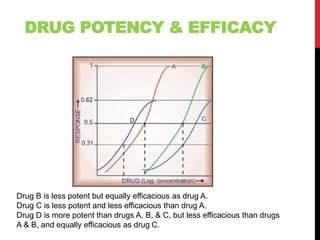
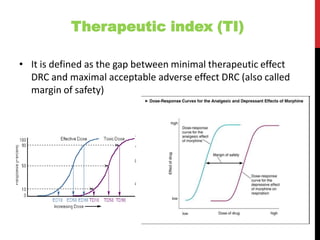
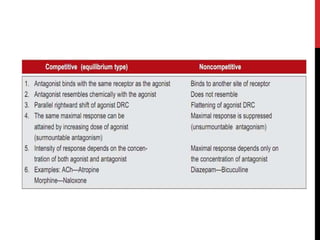
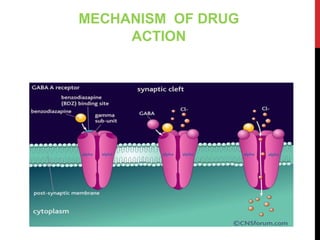
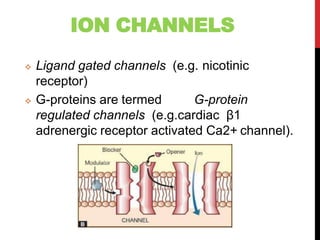
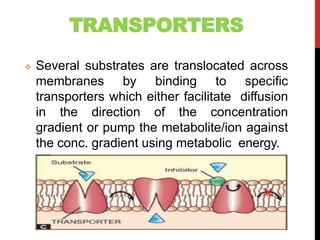
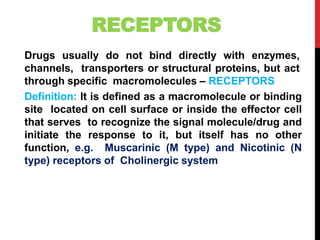
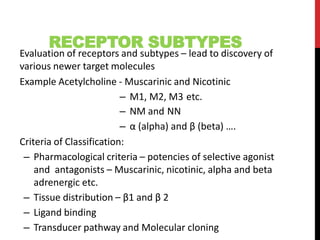
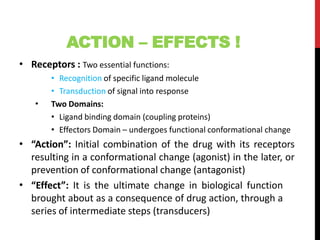
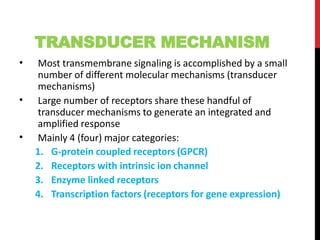
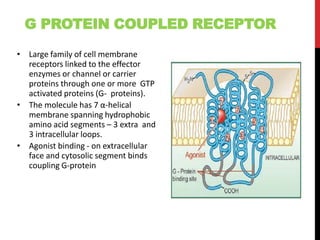
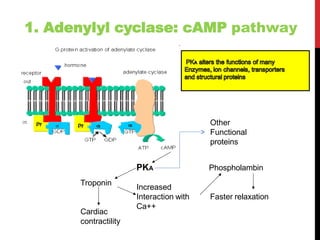
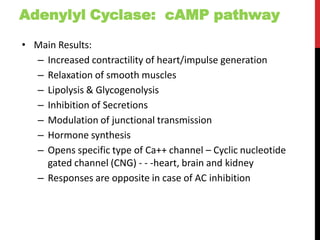
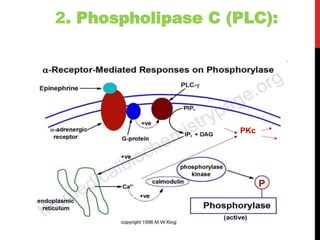
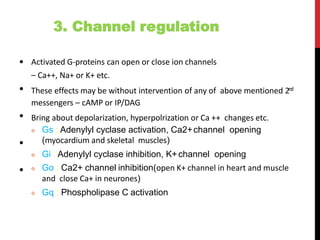
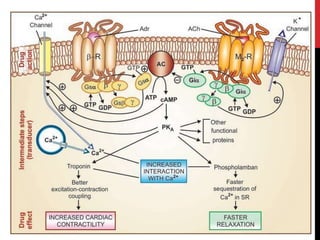
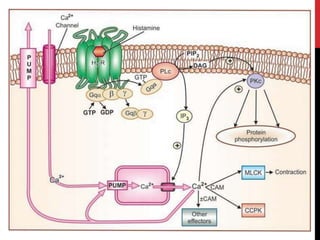
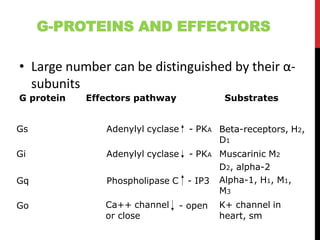
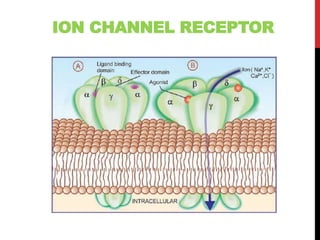
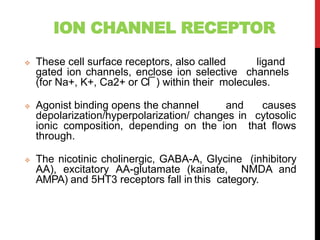
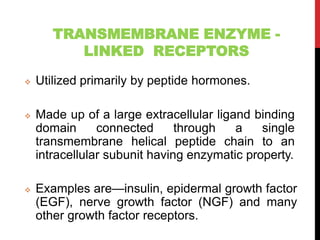
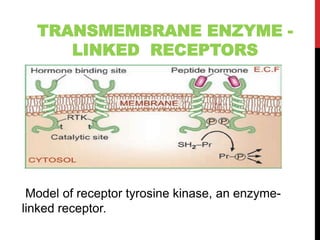
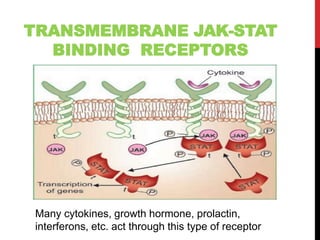
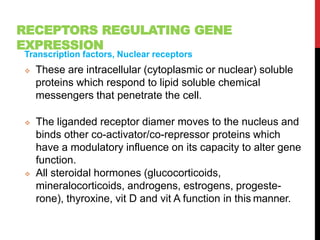
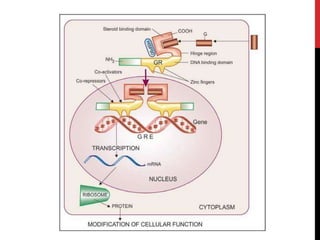
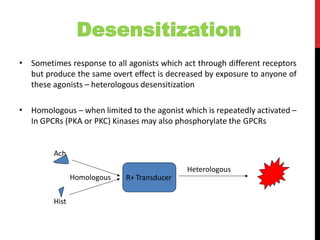
