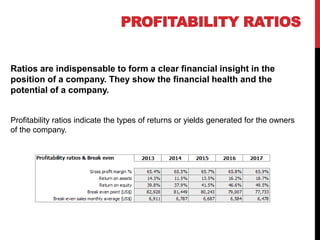
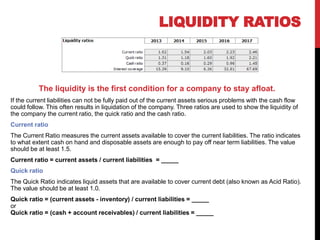
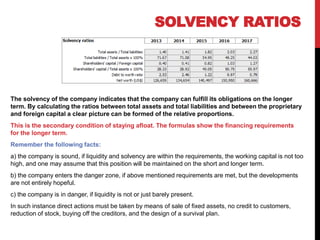
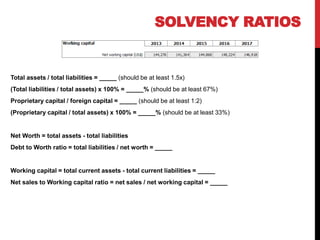
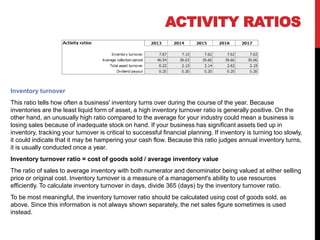
The document outlines essential financial ratios for assessing a company's financial health, including profitability, liquidity, and solvency ratios. Key metrics such as gross profit margin, return on assets, and current ratio are discussed, emphasizing their importance in evaluating management effectiveness and making informed business decisions. Additionally, the document highlights the significance of asset turnover, dividend payout ratio, and the break-even point in financial analysis.