Embed presentation
Download to read offline

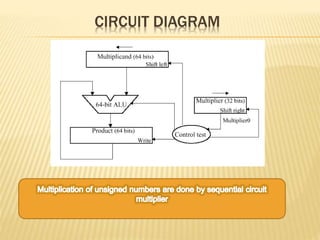

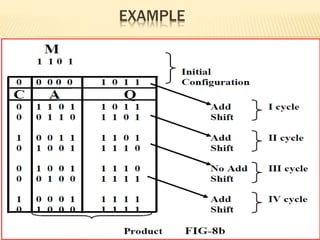
A sequential circuit multiplier loads a multiplicand into the M register and multiplier into the Q register. It initializes the C and A registers to zero. It then repeats the following steps the number of times as the number of bits in the multiplier: if the least significant bit of Q is 1, it adds M to A and stores the carry in C, otherwise it just shifts the contents of the CQA registers right by one bit. After all steps, the high-order half of the product is in A and low-order half is in Q.



