Antibiotics part 2
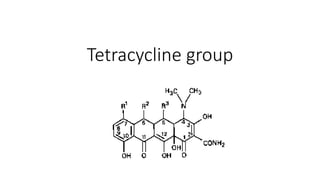
- 2. Tetracyclines • Antibiotics obtained as by-products from the metabolism of various species of Streptomyces • Thus, tetracycline (by catalytic hydrogenation) and clomocycline are obtained from chlortetracycline, which is itself produced from Strep. aureofaciens. • Methacycline is obtained from oxytetracycline (produced from Strep, rimosus) and hydrogenation of methacycline gives doxycycline. • Demethylchlortetracycline is produced by a mutant strain of Strep, aureofaciens. • Minocycline is a derivative of tetracycline.
- 3. • They block protein synthesis hence preventing bacterial reproduction. • It binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit to prevent the amino-acyl tRNA from binding to the A site of the ribosome.
- 4. • Resistance to the tetracyclines develops relatively slowly, but there is cross-resistance • Suprainfection ('overgrowth') with naturally tetracycline-resistant organisms sold under the brand name Sumycin
- 5. Glycylcyclines • The glycylcyclines represent a new group of tetracycline analogues. • They are novel tetracyclines substituted at the C-9 position with a dimethylglycylamido side-chain. • They possess activity against bacteria that express resistance to the older tetracyclines by an efflux mechanism
- 7. Aminoglycoside • Aminoglycoside antibiotics contain amino sugars in their structure.
- 8. • Deoxystreptamine containing members are neomycin, framycetin, gentamicin, kanamycin, tobramycin, amikacin, netilmicin and sisomicin. • Both streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin produce streptidine, whereas the aminocyclitol spectinomycin has no amino sugar.
- 9. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Bacteraemia Nephrotoxic Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Sepsis -Renal failure Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Pseudomonas infections Ototoxic Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Tuberculosis -auditory impairment Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Staphylococcus aureus caused food posioning Neuromuscular junction breakdown Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Staph infections Hypersensitivity Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Mycobacterium infections Anaphylaxis (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus Usually taken with β- lactam antibiotics Mycobacterium
- 10. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors
- 11. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Very Poor oral absorption
- 12. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Very Poor oral absorption Low lipid diffusion
- 13. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Very Poor oral absorption Low lipid diffusion Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption
- 14. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Very Poor oral absorption Low lipid diffusion Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Injected via Intra- muscular Injection
- 15. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Very Poor oral absorption Examples: Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Streptomycin Paromomycin
- 16. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Paromomycin
- 17. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Staphylococcus Mycobacterium
- 18. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus Mycobacterium
- 19. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Bacteraemia Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Sepsis Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Pseudomonas infections Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Tuberculosis Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Staphylococcus aureus caused food posioning Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Staph infections Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Mycobacterium infections (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus Mycobacterium
- 20. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Bacteraemia Nephrotoxic Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Sepsis -Renal failure Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Pseudomonas infections Ototoxic Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Tuberculosis -auditory impairment Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Staphylococcus aureus caused food posioning Neuromuscular junction breakdown Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Staph infections Hypersensitivity Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Mycobacterium infections Anaphylaxis (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus Mycobacterium
- 21. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Bacteraemia Nephrotoxic Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Sepsis -Renal failure Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Pseudomonas infections Ototoxic Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Tuberculosis -auditory impairment Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Staphylococcus aureus caused food posioning Neuromuscular junction breakdown Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Staph infections Hypersensitivity Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Mycobacterium infections Anaphylaxis (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus skin rash or itchiness. unusual drowsiness,. Mycobacterium dizziness, or weakness increased thirst
- 22. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 30s Ribosomes Inhibitors Aminoglycoside Gram –ve aerobes Bacteraemia Nephrotoxic Very Poor oral absorption Examples: E. coli Sepsis -Renal failure Low lipid diffusion Neomycin Pseudomonas Pseudomonas infections Ototoxic Poor Gastro-intestinal absorption Gentamycin Klebsiella Tuberculosis -auditory impairment Injected via Intra- muscular Injection Kanamycin Proteus (Enterobacter) Staphylococcus aureus caused food posioning Neuromuscular junction breakdown Bacteriostatic against Gram –ve Streptomycin Enteric bacteria Staph infections Hypersensitivity Bactericidal against Gram +ve Paromomycin Gram +ve aerobes Mycobacterium infections Anaphylaxis (if taken for prolonged period) Staphylococcus skin rash or itchiness. unusual drowsiness,. Usually taken with β- lactam antibiotics Mycobacterium dizziness, or weakness increased thirst
- 23. • Streptomycin was isolated by Waksman in 1944, and its activity against M. tuberculosis ensured its use as a primary drug in the treatment of tuberculosis. • Streptomycin also shows activity against other types of bacteria, for example against various Gram-negative bacteria and some strains of staphylococci. • Dihydrostreptomycin has a similar antibacterial action but is more toxic.
