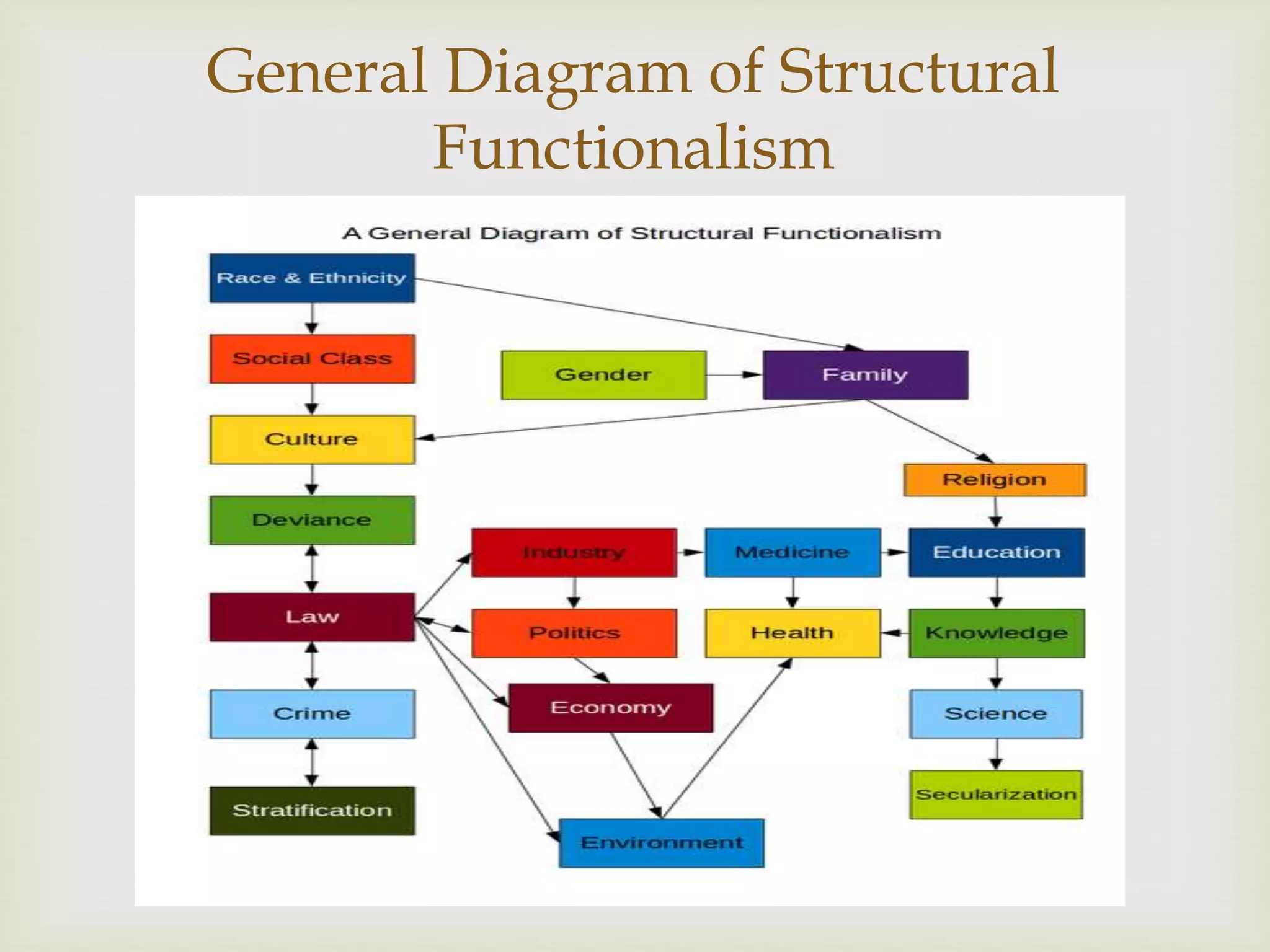
Structural functionalism views society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability. It analyzes the function of components like the educational, religious, and criminal justice systems, and how they contribute to social order and change. The theory was influenced by Émile Durkheim, who believed society exerted influence on individuals. Basic concepts in structural functionalism include social structure, social function, manifest and latent functions. Its basic principles are maintenance of social stability, collective functioning, and understanding social evolution.