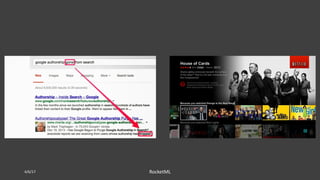
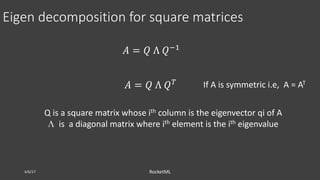
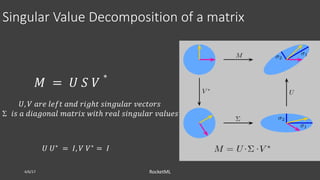
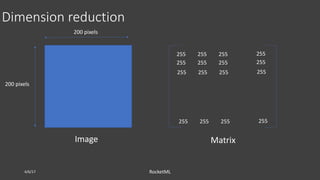
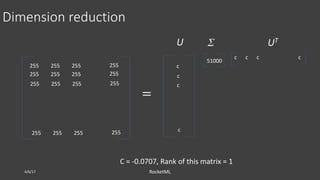
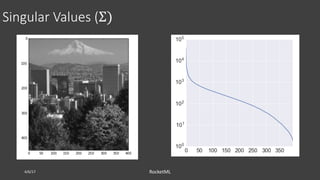
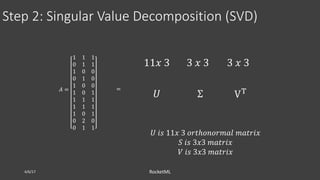
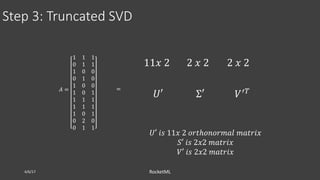
The document discusses theoretical frameworks behind image compression and semantic search, focusing on techniques like singular value decomposition (SVD), eigenvalue decomposition, and their applications in various fields such as natural language processing and data compression. It outlines the process of using SVD for dimensionality reduction to enhance semantic search capabilities and provides a step-by-step example of ranking documents based on relevance to a query. Furthermore, it highlights various computational methods and references essential literature in the field.





![Vectors
4/6/17 RocketML
x1
x2
[2,2]
[2,1]
x1
x2
x3
[2,2,2]
x1, x2, x3, x4, … are features. In NLP, these are n-grams
2D 3D Hyper Space
[2,3,3,5, … ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-7-320.jpg)
![Matrix Vector Multiplication
4/6/17 RocketML
2 0
0 1
1
1
=
2
1
x1
x2
[2,1][1,1]
Ax
x
A x Ax
2 0 0
0 1 2
x1
x2
x3
[1,1,2]
1
1
2
2
5
=
x1
x2
[2,5]
3D 2D
A x Ax
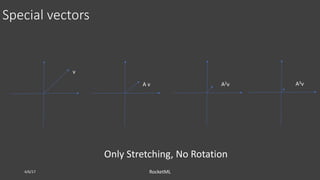
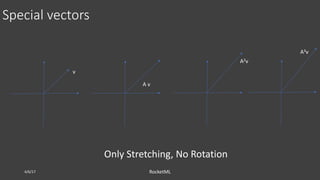
Stretching, Rotation
Stretching, Rotation,
dimension changes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-8-320.jpg)
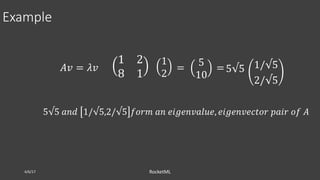



![Reconstruction using few singular values
4/6/17 RocketML
𝑈[: , 1: 2] 𝑆[1: 2] 𝑉[: , 1: 2] 𝑇 𝑈[: , 1: 3] 𝑆[1: 3] 𝑉[: , 1: 3] 𝑇](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-20-320.jpg)
![More singular values
4/6/17 RocketML
𝑈[: , 1: 20] ∗ 𝑆[1: 20] ∗ 𝑉[: , 1: 20] 𝑈[: , 1: 200] ∗ 𝑆[1: 200] ∗ 𝑉[: , 1: 200]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-21-320.jpg)
![Normalize Cumulative Sum
4/6/17 RocketML
𝑆 = [ 𝜎
]
^
𝑠_ =
1
𝑆
[ 𝜎_
_?@
^](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-22-320.jpg)




![Step 4: Find new query vector in reduced 2-
dimension space
4/6/17 RocketML
“𝑔𝑜𝑙𝑑 𝑠𝑖𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑟 𝑡𝑟𝑢𝑐𝑘”
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
q =
𝑎
𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑑
𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑑
𝑑𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑦
𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑒
𝑔𝑜𝑙𝑑
𝑖𝑛
𝑜𝑓
𝑠ℎ𝑖𝑝𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑠𝑖𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑟
𝑡𝑟𝑢𝑐𝑘
𝑞e
= 𝑞 𝑈eA
𝑆e?@
𝑞′ = [−0.21, −0.1821]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-29-320.jpg)
![Step 5: Rank documents based on cosine
similarity
4/6/17 RocketML
−0.4945 −0.6458 −0.5817
0.6492 −0.7914 0.2469
𝑞′ = [−0.21, −0.1821]
Sentences
[ −0.0541 0.9910 0.4478]
1 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/santi-adavani-semantic-search-osbridge-2017-170627154422/85/Theory-behind-Image-Compression-and-Semantic-Search-30-320.jpg)