- 24. • Gentamicin is active against many strains of Gram-positive and Gram- negative bacteria, including some strains of Ps. aeruginosa. • Activity greatly increases at 8 pH. • Kanamycin - active in low concentrations against various Gram- positive (including penicillin-resistant staphylococci) and Gram- negative bacteria. • Second-line drug in the treatment of tuberculosis.
- 25. • Paromomycin - treatment of intestinal amoebiasis (it is amoebicidal against Entamoeba histolytica) and of acute bacillary dysentery. • Neomycin is poorly absorbed - given orally - used in the form of lotions and ointments for topical application against skin and eye infections.
- 26. Rifamycins
- 27. • The rifamycins comprise a comparatively new antibiotic group and consist of rifamycins A to E. • From rifamycin B produce rifamide (rifamycin B diethylamide) and rifamycin SV, which is one of the most useful and least toxic of the rifamycins.
- 28. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects inhibition of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA synthesis Rifamycin Gram +ve tuberculous meningitis upset stomach Bactericidal Rifamycins A to E Staph and Streptococcus non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections heartburn Active Orally rifamycin B produce rifamide Mycobacterium tuberculosis nausea resistant mutants may arise very rapidly And rifamycin SV (least toxic) M. avium menstrual changes should be combined with another antibiotic Rifampicin Few Gram -ve headache Rifabutin But not Enterobacteriaceae or pseudomonads drowsiness, or dizziness
- 29. • Rifampicin is a bactericidal antibiotic • It is active against Gram-positive bacteria • and some Gram-negative bacteria • It has been found to have a greater bactericidal effect against M. tuberculosis than other anti-tuberculosis drugs, • It is active orally, penetrates well into cerebrospinal fluid and is thus of use in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis.
- 30. • Rifampicin possesses significant bactericidal activity at very low concentrations against staphylococci. • Since, resistant mutants may arise very rapidly, both in vitro and in vivo. • It has thus been recommended that rifampicin should be combined with another antibiotic, e.g. vancomycin, in the treatment of staphylococcal infections.
- 31. • A newly introduced rifamycin is rifabutin. • This may be used in the prophylaxis of M. avium complex infections in immunocompromised patients • and in the treatment, with other drugs, of non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections.
- 32. Macrolides
- 33. Old Members • The macrolide antibiotics are characterized by possessing molecular structures that contain large (12-16-membered) lactone rings linked through glycosidic bonds with amino sugars. (Streptomyces venezuelae)
- 34. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors
- 35. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides
- 36. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Examples: Oleandomycin Erythromycin Ezithromycin Clarithromycin Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 37. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Oleandomycin Erythromycin Ezithromycin Clarithromycin Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 38. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Erythromycin Ezithromycin Clarithromycin Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 39. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Ezithromycin Clarithromycin Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 40. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 41. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Bateriostatic Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 42. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Bateriostatic Arithromycin Spiramycin Picromycin
- 43. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Spiramycin Picromycin
- 44. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Spiramycin Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae
- 45. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Spiramycin Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae
- 46. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Lyme's disease Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella Syphilis increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae STDs (Gonorrhoea) Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Spiramycin Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae
- 47. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Lyme's disease Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella Syphilis increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae STDs (Gonorrhoea) Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Mycoplasma infections Spiramycin Pertussis Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae Diphtheria
- 48. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Milder side effects Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Lyme's disease Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella Syphilis increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae STDs (Gonorrhoea) Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Mycoplasma infections Spiramycin Pertussis Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae Diphtheria
- 49. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Milder side effects Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Nausea and Vomiting Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Diarrhea Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Lyme's disease Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella Syphilis increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae STDs (Gonorrhoea) Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Mycoplasma infections Spiramycin Pertussis Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae Diphtheria
- 50. Mode of Action Class and Example Spectrum of Activity Therapeutic use Side Effects 50s Ribosome Inhibitors Macrolides Gram +ve bacteria Tetanus Milder side effects Rapid Oral absorption Examples: Staphylococcus Staph infections Nausea and Vomiting Acid sensitive (degraded easily in GI tract) Oleandomycin Streptococcus Streptococcus infections Diarrhea Enteric coated tablets Erythromycin Gram -ve bacteria Lyme's disease Very few cases of: Activity is pH dependent Ezithromycin Legionella Syphilis Jaundice increasing with pH up to about 8.5 Clarithromycin Neisseria gonorrhoeae STDs (Gonorrhoea) Hepatoxic Bateriostatic Arithromycin Mycoplasma Mycoplasma infections Spiramycin Pertussis Picromycin Not against the Enterobacteriaceae Diphtheria
- 51. • Erythromycin Estolate is more stable to the acid of gastric juice and is thus employed for oral use. • Oleandomycin, its ester (triacetyloleandomycin) and spiramycin have a similar range of activity as erythromycin but are less active. Resistance develops only slowly in clinical practice. • However, cross-resistance may occur between all four members of this group
- 52. New Member • The new macrolides are semisynthetic molecules that differ from the original compounds in the substitution pattern of the lactone ring system • Roxithromycin has similar in vitro activity to erythromycin but enters leucocytes and macrophages more rapidly with higher concentrations in the lysosomal component of the phagocytic cells. • It is likely to become an important drug against Legionella pneumophila. • Clarithromycin is also of potential value.
