Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


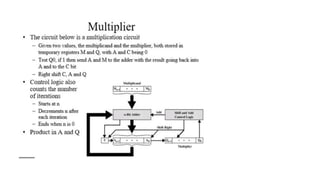

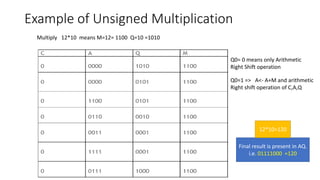
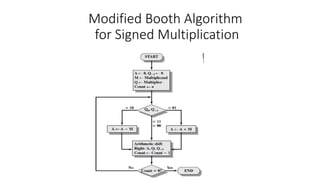




The document outlines the Booth algorithm for multiplication, which simplifies the multiplication process by using repeated addition, analogous to traditional pen-and-paper methods. It differentiates between unsigned and signed multiplication techniques, detailing how the algorithm operates with examples and illustrating the final result in binary format. Additionally, it includes assignments for computing multiplication using both the standard and modified Booth algorithms.








