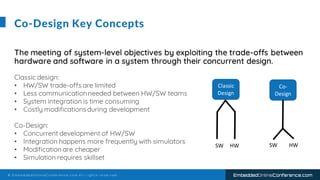
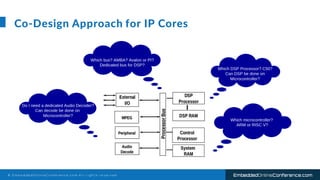
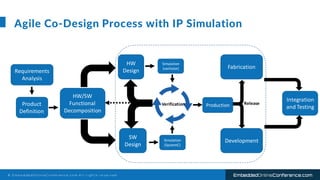
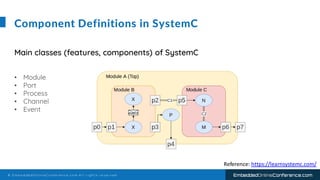
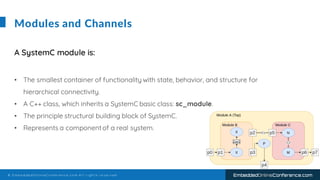
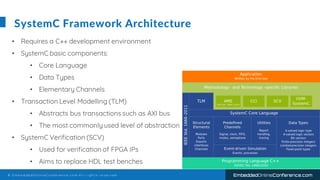
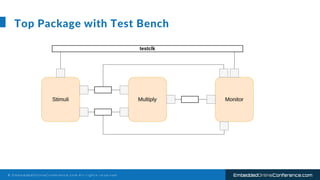
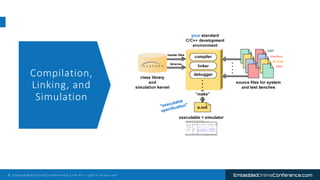
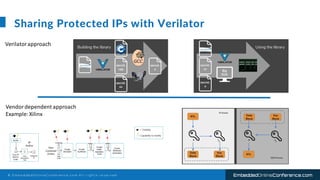
The document outlines a conference presentation by Dr. Seyed Amir Alavi on firmware co-design and development for IP cores using C++ and SystemC, focusing on the utilization of Verilator for simulation. It discusses key concepts of co-design, motivations for a concurrent hardware/software development process, and introduces SystemC as a modeling language for embedded system design. Additionally, the presentation covers advanced use cases and provides a tutorial on employing various tools like Verilator and GTKWAVE in the design process.