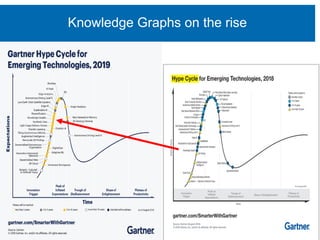
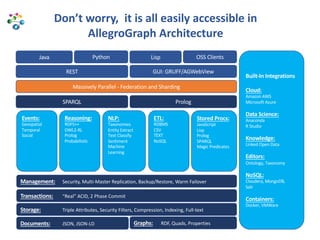
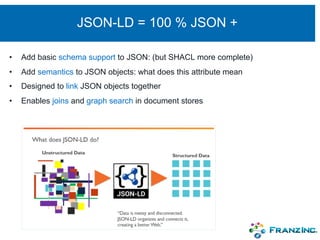
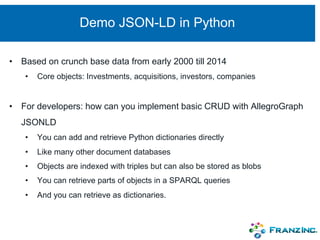
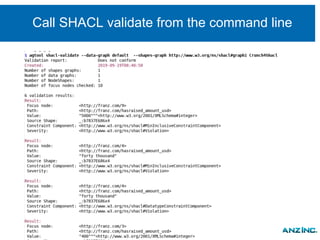
The document discusses the rapid rise of knowledge graphs and the utility of JSON-LD and SHACL in their construction and data validation. JSON-LD simplifies adding, retrieving, and deleting objects in knowledge graphs, while SHACL provides a way to enforce data integrity and impose constraints. The combination of these technologies makes knowledge graphs more accessible and manageable for developers.