This document discusses pharmacodynamics and the mechanisms of drug action. It describes how drugs can act through physical/chemical properties, stimulation, depression, irritation, replacement or cytotoxic effects. However, most drugs act by interacting with biomolecules like enzymes, ion channels, transporters or receptors. The four main types of receptor-mediated drug actions are agonism, antagonism, partial agonism, and inverse agonism. Downstream effects are mediated through four major transduction pathways: G-protein coupled receptors, receptors with intrinsic ion channels, enzyme-linked receptors, and transcription factors.




















![Dose - Response Relationship
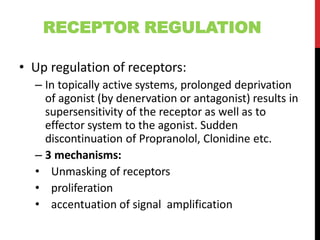
• Drug administered – 2 components of dose- response
– Dose-plasma concentration
– Plasma concentration (dose)-response relationship
• E is expressed as
Emax X [D]
Kd + [D]
E is observed effect of drug dose [D], Emax = maximum response,
KD = dissociation constant of drug receptor complex at which
half maximal response is produced
E max](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicsdp-200727064927/85/Pharmacodynamics-By-Dr-Debasish-Pradhan-49-320.jpg)
![Dose-Response Curve
dose Log dose
%response
%response
100% -
50% -
100% -
50% -
Emax X [D]
E =
Kd + [D]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicsdp-200727064927/85/Pharmacodynamics-By-Dr-Debasish-Pradhan-50-320.jpg)