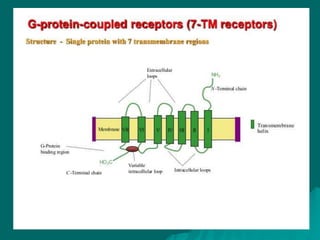
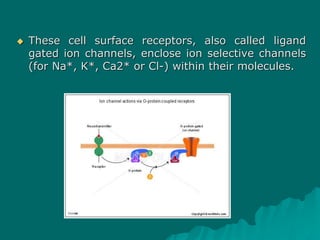
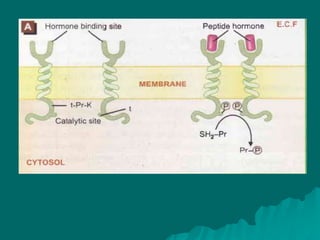
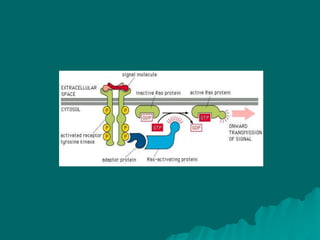
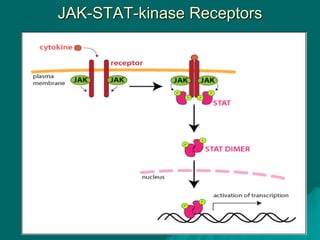
Pharmacodynamics is the study of how drugs affect the body, focusing on their biochemical and physiological mechanisms of action at both organ and cellular levels. Drugs primarily interact with targeted biomolecules such as enzymes, ion channels, transporters, and receptors to exert their effects, which may involve competitive or noncompetitive inhibition, among other mechanisms. The document also details various receptor types, their functions, and the concepts of dose-response relationships and drug interactions.































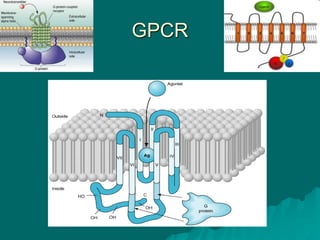








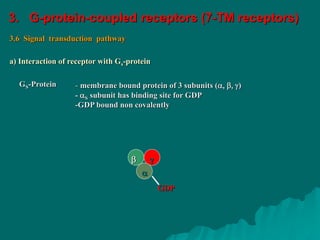






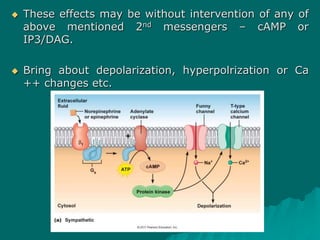
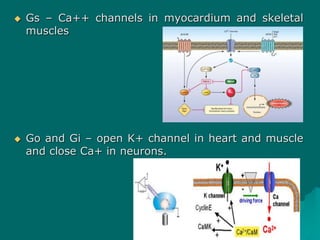





















![Dose-Response Relationship
Dose-plasma concentration
Plasma concentration (dose)-
response relationship
E =
Emax X [D]
KD + [D]
E is observed effect of drug dose [D], Emax = maximum response,
Kd = dissociation constant of drug receptor complex
When a drug is administered systemically, the
dose-response relationship has two components:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpharmacodynamics-201211094408/85/Pharmacodynamics-89-320.jpg)