Editor's Notes
- 1. although some members may now be thought of as being semisynthetic. There are several clinically important tetracyclines, characterized by four cyclic rings The tetracyclines are broad-spectrum antibiotics, i.e. they have a wide range of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Hydrogenation – to treat with hydrogen – is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum.
- An aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS) is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its tRNA This is because bacteria actively pump tetracycline into their cytoplasm, even against a concentration gradient, whereas mammalian cells do not. This accounts for the relatively small off-site effect of tetracycline on human cells.
- 1. i.e. an organism resistant to one member is usually resistant to all other members of this group. 2. for example Candida albicans and other yeasts, and filamentous fungi, affecting the mouth, upper respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract, may occur as a result of the suppression of tetracycline-susceptible microorganisms. The tetracyclines are no longer used clinically to the same extent as they were in the past because of the increase in bacterial resistance. Cross-resistance is the tolerance to a usually toxic substance as a result of exposure to a similarly acting substance. This includes acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is taken by mouth
- Active efflux is a mechanism responsible for moving compounds, like neurotransmitters, toxic substances, and antibiotics, out of the cell; this is considered to be a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This mechanism is important in medicine as it can contribute to bacterial antibiotic resistance They block protein synthesis hence preventing bacterial reproduction. Both classes of antibiotics bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit to prevent the amino-acyl tRNA from binding to the A site of the ribosome. However, the glycylcyclines appear to bind more effectively than the tetracyclines.
- #Streptidine, a metabolic derivative produced by streptomycin #Also known as Aminoglycoside-aminocyclitol antibiotics Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial therapeutic agents that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar)
- Streptidine, a metabolic derivative produced by streptomycin
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Bacteremia -the presence of bacteria in the blood Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by your body’s response to an infection. Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that needs to be treated right away. If you have an anaphylactic reaction, you need an epinephrine (adrenaline) shot as soon as possible
- Unfortunately, its toxicity and the rapid development of resistance have tended to modify its usefulness, and although it still remains a front-line drug against tuberculosis it is usually used in combination with isoniazid and p(4)-aminosalicylic acid Dihydrostreptomycin is a derivative of streptomycin that has a bactericidal property.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa TB can be treated effectively by using first line drugs (FLD) isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), ethambutol (EMB) and streptomycin (SM).
- A desirable property of newer aminoglycoside antibiotics is increased antibacterial activity against resistant strains, especially improved stability to aminoglycoside modifying enzymes The most important of these antibiotics are amikacin, tobramycin, netilmicin and especially gentamicin.
- The antibacterial activity of rifamycins relies on the inhibition of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA synthesis. This is due to the high affinity of rifamycins for the prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
- The rifamycins comprise a comparatively new antibiotic group Inhibits Protein synthesis of prokaryotes It is active orally, penetrates well into cerebrospinal fluid and is thus of use in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Rifampicin possesses significant bactericidal activity at very low concentrations against staphylococci. It has thus been recommended that rifampicin should be combined with another antibiotic, e.g. vancomycin (glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall), in the treatment of staphylococcal infections.
- It is active against Gram-positive bacteria (including Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and some Gram-negative bacteria (but not Enterobacteriaceae or pseudomonads). bacteriostatic” means that the agent prevents the growth of bacteria (i.e., it keeps them in the stationary phase of growth
- Gram+ vancomycin, in the treatment of staphylococcal infections It is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall
- treatment given or action taken to prevent disease non-tuberculous mycobacteria -are mycobacteria which do not cause tuberculosis or leprosy
- The most important members of this group are erythromycin, oleandomycin, triacetyloleandomycin and spiramycin. Brokmann and Hekel in 1951 Streptomyces venezuelae, a species of Gram-positive bacterium
- Inhibits Protein synthesis of prokaryotes
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- Clostridium tetani Borrelia –lymes desease –not gram +ve or -ve treponema pallidum –syphilis –gram –ve Bordetella pertussis –Pertussis (whooping cough) Corynebacterium diphtheriae –gram +ve Hepatotoxic –damaging liver cells
- esters are chemical compounds derived from an acid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one –OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an –O–alkyl (alkoxy) group.
- White blood cells a large phagocytic cell found in stationary form in the tissues or as a mobile white blood cell, especially at sites of infection. In vitro outside the body Semi synthetic
