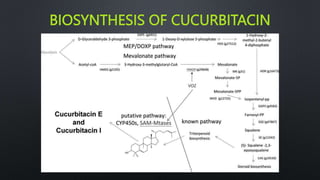
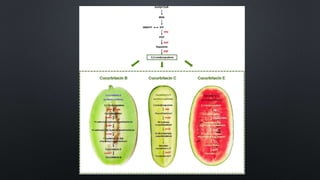
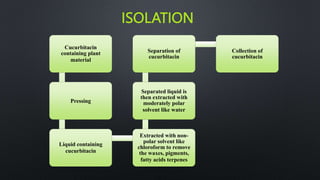
The document discusses terpenoids, specifically cucurbitacin, detailing their chemical characteristics, biosynthesis, isolation, purification, and medicinal uses. Cucurbitacin, a bitter compound found in the Cucurbitaceae family, has various therapeutic effects including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Methods for isolating and purifying cucurbitacin are also outlined, along with references for further reading.