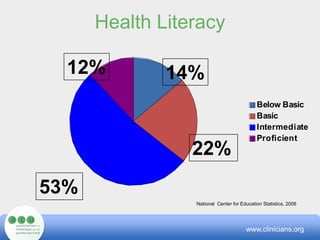
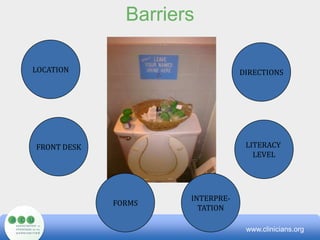
The document outlines methods for health and social service providers to enhance communication with clients, focusing on the impact of language, culture, and literacy on access to services. It presents federal civil rights legislation pertaining to limited English proficiency, barriers to effective communication, and strategies for creating consumer-friendly environments. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of culturally competent care and low-cost tools to mitigate communication challenges.